Zhijun Ye1, Gang Ning1, Xuesheng Li2, Qing Li3, Haibo Qu1, and Thomas Benkert4
1West China Second University Hospital, Chengdu, China, 2West China Sencond University Hospital, Chengdu, China, 3MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Shanghai, China, 4MR Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany
1West China Second University Hospital, Chengdu, China, 2West China Sencond University Hospital, Chengdu, China, 3MR Collaboration, Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Shanghai, China, 4MR Application Predevelopment, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany
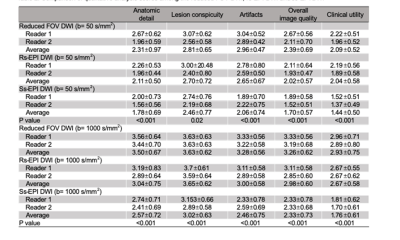
The performance of reduced FOV DWI, reading-segmented echo-planar DWI and conventional single-needle (ss)-EPI DWI techniques in the diagnosis of cervical cancer was compared to find a better DWI technique in terms of image quality and clinical utility.
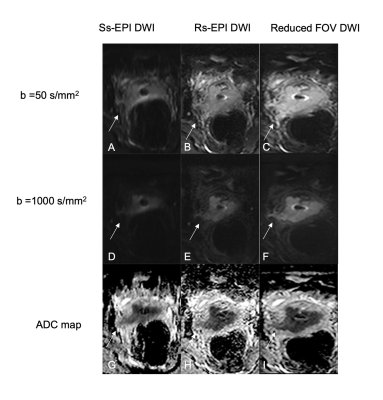
Images in a 56-year-old woman with biopsy-proven squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. Diffusion-weighted MR images and ADC maps show a cervical mass with an irregular margin, restricted diffusion and disruption of the cervical stromal rim. Compared with ss-EPI DWI and rs-EPI DWI, rFOV DWI images show the lesion with a clear border and fewer artifacts, and clearly demonstrate the findings of parametrial invasion in the right side (arrow).