Gehua Tong1, Sairam Geethanath2, Enlin Qian1, and John Thomas Vaughan, Jr. 2
1Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, United States, 2Columbia Magnetic Resonance Research Center, Columbia University, New York, NY, United States
1Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, United States, 2Columbia Magnetic Resonance Research Center, Columbia University, New York, NY, United States
A framework for testing, validating, and sharing open-source MR sequences was developed to improve their accessibility, repeatability, and safety. The framework was demonstrated for two common sequences, which were packaged and shared in an open-source repository.
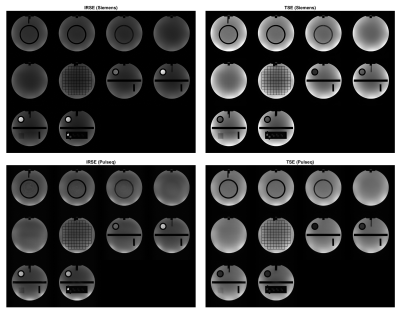
Figure 2: Open-source qualitative IRSE and TSE sequences are compared to vendor gold standards. Parameters are FOV = 250 mm, N = 256, slice thickness = 5 mm, and FA = 90 deg. IRSE has TR = 2000 ms, TE = 12 ms, TI = 100 ms (125 ms for Siemens); TSE has TR = 2741 ms, TE = 50 ms, turbo factor = 4
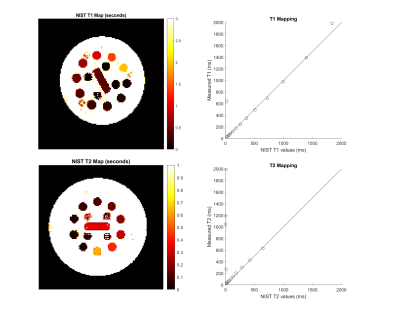
Figure 3: T1 and T2 maps obtained from IRSE and TSE sequences (N = 128, FOV = 250 mm, slice thickness = 6 mm, FA = 90, 180 deg). The Pearson coefficient of correlation is 0.9557 for T1 spheres (0.9983 for spheres 1-13) and -0.0849 for T2 spheres (0.9994 for spheres 1-10). Shorter TIs and TEs than applied are required to accurately map the highest-index spheres.
