Digital Poster
Dementia: Quantification & Assessment
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

 |
Computer Number: 81
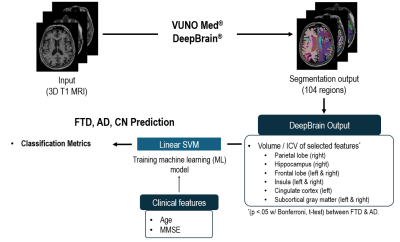
4349. Diagnosis
of Frontotemporal Dementia on Brain MR Images by Using Automated
Brain Volumetry
S. H. Lee, W. Jung, H. Cho, D-H Kim, M. Park
Vuno Inc., Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: Our automated brain volumetry model demonstrated
promising diagnostic accuracy for FTD, offering a potential
tool for differentiating FTD from AD and normal in clinical
settings.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 82
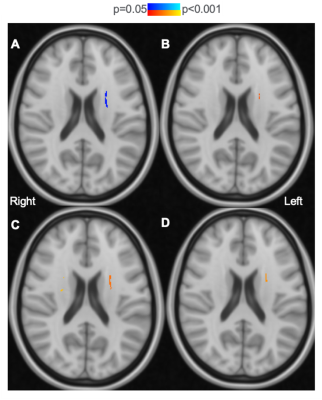
4350. First
Application of the Standard Model of Diffusion to Subjective
Cognitive Decline Reveals Novel Insights into White Matter
Microstructure
R. Flaherty, Y. Sui, Z. Youss, H. Rusinek, A. Masurkar, M.
Lazar
New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: Our findings suggest the Standard Model Imaging
(SMI) can detect pathological changes in compartment
diffusivities assumed to be indistinguishable or stable in
other popular diffusion models. These findings are
consistent with demyelination. Further research on
demyelination in SCD is needed.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 83
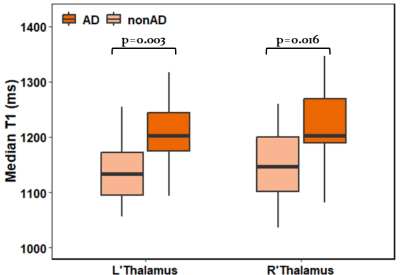
4351. Evaluation
of Tissue Characteristics Using Magnetic Resonance
Fingerprinting in Dementia Patients with Various Clinical Stages
C-W Fang, X-Z Lu, H-J Hsieh, C-J Lu, J-M Wang
National Taiwan University Hospital, Yunlin Branch, Yunlin, Taiwan
Impact: The potential of Magnetic resonance
fingerprinting as a biomarker in patients with dementia was
revealed. The changes of tissue characteristics in thalamus
and putamen play a role in clinical dementia symptoms.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 84
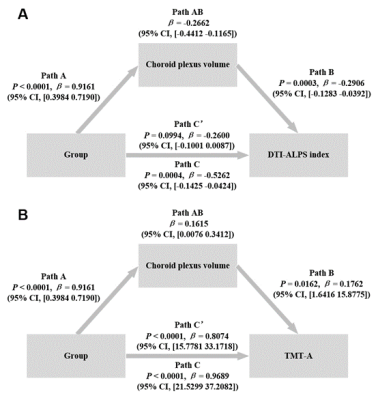
4352. Choroid
plexus volume mediates glymphatic and executive dysfunction in
end-stage renal disease patients with mild cognitive impairment
Z. Luo, L. Bo, X. Chen, Y. Chen, H. Zhang, Z. Han, J. Wang,
Z. Wang, X. Wang, X. Zhu, Q. Zhu, H. Yuan, W. Gu, S. Liu, S.
Ma, J. Mu, Y. Liu
First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China
Impact:
This study identifies choroid plexus volume as a potential mediator of glymphatic dysfunction and executive dysfunction in ESRD-MCI, suggesting its role in cognitive impairment pathophysiology. This finding offers a target for interventions to address cognitive decline in ESRD patients. |
|
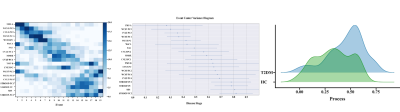 |
Computer Number: 85
4353. Sequence
of cognitive decline and brain atrophy patterns in type 2
diabetes patients estimated using an event-based model of
disease progression
M. Ni, B. Hu, Y. Yu, G. Cui
Tangdu Hospital, Xi`an, China
Impact: These discoveries offer new insights into
understanding the cognitive impairments and brain structural
changes associated with T2DM.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 86
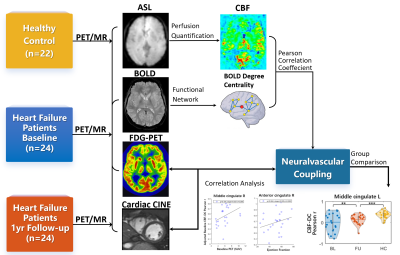
4354. Altered
Neurovascular Coupling in Heart Failure: Insights from a 1-Year
Follow-Up Study on Cerebral Hemodynamics and Cognitive Decline
C. Zheng, Y. Cui, R. Qin, C. Sun, Y. Hu, Y. Yang, J. Lu
Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Impact: This study provides new insights into cognitive
impairment and potential imaging biomarkers for brain injury
in HF.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 87
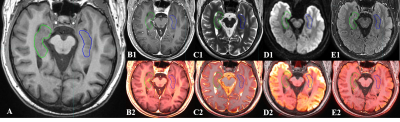
4355. Quantitative
study of changes in the hippocampus after radiotherapy via
multisequence magnetic resonance imaging radiomics
l. rui, g. zhong, D. Pylypenko, y. yong
Shandong First Medical University, jinan, China
Impact: This study highlights the potential of
multi-sequence MRI radiomics as a valuable tool for
detecting and tracking hippocampal changes following WBRT,
offering new insights for early intervention and improved
management of cognitive decline in brain metastases
patients.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 88
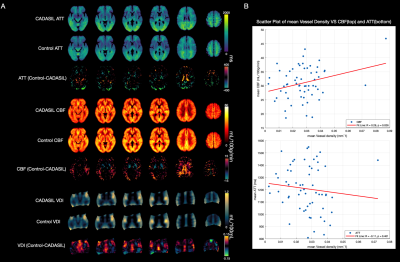
4356. Changes
in Cerebral Small Vessel Density and Hemodynamics in CADASIL
Patients Revealed by high-resolution Black-Blood MRI and
Multi-Delay pCASL
Z. Yang, Z. Liu, F. Guo, S. Mendoza, Y. Li, Y. Ying, X.
Cheng, Y. Shi, Q. Yang, D. Wang
USC Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute, Los Angeles, United States
Impact: This study employed a high-resolution black
blood MRI alongside 5-PLD pCASL to offer comprehensive
assessments of the alterations of cerebral small vessel
density and hemodynamics and their relationships with
cognitive impairments in CADASIL patients.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 89
4357. Association
between LE8 and Variations in Brain MRI Characteristics
Y. Li, L. Han
Department of Radiology,Beijing friendship hospital,Capital Medical University, beijing, China
Impact: This study employed a prospective cohort
to elucidate how the LE8 score influences the
characteristics of brain MRI characteristics. Consequently,
the eight modifiable factors offers a potential pathway for
individuals to actively improve or preserve their brain
health.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 90
4358. Assessing
pulsatility of cerebral perforating arteries with 3T high-res
dual-VENC PC-MRI: Development, validation, and aging evaluation.
J. Tang, T. Zhao, M. Gamez, P. Gorelick, H. Chui, L. Yan
Northwestern University, Chicago, United States
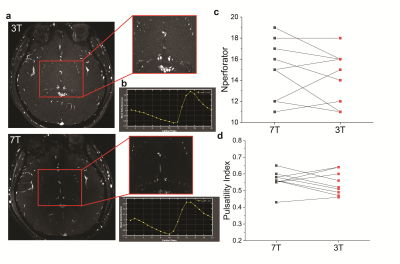
Impact: We developed a reliable 3T technique to assess
LSA pulsatility, which could serve as a imaging marker for
aging and cerebral vessel disease. Given the widespread use
of 3T, this technique shows strong potential for future
research and clinical applications.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 91
4359. Free
Water mediates the association between glymphatic dysfunction
and executive function performance
X. Liu, P. Maillard, G. Barisano, A. Caprihan, S. Cen, X.
Shao, K. Jann, J. M. Ringman, H. Lu, K. Arfanakis, C. S.
DeCarli, B. T. Gold, S. Seshadri, C. L. Satizabal, A. S.
Beiser, M. Habes, J. H. Kramer, L. Stables, H. Singh, K. G.
Helmer, S. M. Greenberg, D. J. Wang
University of Southern California, Los Angeles, United States
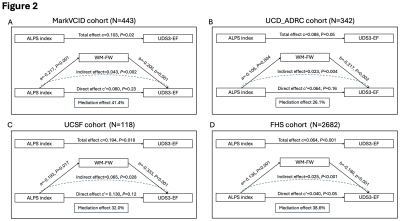
Impact: Our findings provide a strong clinical rationale
for the use of the ALPS index as a marker of cSVD-related
VCID.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 92
4360. Improving
machine learning classification of Alzheimer's disease and
normal pressure hydrocephalus using MRE-derived compressibility
metric
P. Karki, M. Murphy, A. Manduca, Y. Le, P. Cogswell, R.
Ehman, J. Huston III
Mayo Clinic, Rochester, United States
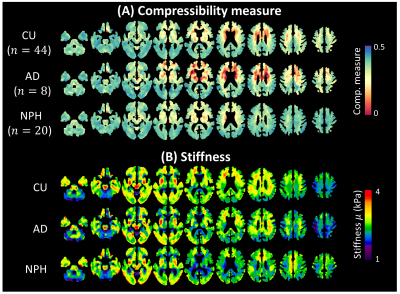
Impact: We used a lobar atlas based regional values of
MR Elastography derived mechanical properties to improve
machine learning classification of cognitively unimpaired
controls, and normal pressure hydrocephalus and Alzheimer’s
dementia patients.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 93
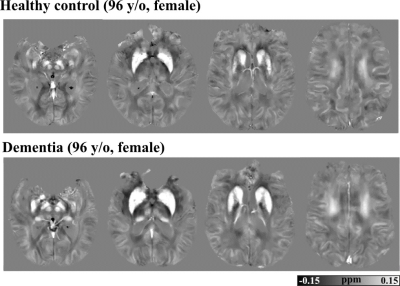
4361. Cerebral
iron load and cognitive impairment: the Atherosclerosis Risk in
Communities (ARIC) Study
L. Chen, D. Zhao, E. Guallar, Z. Xu, Y-P Liu, X. Zhou, B.
Wasserman, X. Li, Y. Qiao
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, United States
Impact: Higher cerebral iron load is associated with
dementia, independent of APOE4 status, cardiovascular risk
factors, and small vessel disease, suggesting its role in
neurodegenerative disease pathogenesis, separate from
vascular contributions
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 94
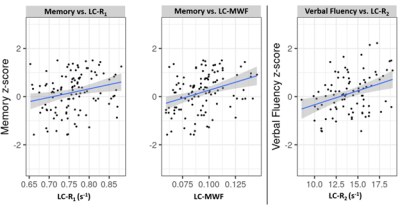
4362. Advanced
multicomponent MR relaxometry detects early changes in the Locus
Coeruleus associated with age-related cognitive decline
J. Bae, Z. Gong, A. Guo, N. Fox, N. Zhang, A. De Rouen, M.
Bouhrara
National Institute on Aging, Baltimore, United States
Impact: Our quantitative MRI metrics, reflecting changes
of LC in structural integrity and myelination, are sensitive
to cognitive changes. This novel imaging biomarkers are
sensitive to early changes in LC to support healthy brain
aging.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 95
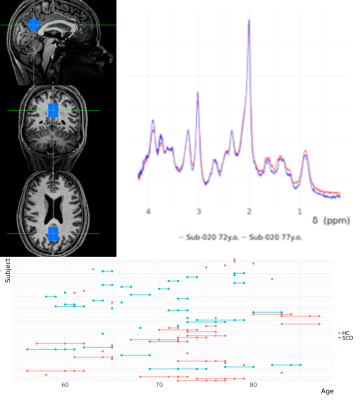
4363. Metabolites
and Macromolecules in healthy aging and subjective cognitive
decline. A longitudinal 7 T 1H-MRS study
A. Dell'Orco, L. Göschel, L. Rieman, S. Aydin, B. Ittermann,
A. Tietze, M. Scheel, A. Fillmer
Charité Universitaetsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Impact: Our results highlight the potential of
macromolecules as biomarkers, also pointing to a biochemical
link between SCD and AD.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 96
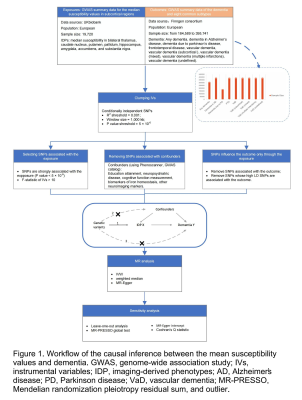
4364. Mendelian
randomization analysis reveals causal relationships between iron
loading in subcortical regions and the risk of developing
dementia
Y. Chen, T. Chen, L. Yang, P. Liang, Z. Cheng, N. Wang, X.
Zhang, Y. Wang, C. Sui, Y. Gao, C. Liang, L. Guo
Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, China
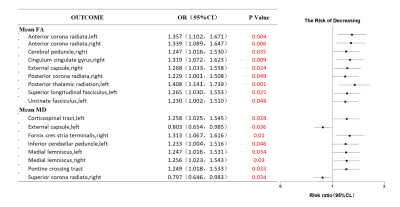
Impact: Iron
deposition in subcortical brain regions raises the risk of
dementia, and subcortical susceptibility values can be used
as an imaging biomarker for the clinical assessment of
dementia.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.