Xiaoqing Wang1,2, Sebastian Rosenzweig1,2, Moritz Blumenthal1, Zhengguo Tan1,2, Nick Scholand1,2, and Martin Uecker1,2,3,4
1University Medical Center Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 2Partner Site Göttingen, German Centre for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK), Göttingen, Germany, 3Cluster of Excellence "Multiscale Bioimaging: from Molecular Machines to Networks of Excitable Cells" (MBExC), University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 4Campus Institute Data Science (CIDAS), University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany
1University Medical Center Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 2Partner Site Göttingen, German Centre for Cardiovascular Research (DZHK), Göttingen, Germany, 3Cluster of Excellence "Multiscale Bioimaging: from Molecular Machines to Networks of Excitable Cells" (MBExC), University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany, 4Campus Institute Data Science (CIDAS), University of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany
This work develops a free-breathing myocardial T1 mapping technique. Initial results have demonstrated that the proposed method could achieve motion-resolved T1 mapping at a spatial resolution of 1.33 × 1.33 × 6 mm3 with good accuracy, precision and reproducibility.
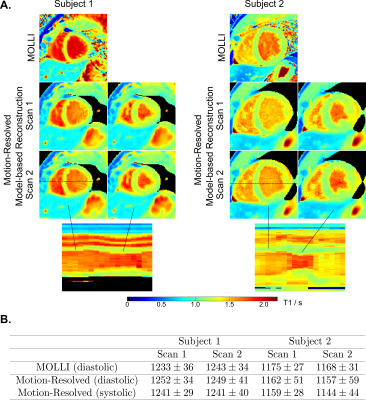
A. MOLLI (mid-diastolic) and the representative motion-resolved myocardial T1 maps (mid-diastolic and mid-systolic) for two repetitive scans and two subjects. The line profiles along the motion dimension are presented in the bottom row for both subjects. B. Quantitative myocardial T1 values (ms, mean $$$\pm$$$ standard deviation) in left-ventricular septum for T1 maps in Figure 4A.