Sina Straub1, Janis Stiegeler1,2, Edris El-Sanosy3, and Till M. Schneider4
1Division of Medical Physics in Radiology, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany, 2Faculty of Physics and Astronomy, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany, 3Division of Radiology, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany, 44Department of Neuroradiology, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany
1Division of Medical Physics in Radiology, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany, 2Faculty of Physics and Astronomy, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany, 3Division of Radiology, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany, 44Department of Neuroradiology, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany
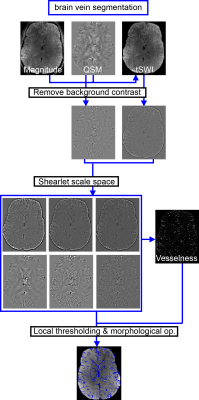
Compared
with a ground truth, the proposed vein segmentation algorithm can accurately
segment venous vasculature and allows for a susceptibility-based differentiation
of deep and superficial vascular territories.
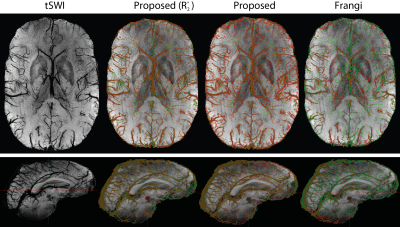
Figure 3: Representative axial and sagittal slices of 16-slices minimum intensity
projections of tSWI data and segmentations. The manually segmented ground truth
is shown in green, overlaid with (from left to right) the segmentation from the
proposed algorithms for a multi-echo acquisition when R2* is available, without
R2*, and for the Frangi method, respectively. These segmentations are shown in
red so that true positives appear orange, false positives red, and false
negatives green.