Maksym Sharma1, Alexander M Matheson1, David G McCormack2, David A Palma1,3, and Grace Parraga1,2,3
1Medical Biophysics, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 2Division of Respirology, Department of Medicine, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 3Department of Oncology, Western University, London, ON, Canada
1Medical Biophysics, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 2Division of Respirology, Department of Medicine, Western University, London, ON, Canada, 3Department of Oncology, Western University, London, ON, Canada
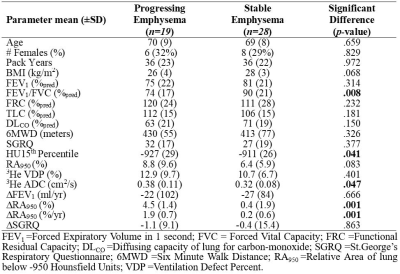
We developed a machine-learning pipeline that identified hyperpolarized 3He MRI texture features that independently and uniquely correlated and predicted rapidly worsening emphysema nearly 3 years later, measured as CT RA950, using a Decision Tree algorithm that achieved 82% accuracy.
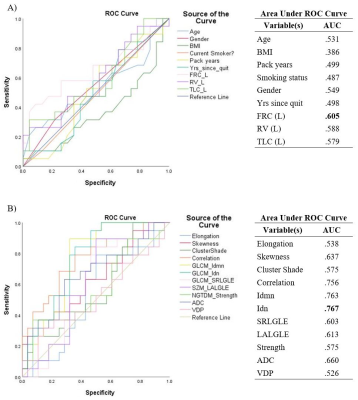
Figure 2. Logistic regression analysis of individual variables in A) clinical and
B) MRI model. The above graphs represent the predictive power of individual
variables used in each of the models. Clinical model significantly improved
from adding lung volume variables. Individual texture features outperformed
standard variables calculated from MRI, namely ADC and VDP.