Tsutomu Inaoka1, Masayuki Sugeta1, Noriko Kitamura1, Tomoya Nakatsuka1, Rumiko Ishikawa1, Takamitsu Uchi1, Rui Iwata1, Akinori Yamamoto1, Hisanori Tomobe1, Ryosuke Sakai1, Hidetoshi Yamana1, Shusuke Kasuya1, and Hitoshi Terada1
1Radiology, Toho University Sakura Medical Center, Sakura, Japan
1Radiology, Toho University Sakura Medical Center, Sakura, Japan
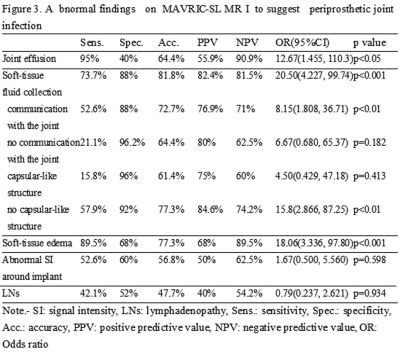
The abnormal findings were better detected by
MAVRIC-SL MRI than by 2D FSE MRI. Joint effusion, soft-tissue edema, and soft-tissue fluid collection suggested periprosthetic joint infection. Soft-tissue edema and soft-tissue fluid collection indicated therapeutic surgical
intervention.
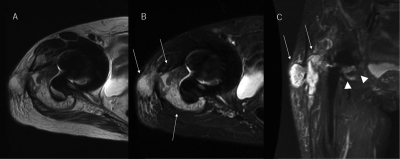
Figure 5. 70s, female. Periprosthetic joint infection of right hip arthroplasty. Therapeutic surgical intervention was needed. (A) 2D FSE T2WI transverse image, (B) 2D FSE STIR transverse image, (C) MAVRIC-SL STIR coronal image. There is a large signal loss at the joint area on 2D FSE T2WI and STIR. Although periprosthetic assessment is not available on 2D FSE T2WI and STIR, soft-tissue fluid collection is noted on 2D FSE T2WI and STIR (white arrows). While, soft-tissue fluid collection with communication with the joint is clearly noted on MAVRIC-SL STIR (white arrows and arrow heads).