Chao Han1, Shuai Ma1, Xiang Liu1, Yi Liu1, Changxin Li2, Yaofeng Zhang2, Xiaodong Zhang1, and Xiaoying Wang1
1Department of Radiology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Beijing Smart Tree Medical Technology Co. Ltd., Beijing, China
1Department of Radiology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China, 2Beijing Smart Tree Medical Technology Co. Ltd., Beijing, China
Four radiomics models based on manual/automatic
segmentation of prostate gland/prostate cancer (PCa) lesion from ADC maps were developed
and tested to distinguish high-grade and low-grade PCa, which obtained roughly the
same diagnostic efficacy as preoperative biopsy.
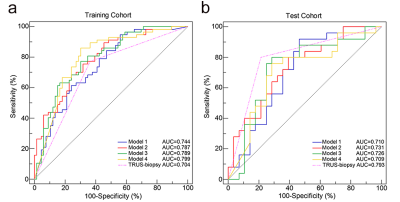
Figure 3. ROC curves of the 4 radiomics models and TRUS
biopsy in the training cohort (a) and test cohort (b). (Model 1 is based on manual segmentation of the prostate
gland. Model 2 is based on manual segmentation of prostate cancer lesions. Model
3 is based on automatic segmentation of the prostate gland by the 3D prostate
segmentation algorithm. Model 4 is based on thresholding segmentation of
prostate cancer lesions by a fast-automatic thresholding algorithm. ROC: receiver operating characteristic; TRUS:
transrectal ultrasound.)
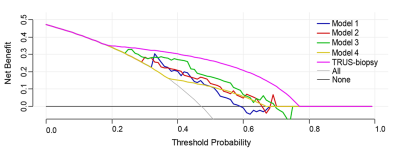
Figure 5. Decision curve analysis comparing the net benefits
of different radiomics models and TURS biopsy for the test cohort. (Model 1 is based on manual segmentation of the prostate
gland. Model 2 is based on manual segmentation of prostate cancer lesions. Model
3 is based on automatic segmentation of the prostate gland by the 3D prostate
segmentation algorithm. Model 4 is based on thresholding segmentation of
prostate cancer lesions by a fast-automatic thresholding algorithm. TRUS: transrectal ultrasound.)