Larry A. Kramer1, Khader M. Hasan1, Brandon R. Macias2, Karina J. Marshall-Goebel3, Steven S. Laurie3, Refaat E. Gabr1, Leela Chaudhary1, and Alan R. Hargens4
1Diagnostic Imaging, UTHSC-Houston, Houston, TX, United States, 2NASA, Houston, TX, United States, 3KBR, Houston, TX, United States, 4Orthopedic Surgery, UCSD, La Jolla, CA, United States
1Diagnostic Imaging, UTHSC-Houston, Houston, TX, United States, 2NASA, Houston, TX, United States, 3KBR, Houston, TX, United States, 4Orthopedic Surgery, UCSD, La Jolla, CA, United States
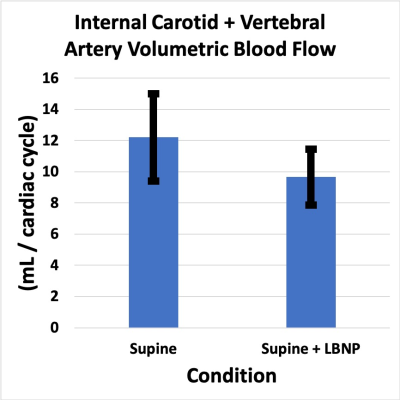
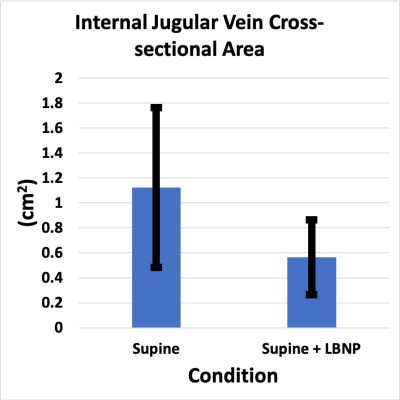
The application of lower body negative pressure in the supine position simulates physiology that is associated with upright posture thereby supporting its use as a potential countermeasure to the development of optic disc edema in astronauts exposed to long-duration spaceflight.