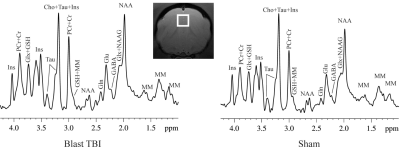
Shiyu Tang1,2, Su Xu1,2, Donna Wilder3, Joseph Long3, Venkata Siva Sai Sujith Sajja3,4, and Rao Gullapalli1,2
1Department of Diagnostic Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States, 2Center for Advanced Imaging Research (CAIR), University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States, 3Blast Induced Neurotrauma Branch, Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, Silver Spring, MD, United States, 4The Geneva Foundation, Tacoma, WA, United States
1Department of Diagnostic Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States, 2Center for Advanced Imaging Research (CAIR), University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States, 3Blast Induced Neurotrauma Branch, Walter Reed Army Institute of Research, Silver Spring, MD, United States, 4The Geneva Foundation, Tacoma, WA, United States
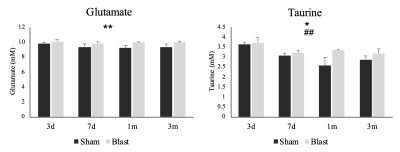
Metabolic changes using magnetic resonance spectroscopy and behavioral changes following blast injury were assessed. Metabolic changes in glutamate and taurine were observed concomitant increase in impulsivity at 1- and 3-months post blast TBI.