Jan Malte Oeschger1, Karsten Tabelow2, and Siawoosh Mohammadi1,3
1Institute of Systems Neuroscience, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany, 2Weierstrass Institute for Applied Analysis and Stochastics, Berlin, Germany, 3Department of Neurophysics, Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Leipzig, Germany
1Institute of Systems Neuroscience, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany, 2Weierstrass Institute for Applied Analysis and Stochastics, Berlin, Germany, 3Department of Neurophysics, Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Leipzig, Germany
The reduced axial symmetric DKI model is well suited to estimate DKI and
biophysical tissue parameters. Combination with Rician noise bias correction
improves parameter estimation, especially for DKI parameters along the main
fiber direction.
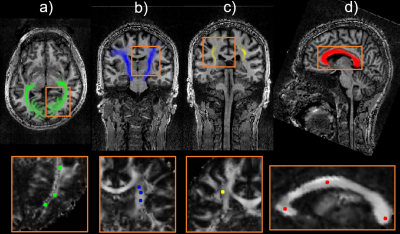
Figure 1: Top: In-vivo DWI images and white matter
regions of interest (ROI) identified with the Jülich fiber atlas10, a)
optic radiation (or), b) cortico spinal tract (ct), c) superior longitudinal
fasciculs (slf) and d) callosum body (cb). In every one of the four ROIs, three
voxels were chosen (FA images bottom, for slf only one is shown here) and DKI
parameters were estimated with the standard DKI model without RBC. These 12
sets of DKI parameters were then used to generate ground truth signals for the simulation.
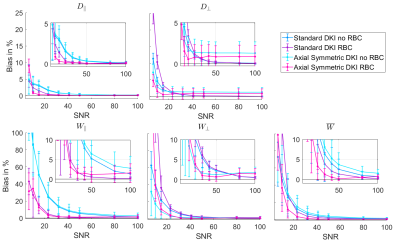
Figure 2: Bias and standard deviation for the estimated AxDKI model parameters,
averaged over 2500 noise samples per SNR across all ROIs.
Note the differently scaled y axes for the diffusion (top) and kurtosis parameters
(bottom). The axial-symmetric fit with RBC (magenta line) produces the overall
least biased estimators.
