Jacqueline Chen1, Mark Lowe1, Ken Sakaie1, Kenneth Baker2, Andre Machado3, and Stephen Jones1
1Cleveland Clinic Imaging Institute, Cleveland, OH, United States, 2Cleveland Clinic Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland, OH, United States, 3Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute, Cleveland, OH, United States
1Cleveland Clinic Imaging Institute, Cleveland, OH, United States, 2Cleveland Clinic Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland, OH, United States, 3Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute, Cleveland, OH, United States
We developed a white-matter tractography method that
uses local and global information to improve accuracy, and partial differential
equation solvers for fast whole-brain mapping. Topological maps of the corpus
callosum are generated to demonstrate accuracy and clinical relevance.
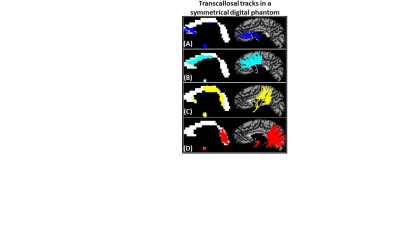
Figure 2: (A) Anterior CC contained tracks from the most anterior and
inferior regions of prefrontal cortex. (B) Mid-Anterior CC contained tracks from caudal
anterior cingulate and
superior & middle frontal cortical regions.
(C) Central
and Mid-Posterior CC contained tracks from cortical regions proximal to
the central sulcus (precentral, paracentral, postcentral) and lateral sulcus
(insula, transverse temporal, superior temporal, supramarginal). (D) Posterior
CC contained tracks from posterior
parietal, inferior temporal and occipital lobes.
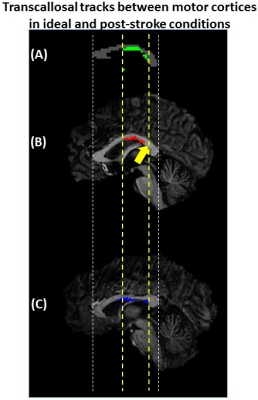
Figure 3: (A) Phantom mid-sagittal CC showing the ideal
intersection of the transcallosal tracks (green) between precentral gyri. (B) The intersection of tracks (red)
between precentral gyri for Patient A shows a region where no
tracks were detected (yellow arrow) but were found in (A). (C) The intersection
of tracks (blue) between precentral gyri for Patient B had a similar
extent along the CC as the phantom.
