Kevin M Koch1, V. Emre Arpinar1, and Matthew Budde2
1Radiology, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, United States, 2Neurosurgery, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, United States
1Radiology, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, United States, 2Neurosurgery, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, United States
Diffusion-weighted imaging of instrumented spinal levels of cervical spondylotic myelopathy subjects was performed using MAVRIC DWI metal artifact-reduction methods, identifying a substantial reduction of diffusivity at the instrumented levels in the cord.
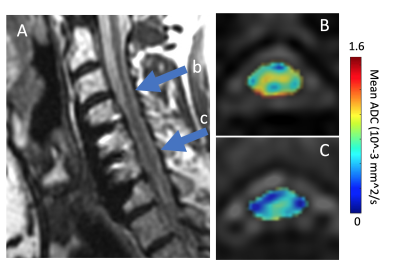
Figure 3: Exemplary MAVRIC DW ADC maps of the cord in a CSM subject at the indicated levels (A), which are (B) unfused (above the hardware) and (C) fused by the hardware construct. The clear reduction in ADC in this subject at the fused levels is readily visible.
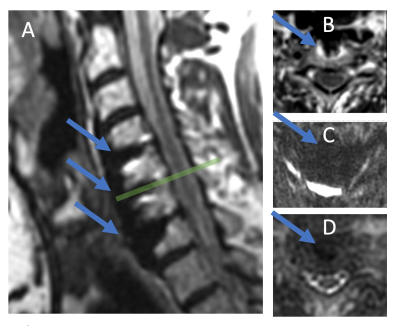
Figure 1: A) Sagittal plane of isotropic T2w MAVRIC SL acquisition indicating fusion hardware and the location of displayed axial sections. B) Axial reformat of MAVRIC acquisition at C5 level indicating proximity of hardware to spinal cord. C) Conventional FOCUS (reduced field-of-view EPI) DWI b=0 image is non-diagnostic and completely disrupted due to hardware presence. D) MAVRIC DWI b=0 image allows for diffusion-weighted analysis of cord, even in near vicinity of hardware.