Rama Jayasundar1, Dushyant Kumar1, Rajesh Mishra1, Priyanka Jain2, Jaideep Sachdeva3, Chahat Kumar1, Priyanka Bhagat4, and Padma Srivastava4
1Department of NMR, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India, 2Centre for Development of Advanced Computing, New Delhi, India, 3Manipal University, Jaipur, India, 4Department of Neurology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India
1Department of NMR, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India, 2Centre for Development of Advanced Computing, New Delhi, India, 3Manipal University, Jaipur, India, 4Department of Neurology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India
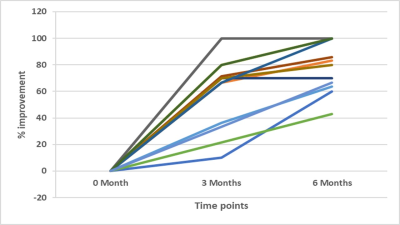
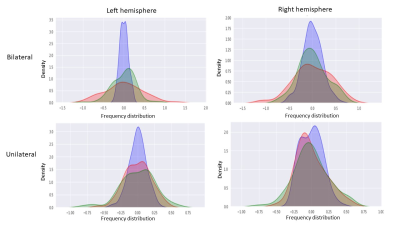
Stroke is a debilitating disease with long term effects. With
increasing interest in use of yoga in post-stroke recovery, this fMRI study has
demonstrated increase in the BOLD activity in the left pre-central gyrus region in ischemic stroke patients, 3
and 6 months post-yoga intervention.