Lijun Zhang1, Jinfan Tian2, Xueyao Yang2, Jing An 3, Yi He4, and Xiantao Song2
1Department of Radiology, Beijing AnZhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 2Department of Cardiology, Beijing AnZhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 33Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd, Beijing, China, 4Department of Radiology, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
1Department of Radiology, Beijing AnZhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 2Department of Cardiology, Beijing AnZhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China, 33Siemens Shenzhen Magnetic Resonance Ltd, Beijing, China, 4Department of Radiology, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
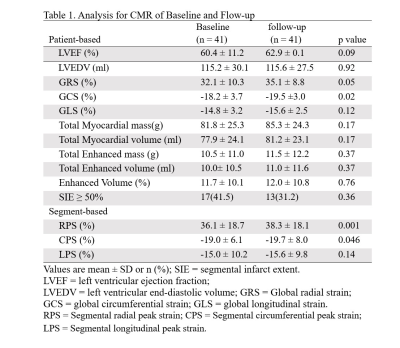
The main findings of the present study are as follows: (1) global and segmental strains improved
over time, and GCS showed a significant treatment effect of successful CTO-PCI; (2) GCS and GLS determined by CMR-FT were
strongly correlated with LVEF.
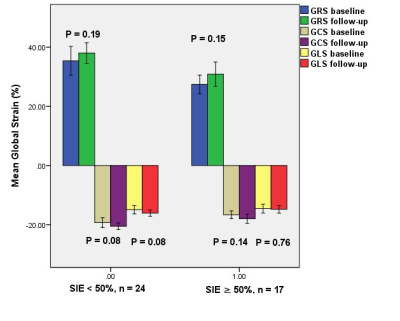
Figure 2. Comparison of left
ventricular global
strain parameters
between baseline and follow-up based on per-patient subgroup analysis.
In the subgroup per-patient analysis, the global peak systolic radial
strain (GRS), global circumferential strain (GCS), and global longitudinal
strain (GLS) of the viable (SIE < 50%) and nonviable (SIE ≥ 50%) groups were
not significantly improved after successful CTO-PCI in 1-year follow-up.