Roya Afshari1,2, Francesco Santini1,2, Rahel Heule3,4, Craig Meyer5, Josef Pfeuffer6, and Oliver Bieri1,2
1Department of Radiology, Division of Radiological Physics, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland, 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland, 3Department of High Field Magnetic Resonance, Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, Tübingen, Germany, 4Department of Biomedical Magnetic Resonance, University of Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, 5Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Virginia, Virginia, VA, United States, 6Department of Application Development, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany
1Department of Radiology, Division of Radiological Physics, University Hospital Basel, Basel, Switzerland, 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland, 3Department of High Field Magnetic Resonance, Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, Tübingen, Germany, 4Department of Biomedical Magnetic Resonance, University of Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, 5Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Virginia, Virginia, VA, United States, 6Department of Application Development, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany
Using a spiral prototype sequence, accurate
whole brain B1-corrected quantitative magnetization transfer (qMT)
imaging is feasible within less than 5 minutes in the clinical setting at 3T.
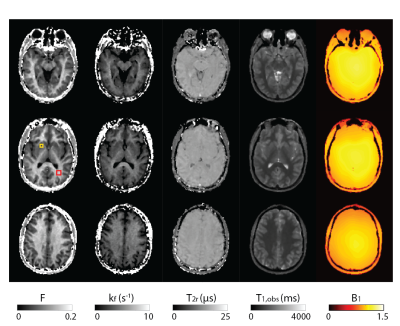
Figure 2: Illustrative axial views at
three positions for all the retrieved parameter maps. From left to right: the bound
pool fraction (F), the exchange rate (kf), the transverse relaxation
time of the bound pool protons (T2r), the observable longitudinal
relaxation time of the free pool protons (T1,obs), and the B1-map.
Yellow and red ROIs shown on the middle row of the F slices were used for the data
presented in Table 1.
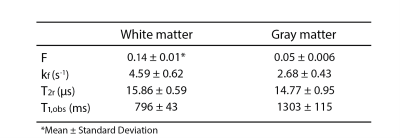
Table 1: Mean and standard deviation of the bound pool fraction (F), the exchange rate
(kf), the transverse relaxation time of the bound pool protons (T2r),
the observable longitudinal relaxation time of the free pool protons (T1,obs)
calculated over ROIs selected in white matter (red rectangle) and gray matter (yellow
rectangle) shown in the middle row of F slices in Figure 2.
