Iris Asllani1,2, Francesco Di Lorenzo1, Balazs Orzsik1, Guillaume Madelin3, Neil Harrison4, and Mara Cercignani1
1University of Sussex, Brighton, United Kingdom, 2Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, NY, United States, 3New York University, New York, NY, United States, 4University of Cardiff, Cardiff, United Kingdom
1University of Sussex, Brighton, United Kingdom, 2Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, NY, United States, 3New York University, New York, NY, United States, 4University of Cardiff, Cardiff, United Kingdom
- Anodal tDCS of M1 was associated with an increase in gray matter sodium concentration [Na]GM in the stimulated area measured using partial volume corrected 23MRI.
- Subjects exhibited a widespread pattern of increased [Na]GM.
- There were no changes in [Na]GM associated with sham tDCS.

Fig.3: Areas in GM that survived the Δ%[NA] > 10% are shown for 2 randomly selected subjects. The arrows point to the "blob" that was identified under the marker on the MPRAGE (as demonstrated in Fig.1). The widespread pattern of Δ%[NA] was similar across the group.
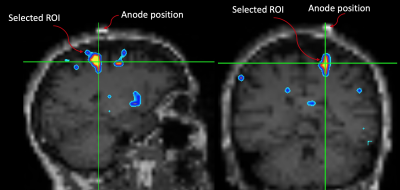
Fig.1: The motor ROI was selected by overlapping the GM Δ%[NA] image onto the subject's down-sampled MPRAGE. A MatLab script was written to identify "blobs" where Δ%[NA] > 10%. The script yields a blob ID number which is then used to extract the motor ROI for further analyses. Note the spatial relationship between the marker and the ROI.