Carlos Milovic1, Jose Manuel Larrain2,3, and Karin Shmueli1
1Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Department of Electrical Engineering, Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile, Santiago, Chile, 3Biomedical Imaging Center, Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
1Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 2Department of Electrical Engineering, Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile, Santiago, Chile, 3Biomedical Imaging Center, Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
We
used a pretrained Total Deep Variation denoising network to
regularize iterative QSM. It gave better error metrics than
state-of-the-art Total Variation and Total Generalized Variation
regularizations in brain phantoms and subtly improved susceptibility
map appearance in vivo.
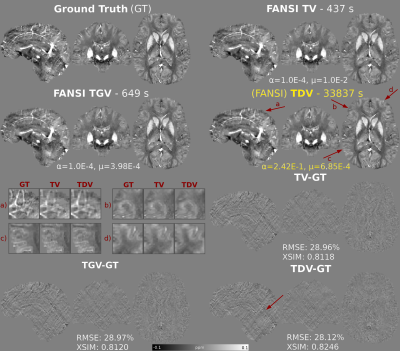
Figure
3: Optimal reconstructions of the RC2 numerical phantom for all
regularization methods (TDV, TV and TGV). TDV
results show better depiction of the veins and streaking artifact
suppression relative to TV and TGV (relevant areas highlighted with
red arrows).
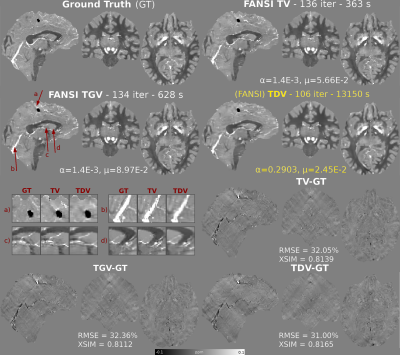
Figure
1: Optimal reconstructions and error maps of COSMOS-based forward
simulations (RC1) for all regularization methods (TDV, TV and TGV). A
sagittal, coronal and axial slice are shown. All methods were
terminated after 500 iterations.
TDV shows better depiction of cortical areas and less staircasing and
streaking artifacts (highlighted with red arrows) than TV and TGV and
achieves better RMSE and XSIM scores. Detailed comparisons between TV
and TDV are shown for each labeled region (a-d).
