Do-Wan Lee1, Yeon Ji Chae2, Monica Young Choi2, Jae-Im Kwon3, Joongkee Min3, Chul‐Woong Woo3, Hwon Heo2, Dong‐Cheol Woo2,3, Jeong Kon Kim1, Kyung Won Kim1, Hyo Jeong Chin4, and Dong‐Hoon Lee4
1Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Department of Convergence Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 3Convergence Medicine Research Center, Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 4Department of Radiological Science, College of Health Sciences, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea, Republic of
1Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 2Department of Convergence Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 3Convergence Medicine Research Center, Asan Institute for Life Sciences, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 4Department of Radiological Science, College of Health Sciences, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea, Republic of
The present study demonstrates how axonal demyelination affects cerebral
metabolites in the gray matter of the hippocampal region, quantified using 7-T
proton MR spectra.
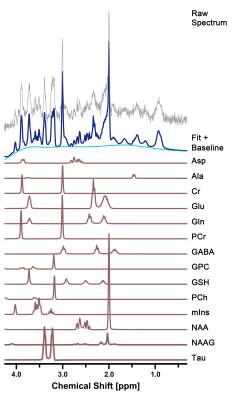
Figure 2. Representative
in vivo 1H MR spectra in the right hippocampus of cuprizone-treated
rats. The figure shows the raw spectrum (gray), fitted spectrum (navy),
baseline (light blue), and 14 individual metabolite fits below (brown).
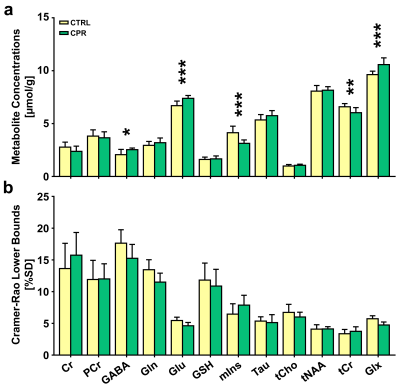
Figure 3. Bar graph indicating the mean cerebral
metabolite concentrations (a) and Cramer-Rao lower bounds (CRLBs) (b) in the
right hippocampal region in control (CTRL) and cuprizone-treated (CPR) rats,
quantified using the Linear Combination of Models software. The vertical lines
on each of the bars indicate the (+) standard deviation of the mean values. *p
< 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.005.