Baiyan Jiang1, Ki-wai, Kevin Ho2, Xiao Fan1, Jian Hou1, Chun-man Lawrence Lau2, James Griffith1, and Weitian Chen1
1Imaging & Interventional Radiology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Sha Tin, Hong Kong, 2Orthopaedics & Traumatology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Sha Tin, Hong Kong
1Imaging & Interventional Radiology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Sha Tin, Hong Kong, 2Orthopaedics & Traumatology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Sha Tin, Hong Kong
It is difficult to detect glycosanimoglycan signal using CEST under 3T due to its fast chemical exchange characteristics and strong direct water saturation effect. In this preliminaray study, we demonstrated the possibility of GAG detection using AC-iTIP method under 3T field strength.
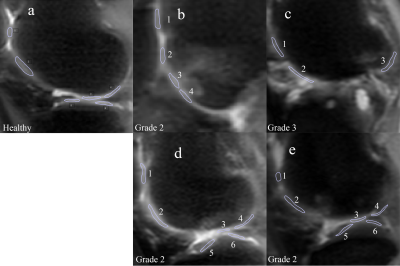
Figure 2. ROIs on a healthy volunteer (a) and 4 OA patients (b-d). Patient b has OA developed
around ROI 3 and 4. Patient c has almost no cartilage left. Patient d has OA in
ROI 1 and patient e has OA in ROI 1 and 2.
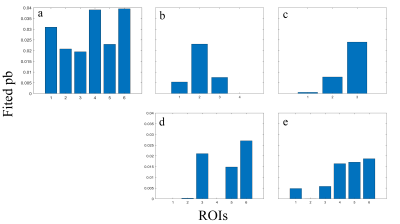
Figure 4. Fitted
pb values comparing healthy volunteer (a) and 4 OA patients (b-d), arranged in
the same order as in figure 2. Note that fitted pb values have a similar trend compared
to figure 3. Fitted pb values of OA patients are generally lower than the
healthy volunteer. Fitted pb values can also be correlated to cartilage regions
with obvious OA symptom.