Digital Poster
Preclinical fMRI
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

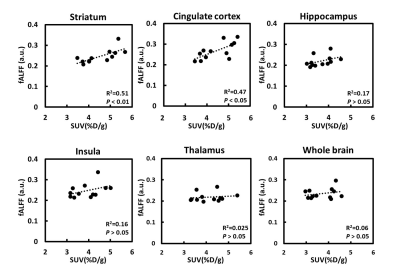 |
Computer Number: 65
3564. Regional
correlation between fractional amplitude of low-frequency
fluctuation (fALFF) and brain glucose uptake in anesthetized
rats
W-Y Chen, S-M Huang, B-F Lin, S-L Peng
China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan
Impact: The findings suggest that fALFF could serve as a
non-invasive marker for glucose metabolism in certain brain
areas under anesthesia. These results may advance the use of
fALFF in rodent studies on brain function, especially when
PET data is unavailable.
|
|
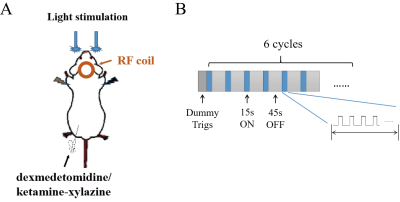 |
Computer Number: 66
3565. No
negative BOLD Responses observed in the SC of visual pathways in
Sprague-Dawley Rat
Z. Yu, H. Wang, Y. Zhuo, Z. Zuo
Institute of Biophysics, CAS, Beijing, China
Impact: We observed similar BOLD responses in LGN and V1
of SD and LE rats. However, unlike LE rats exhibited
negative BOLD responses in SC at high frequencies, SD rats
exhibited positive BOLD responses in SC, suggesting
strain-dependent neurovascular coupling differences.
|
|
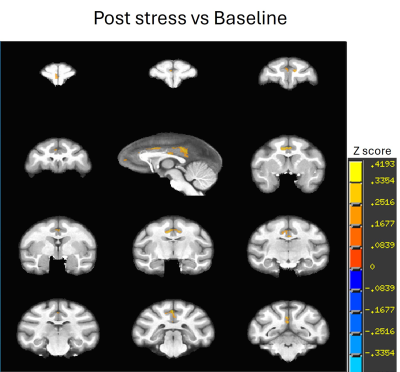 |
Computer Number: 67
3566. The
Functional Connectivity Changes of Default-Mode Network in
Monkeys after Acute Stress Exposure
C-X Li, X. Zhang, M. Treadway, V. Michopoulos
Emory University, Atlanta, United States
Impact: Monkeys could replicate the FC alteration in
humans after stress and provide a unique platform for
preclinical stress-related disorders.
|
|
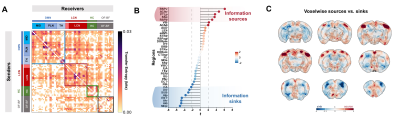 |
Computer Number: 68
3567. Directed
fMRI connectivity mapping reveals a flexible functional
hierarchy in the mouse brain
S. Gini, L. Kocillari, M. Celotto, L. Coletta, S. Panzeri,
A. Gozzi
Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia , Rovereto, Italy
Impact: Our study shows that resting state fMRI can be
reliably used to probe directed information transfer between
brain regions.
|
|
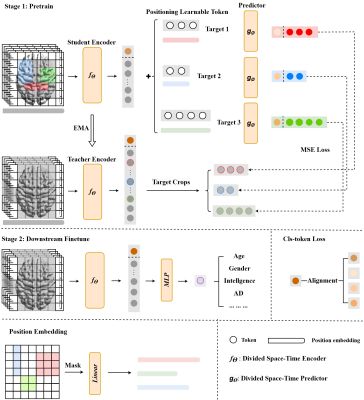 |
Computer Number: 69
3568. End-to-End
Spatial and Temporal Brain Region Feature Representation
Learning from fMRI
X. Wang, M. Liu, H. Huang, H. Jiang, Q. Wang
Shanghaitech University, Shanghai, China
Impact: This project introduces a foundational model
with voxel-level inputs and spatio-temporal attention,
enhancing fMRI representation accuracy, generalization, and
insights into brain networks.
|
|
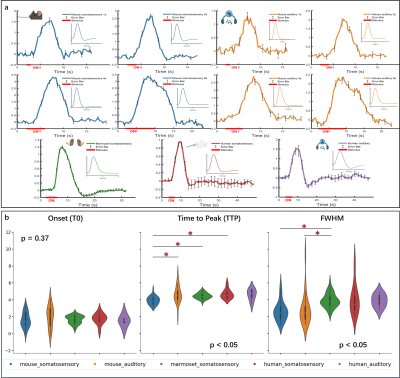 |
Computer Number: 70
3569. Characterizing
hemodynamic responses across species in the awake state
Q. Chen, C. Yen, A. Koretsky, A. Silva, Z. Liang, Z. Ma
ShanghaiTech Unversity, Shanghai, China
Impact: Our findings reveal species-specific hemodynamic
differences in the awake state, enhancing translational
research between awake animal models and human neuroimaging.
|
|
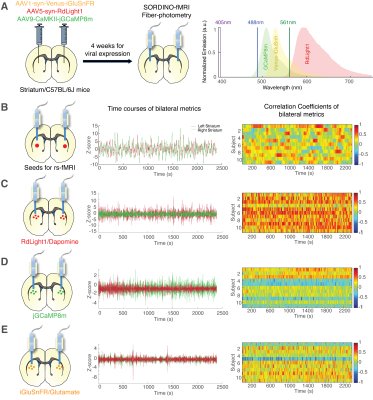 |
Computer Number: 71
3570. Simultaneous
fMRI and triple-sensor fiber photometry reveal the neurochemical
correlates of bilateral striatal connectivity
W-T Zhang, S. Song, L-M Hsu, R. Nonneman, W-W Wang, M.
Sardinas, H-H Chao, Y-Y I. Shih
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, United States
Impact: This work provides evidence-based interpretation
of the rs-fMRI connectivity between striatum of the two
hemispheres, which is crucial for motor control, cognition,
motivation behavior, and several neurological disorders.
|
|
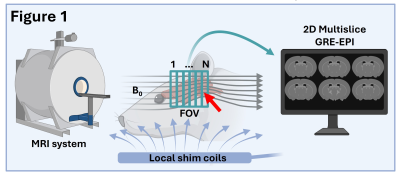 |
Computer Number: 72
3571. Local
shim coils improve B0 homogeneity achieving high signal to noise
in preclinical echo-planar imaging recordings
D. Cleppien, S. Nassirpour, P. Chang, A. Stroh
Leibniz Institute for Resilience Research, Mainz, Germany
Impact: In preclinical fMRI, local shim coils reduce B0-inhomogeneities
more effectively than the established method based on
spherical harmonics achieving higher signal to noise and
less distortions in echo-planar imaging recordings.
|
|
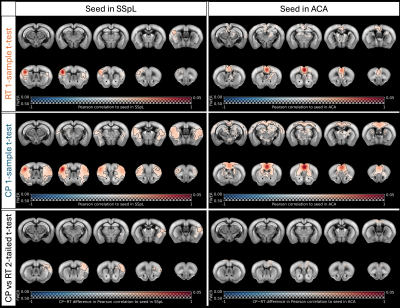 |
Computer Number: 73
3572. The
value of a cryoprobe to mouse resting-state fMRI
E. Kim, E. MacNicol, A. Baric, D. Cash
King's College London, London, United Kingdom
Impact: Mouse rsfMRI is difficult but feasible through
careful optimization (animal handling, anaesthesia, pulse
sequence parameters, etc.). A cryoprobe can significantly
improve the quality of mouse rsfMRI studies and may enhance
the detection of biological effects with smaller group
sizes.
|
|
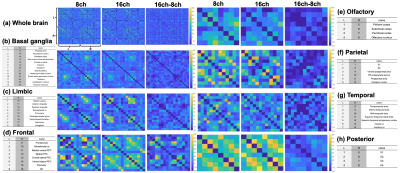 |
Computer Number: 74
3573. The
effect of multichannel coils on the brain network of the common
marmoset
H. Tamada, J. Hata, T. Marusaki, H. Oshiro, K. Muta, T.
Okuno, M. Abe, H. Okano
Tokyo Metropolitan University, Tokyo, Japan
Impact: This study reveals differences in SNR, image
uniformity, and functional connectivity across brain regions
using multichannel coils in common marmoset fMRI, providing
useful insights for coil selection and improving brain
function analysis accuracy in various research fields.
|
|
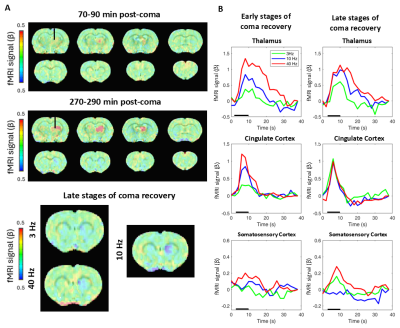 |
Computer Number: 75
3574. Effect
of frequency-dependent central thalamic stimulation in
unconscious and comatose rats
L. Gomez Cid, Y. Jian, X. Liu, P. Pais-Roldan, D. Hike, A.
Zhou, B. Edlow, X. Yu
Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, United States
Impact: This study contributes to the understanding of
how frequency-dependent central thalamus-stimulation can
promote cortical reactivation and coma recovery.
|
|
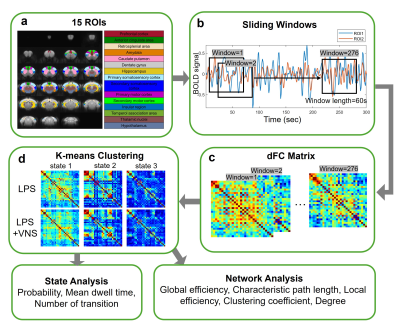 |
Computer Number: 76
3575. Dynamic
Resting State Functional Connectivity in a Sepsis Mouse Model
After Vagus Nerve Stimulation Treatment
W-Y Liao, H-W Sung, C-H Mac, D. Nguyen, H-H Peng
National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan
Impact: After VNS, the brain connectivity of sepsis mice
tended to distribute evenly. The probability of segregated
state decreased. The connectivity with the insular region
was substantially modulated after VNS treatment.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 77
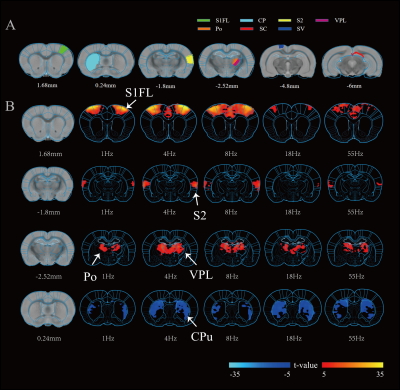
3576. Frequency-dependent
BOLD fMRI to somatosensory stimuli in
dexmedetomidine-anesthetized rats
Z. Yu, H. Wang, Y. Zhuo, Z. Zuo
Institute of Biophysics, CAS, Beijing, China
Impact: Bilateral forelimb stimulation activated S1FL,
S2, VPL, and Po under dexmedetomidine anesthesia.
High-frequency stimulation also induced strong onset
activation in these regions, while no offset activation.
This suggests dexmedetomidine is a promising anesthetic
reflecting the physiological state like awake animals.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 78
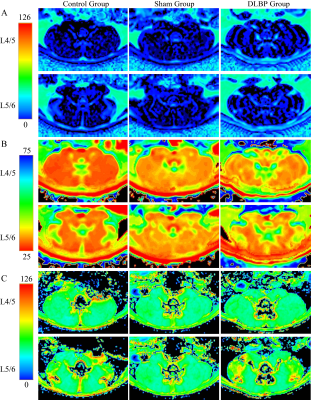
3577. Association
Among Multimodal MRI Parameters, Inflammation, and Pain in a Rat
Model of Discogenic Low Back Pain
Y. Guo, B. He
The First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
Impact: Future research could consider conducting
longitudinal studies to evaluate the correlation between
inflammation and MRI parameters during inflammatory
response. This would help further validate multimodal MRI as
a reliable imaging biomarker.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 79
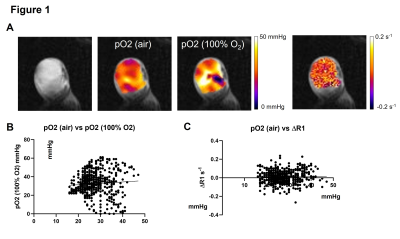
3578. Vasodynamic
changes significantly impact the interpretation of TOLD MRI
M. Horikawa, S. Kishimoto, K. Horie, N. Devasahayam, N.
Koyasu, K. Yamamoto, J. Brender, M. Krishna
NCI, Bethesda, United States
Impact: In this study, hypoxic regions showed improved
pO₂ without a corresponding R1 increase, indicating that
factors beyond pO₂—such as blood perfusion, volume, and
interstitial exchanges—also influence R1 values and may
obscure isolated pO₂ effects.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.