Suk-tak Chan1, Karleyton C. Evans2, Tian-yue Song1, Andre van der Kouwe1, Bruce R. Rosen1, Yong-ping Zheng3, and Kenneth K. Kwong1
1Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 2Biogen, Inc., Cambridge, MA, United States, 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Kowloon, Hong Kong
1Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 2Biogen, Inc., Cambridge, MA, United States, 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Kowloon, Hong Kong
CVR to endogenous CO2 at
rest showed significant inter-subject variability and was substantially
different from CVR to external CO2 challenge. Such inter-subject
variability, not reduced by correction of respiratory effects, also showed up
less prominently in CVR to endogenous O2 at rest.
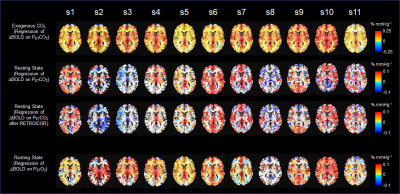
Fig
1. Individual CVR maps show significant
CVR changes under external CO2 challenges (n=11) (1st
row). Individual CVR maps to endogenous
maps showed significant inter-subject variability (2nd row). Such inter-subject variability was not
reduced by correction of respiratory effects using RETROICOR (3rd
row). CVR maps to endogenous O2 show less inter-subject variability
than CVR maps to endogenous CO2 (4th row).
