Digital Poster
White Matter: Aging & Diseases
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

 |
Computer Number: 113
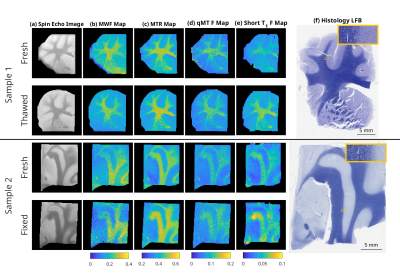
1484. Impact
of Tissue Sample Preparation Method on Myelin-Sensitive
Quantitative MR Imaging and Histological Analysis

A. Murguia, A. Jacobson, S. Swanson, U. Scheven, J-F
Nielsen, J. Fessler, N. Seraji-Bozorgzad
University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, United States
Impact: Tissue freezing is a reasonable alternative
preservation method to tissue fixation for use in qMRI
analysis. Brain banks that store frozen tissue could use
these samples for future qMRI and histological studies.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 114
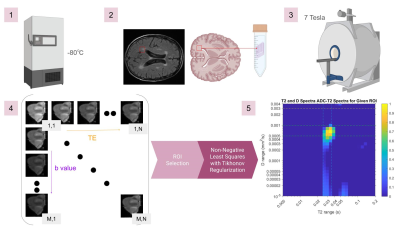
1485. Combined
Diffusion Relaxometry: Phantom Validation and Ex Vivo
Characterization of Alzheimer’s Disease Lesions
A. Jacobson, A. Murguia, S. Swanson, U. Scheven, J-F
Nielsen, J. Fessler, N. Seraji-Bozorgzad
University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, United States
Impact:
The D-T2 phantom can serve as a standard for validating D-T2 imaging protocols. Applying D-T2 to assess ADRD lesions could allow for more disease-specific diagnostics with MRI. |
|
 |
Computer Number: 115
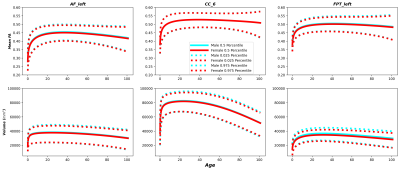
1486. White
Matter Microstructure and Macrostructure Brain Charts across the
Human Lifespan: 23,971 participants from 25 studies
M. Kim, C. Gao, S. Bogdanov, K. Ramadass, N. Newlin, P.
Kanakaraj, D. Archer, T. Hohman, S. Resnick, L. Beason-Held,
L. Cutting, L. Barquero, T. Nguyen, K. Humphreys, Y. Niu, S.
Vinci-Booher, C. Cascio, Z. Li, P. Zhang, B. Landman, K.
Schilling
Vanderbilt University, Nashville, United States
Impact: This research provides standardized WM brain
charts for population comparison, enabling tract-specific
assessments of brain development and aging, and identifying
key developmental milestones for each tract.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 116
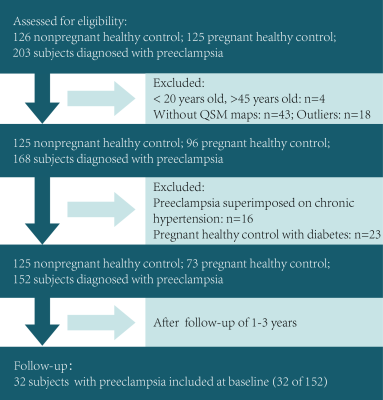
1487. Cross-sectional
and longitudinal assessment of iron levels in the white matter
of the limbic system in preeclampsia patients
C. Sui, L. Guo, L. Yang, T. Chen, M. Li, Q. Zhang
Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China
Impact: Changes in susceptibility values in the Papez
circuit provide more information for understanding the
pathological mechanism of cognitive decline in preeclampsia
patients.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 117
1488. Metabolic
and structural white matter integrity in drug-resistant temporal
lobe epilepsy: A multimodal study using MRSI and DTI
H. Zhang, B. Cai, Y. Zhao, Y. Li, W. Jin, Y. Cui, J. Li, M.
Zhang, Z. Liang, J. Luo
School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Impact: This work highlights NAA as an independent
marker for white matter metabolic integrity of temporal lobe
epilepsy patients in comparison to DTI-FA.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 118
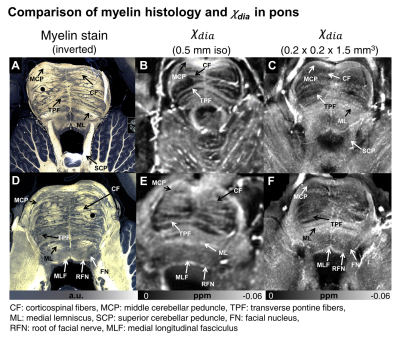
1489. Visualization
of in-vivo brainstem myeloarchitecture via χ-separation at 7T

J. Kim, C. Oh, A-M Oros-Peusquens, N. J. Shah, C-H Shon,
H. Song, J. Lee
Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact:
This study demonstrates that 7T χ-separation can generate high-resolution (<0.5 mm) diamagnetic susceptibility (mostly myelin) maps of in-vivo brainstem, closely matching myelin histology. This may benefit detailed analysis of structure and myelin concentration changes in brainstem, relevant to neurodegenerative diseases. |
|
 |
Computer Number: 119
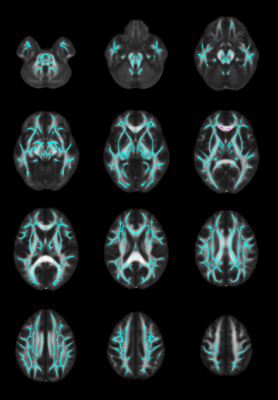
1490. Factors
Affecting White Matter Recovery After Medulloblastoma Treatment:
A Six-Year TBSS Analysis
J. Glass, J. Steffl, T. Patni, Y. Li, G. Robinson, A.
Gajjar, T. Merchant, W. Reddick
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, United States
Impact:
This study identified medulloblastoma survivors at higher risk for slower recovery of microstructural effects. These findings can be used to design targeted interventions to lessen the impact of current therapies on the developing brain. |
|
 |
Computer Number: 120
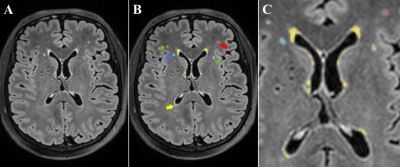
1491. Dynamic
changes of white matter hyperintensities volume after
neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients
Y. Hu, W. Lei, J. Zhang, T. Yin
Department of Radiology, Chongqing University Cancer Hospital, School of Medicine, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, Chongqing, China
Impact: Our preliminary findings indicate that the
effects of chemotherapy on WMH volume are mainly acute or
subacute, highlighting the importance of early intervention
for the prevention of chemotherapy-related cognitive
impairment.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 121
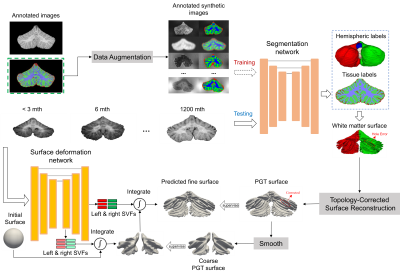
1492. Lifespan
Mapping of the Human Cerebellum: Tissue Segmentation and Surface
Reconstruction
G. Lin, J. Zhao, K. Huynh, W. Lyu, S. Ahmad, P. Yap
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, United States
Impact: This work addresses the gap in lifespan
cerebellar analysis by providing a reliable solution for
segmentation and surface reconstruction to advance our
understanding of cerebellar development.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 122
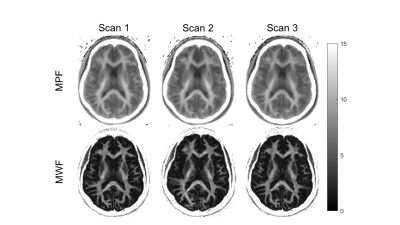
1493. Repeatability
of Myelin and Myelin Water Quantification Using Short-TR
Adiabatic Inversion-Recovery (STAIR) Sequences
J. Lo, J. Wang, D. Tran, H. D. Chae, G. Nemeh, J. Athertya,
S. H. Shin, Y. Ma, J. Du
University of California San Diego, La Jolla, United States
Impact: Strong repeatability was demonstrated for two
myelin imaging biomarkers, MPF and MWF, highlighting the
utility of STAIR sequences for reliable myelin mapping and
potential applications in neuroinflammatory and
neurodegenerative diseases.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 123
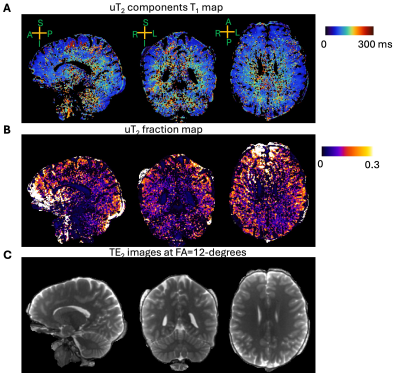
1494. Quantitative
Ultrashort T2 Components Imaging using Variable Flip Angle
Balanced Steady State Free Precession Ultrashort Echo Time MRI
X. Shen, A. Green, R. Henry, U. Emir, P. Larson
University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, United States
Impact: This new UTE-based method used simplified model
to provide reliable fitting results of uT2 fraction, which
was also tested on multiple sclerosis patients, could aid in
future multiple sclerosis diagnosis and evaluation of
re-myelination during treatment.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 124
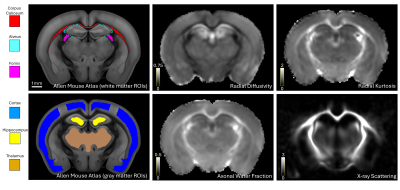
1495. Myelin
Changes in Alzheimer’s Mouse Model using MRI and X-ray
scattering
A. Liu, D. Simmons, C. Alvarez, F. Longo, M. Zeineh, M.
Georgiadis
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: We show the combined application of X-ray
scattering and MRI to probe myelin changes in the white and
gray matter of an AD mouse model. X-ray scattering can help
validate MRI and quantify myelin changes in
neurodegenerative diseases.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 125
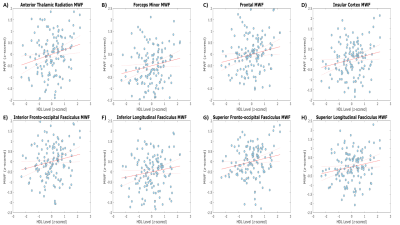
1496. Higher
Levels of Circulating Good Cholesterol Are Associated with
Higher Cerebral Myelination
A. de Rouen, Z. Gong, J. Bae, N. Fox, N. Zhang, A. Guo, M.
Bouhrara
National Institute on Aging, Baltimore, United States
Impact: Higher HDL levels correlate with higher levels
of cerebral myelination, confirming HDL's neuroprotective
effects. This work motivates further investigations aiming
to establish innovative approaches for preventing
neurodegenerative diseases, enhancing cognitive function and
promoting healthier brain aging.
|
|
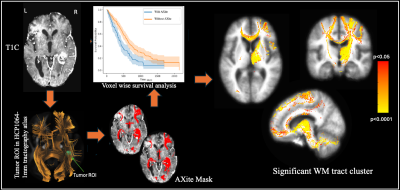 |
Computer Number: 126
1497. MGMT
Status and White Matter Tract Infiltration in Glioblastoma: A
Voxel-Wise Approach to Survival Mapping
B. Nath, S. Bobholz, A. Lowman, S. Duenweg, A. Winiarz, F.
Kyreme, J. Connelly, D. Coss, M. Krucoff, A. Banerjee, P.
LaViolette
Medical College of Wisconsin , Wauwatosa , United States
Impact: Our study highlights the combined impact of
white matter tract infiltration and MGMT status on GBM
prognosis, highlighting pathways associated with worse
survival. These findings could inform personalized treatment
strategies that focus on high-risk WM tracts, enhancing
patient outcomes.
|
|
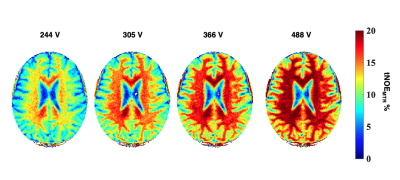 |
Computer Number: 127
1498. Optimization
of Lipid Inversion with Hyperbolic Secant Adiabatic Pulses in
Transient NOE at 7T
B. Benyard, D. Kumar, N. Wilson, R. Reddy
University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, United States
Impact: This approach may improve lipid degeneration
monitoring in neurodegenerative diseases like MS and
Alzheimer’s.
|
|
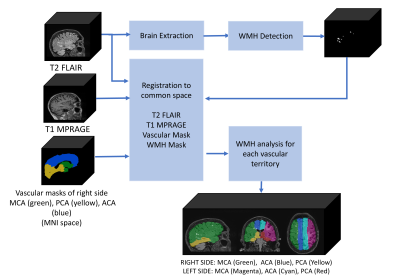 |
Computer Number: 128
1499. Atherosclerosis
severity in the internal carotid artery is associated with
elevated white matter lesion burden in the supplied brain
territories
D. Karakay, H. Wiskoski, A. Peckham, J. Arias, D. Patterson,
K. Rayasam, R. Mushtaq, K. Johnson, T. Trouard, M. Altbach,
A. Bilgin, C. Weinkauf
University of Arizona, Tucson, United States
Impact: Understanding vascular factors that exacerbate
white matter lesion (WML) burden is highly relevant for
treating and mitigating neurodegeneration This work
describes the impact of large vessel disease on
WM degeneration in contrast to previous work focused on
small vessel disease.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.