Ming Lu1,2,3, Gary Drake1,2, Feng Wang1,2, Chaoqi Mu1,4, Limin Chen1,2, John C. Gore1,2,4, and Xinqiang Yan1,2
1Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 2Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 3College of nuclear equipment and nuclear engineering, Yantai University, Yantai, China, 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, United States
1Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 2Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN, United States, 3College of nuclear equipment and nuclear engineering, Yantai University, Yantai, China, 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, United States
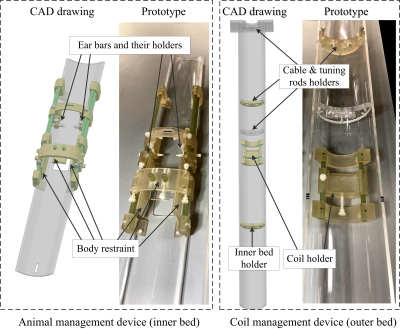
We developed an interchangeable RF coil
system for a 9.4T small animal MRI scanner, allowing for optimal coil selection
for different experiments. Compared to a general-purpose commercial coil, up to
2.4-fold SNR improvement was obtained by using an optimal coil.
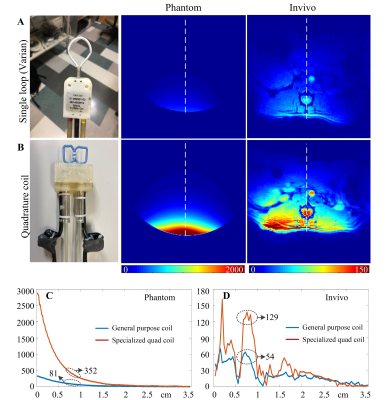
Figure 4 A
and B: Measured SNR on the phantom and a live rat (male Sprague-Dawley
rat, 350 g) using Varian single loop coil and optimal quadrature coil
specialized to L1-L2 spinal cord imaging. SNR maps were calculated from GRE
images with the following parameters: phantom (FOV = 45 × 45 mm2,
TR/TE = 1000/4 ms, FA = 20 degree, Matrix = 192 × 192, Bandwidth = 260.4
Hz/pixel), in vivo (FOV
= 45 x 45 mm2, TR/TE = 200/2.874 ms, FA = 40 degree, Matrix = 128 x
128, bandwidth 390.6 Hz/pixel). C and D: One-dimensional profiles of the measured SNR along
the dotted white line in Figures 4A and B.