Jon-Fredrik Nielsen1, Berkin Bilgic2,3, Jason P Stockmann2, Borjan Gagoski4, Jr-Yuan George Chiou5, Lipeng Ning6, Yang Ji6, Yogesh Rathi5, Jeffrey A Fessler7, Douglas C Noll1, and Maxim Zaitsev8
1fMRI Laboratory, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, United States, 2Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 3Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 4Fetal-Neonatal Neuroimaging and Developmental Science Center, Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 5Radiology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 6Psychiatry, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 7Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, United States, 8High Field MR Center, Center for Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
1fMRI Laboratory, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, United States, 2Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 3Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 4Fetal-Neonatal Neuroimaging and Developmental Science Center, Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 5Radiology, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 6Psychiatry, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 7Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, United States, 8High Field MR Center, Center for Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
The observed B0 fields were in excellent agreement with the predicted output from the toolbox in all cases. We envision this tool as one component of a more harmonized MRI workflow in support of reproducible MRI research.
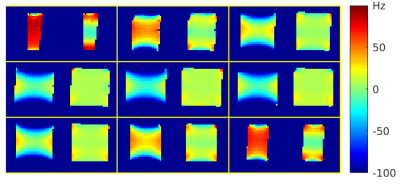
Figure 2. B0 field maps in a uniform cylindrical phantom (Site 1). Left image in each sub-panel: Acquired field map after running the scanner’s built-in linear shim routine. Right image in each sub-panel: Acquired field map after performing 2nd-order shimming using the proposed toolbox. 9 slices are shown.
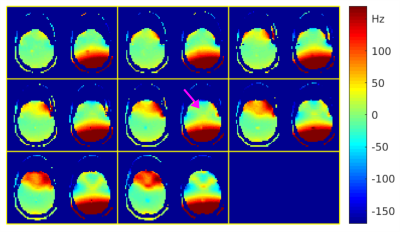
Figure 3. B0 field maps in an anthropomorphic head phantom (Site 1). Left image in each sub-panel: Acquired B0 field map after running the scanner’s built-in global linear shim routine. Right image in each sub-panel: Acquired B0 map after performing localized 2nd-order shimming using the proposed toolbox over a frontal 3D region (in vicinity of purple arrow). 8 slices are shown.
