Guoping Xu1,2, Yogesh Rathi2,3, Joan A Camprodon3,4, and Lipeng Ning2,3
1Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 3Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 4Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States
1Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 3Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States, 4Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States
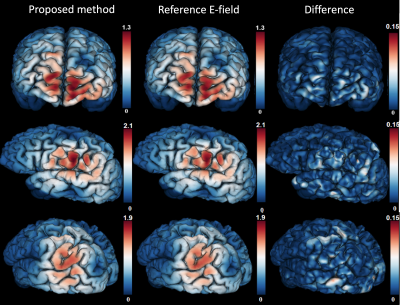
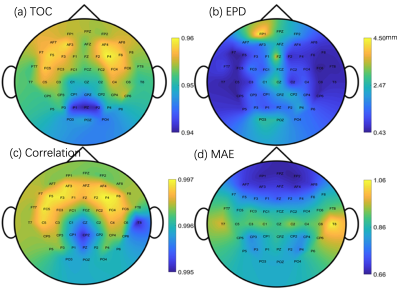
We proposed a deep-neural-network based approach for real-time prediction of TMS-evoked E-field using subject specific MRI. The predicted E-field is similar to the result estimated using finite element methods.