Gregory Avey1, Laura Eisenmenger1, Nathan Kim1, Alexey Samsonov1, James Holmes1, Lloyd Estkowski2, and Tabassum Kennedy1
1University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI, United States, 2GE Healthcare, Madison, WI, United States
1University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI, United States, 2GE Healthcare, Madison, WI, United States
Using Deep Learning (DL) reconstruction to accelerate MRI exam acquisition. DL allows for up to 78% reduction in scan time while matching overall baseline subjective image quality. However, not all acceleration methods are equally favorable to DL acceleration.
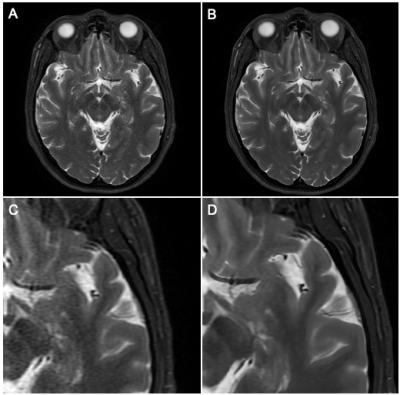
Figure 1. Demonstration of Deep Learning Reconstruction Technique
A. Parallel imaging acceleration factor of 4, conventional Fourier transform reconstruction, 78% reduction in acquisition time from the baseline sequence with increased noise.
B. Same acquisition as in figure A, deep learning reconstruction demonstrating reduction of apparent noise to less than baseline exam with DL reconstruction technique
C. Magnified detail view of A.
D. Magnified detail view of B.