Suk-tak Chan1, Nathaniel Mercaldo2, Kenneth K. Kwong1, Steven M. Hersch3, and Herminia D. Rosas3
1Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 2Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 3Department of Neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States
1Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, MA, United States, 2Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States, 3Department of Neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, United States
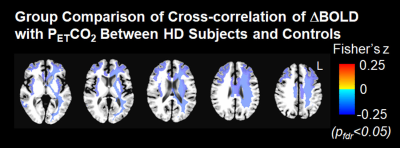
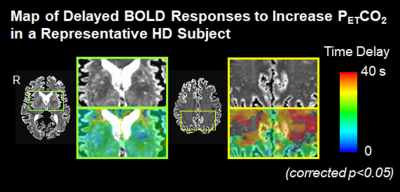
Alterations in
cerebrovascular function was found in HD and the dominance of such alterations in
white matter further suggests the signs of small vessel
disease. The impaired cerebrovascular
reactivity may be an important, not as yet considered, contributor to early
neuropathology in HD.