Christian Waldenberg1, Stefanie Eriksson1, Hanna Hebelka2, Helena Brisby3, and Kerstin Magdalena Lagerstrand1
1Department of Radiation Physics, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2Department of Radiology, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden, 3Department of Orthopaedics, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
1Department of Radiation Physics, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2Department of Radiology, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden, 3Department of Orthopaedics, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
Based
on MRI, texture analysis, and neural networks, a workflow for determining the position
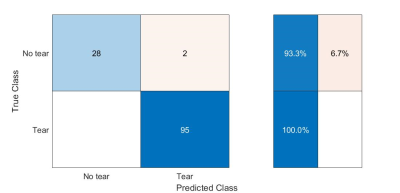
of annular tears in the intervertebral disc was proposed. Classification
sensitivity and specificity of 100% respectively 93% were reached. The position
of 67% of the tears was correctly determined.
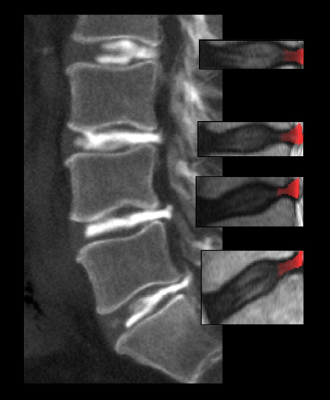
Figure 4: Example of a CT-image displaying the lumbar
spine (L2-S1). All visible IVDs have been injected with a contrast media visible
in white. The contrast media is spread through posterior annular tears and
their location is correctly determined by the proposed algorithm in the T2W MR
image and highlighted in red.