Digital Poster
Epilepsy
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

 |
Computer Number: 145
4111. Molecular
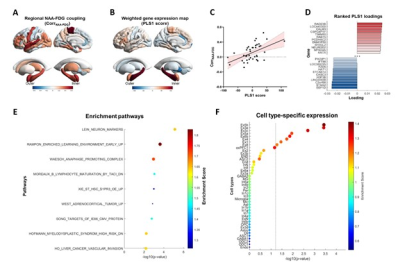
Mechanisms Underlying NAA and FDG Uptake Coupling in Temporal
Lobe Epilepsy: Insights from Imaging Transcriptomics
J. Li, L. Zhao, H. Huang, Y. Zhao, Y. Li, W. Jin, B. Cai, H.
Zhang, M. Zhang, Z. Liang, J. Luo
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Impact: This
study provides insight into the molecular basis of metabolic
coupling in temporal lobe epilepsy, specifically examining
the relationship between NAA levels and FDG uptake. The
findings may shed new light on epileptogenesis and potential
therapeutic targets.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 146
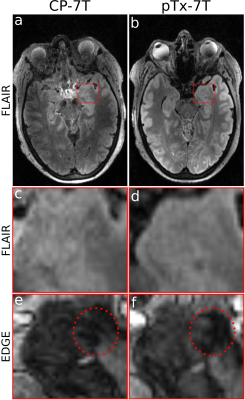
4112. Parallel
transmit 7T MRI improves epileptogenic lesion detection compared
to circularly polarized 7T MRI
K. Klodowski, M. Zhang, D. Scoffings, J. Jen, T. Cope, C.
Rodgers
University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom
Impact: This study confirms that 7T-pTx MRI is more
effective for detection of lesions in drug-resistant focal
epilepsy patients than CP 7T MRI. We are now seeking funding
for a multisite study to prove cost-effectiveness within the
NHS epilepsy surgery pathway.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 147
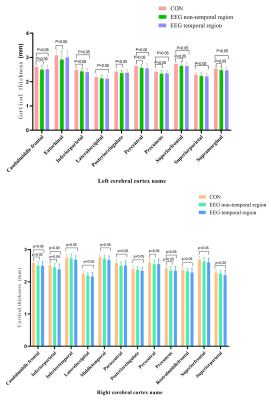
4113. Preoperative
Assessment in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: Integrating EEG with
Cortical Structural and Perfusion Metrics to Identify Cortical
Damage
Z. LING, C. TING, W. ZHUO, S. YAN, L. QIN, C. BING, T. YUAN
General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, YIN CHUAN, China
Impact: This study highlights the extensive cortical
damage in HS patients, particularly in the frontal and
temporal lobes, guiding early surgical interventions. It
enables clinicians to refine preoperative assessments and
encourages further research on targeted therapies for
improved patient outcomes.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 148
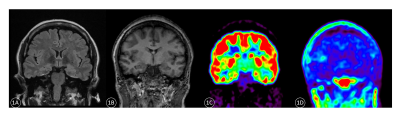
4114. Diagnostic
Value of Hybrid 18F-FDG and 18F-DPA-714 PET/MR in Refractory
Epilepsy
S. Zhang, B. Xu, J. Lu
Xuanwu Hospital Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Impact: Compared to MRI and 18F-FDG
PET/MR, 18F-DPA-714
PET/MR offers clearer and more precise delineation of lesion
borders while maintaining the high positive detection rate,
thus providing valuable guidance for preoperative
localization.
|
|
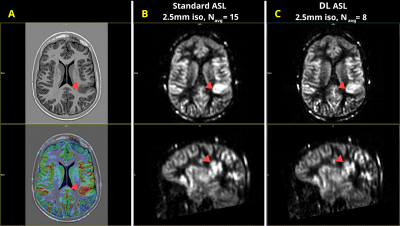 |
Computer Number: 149
4115. Clinical
Feasibility of High-Resolution Brain Perfusion Imaging using
Deep Learning 3D Arterial Spin Labeling
M. Vidorreta, J. Pfeuffer, L. Martínez-Gálvez, R.
Heredia-Padilla, D. Nickel, J. Álvarez-Linera
Siemens Healthineers, Madrid, Spain
Impact: We show that high-resolution ASL perfusion
imaging is feasible in clinical practice and can help detect
areas of abnormal perfusion. Deep learning reconstruction
techniques can further enhance image resolution and reduce
scan times to under 5 minutes without compromising SNR.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 150
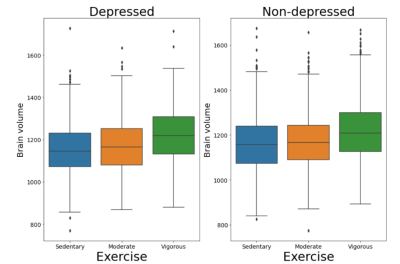
4116. Exercise
is Related to Distinctly Larger Brain Volumes in Depressed
versus Non-Depressed Populations
S. Garg, S. Meysami, N. Akbari, R. Pompa, T. Nguyen, S. Lee,
S. Basar, H. Xu, Y. Chodakiewitz, D. Merrill, D. Durand, S.
Hashemi, C. Raji
Vigilance Health Imaging Network, Vancouver, Canada
Impact: This study highlights the link between physical
activity and brain health in individuals with depression,
demonstrating that exercise may attenuate volumetric
deficits in brain regions, ultimately offering a viable
therapeutic strategy to enhance mental well-being and
cognitive function.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 151
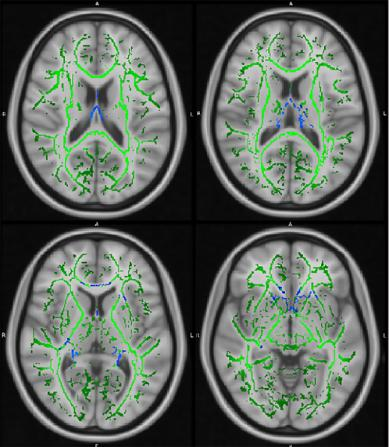
4117. TBSS-based
Distinguishing of White Matter Microstructural Changes between
Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with Normal MRI and Hippocampal Sclerosis
Z. LING, T. YUAN, S. YAN, W. ZHUO, L. QIN
General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, YIN CHUAN, China
Impact: This study’s findings suggest that TLE-HS and
TLE-NL are distinct diseases, potentially guiding more
personalized treatment strategies and improving patient
outcomes. Future research can further investigate the
specific mechanisms underlying these differences to enhance
diagnostic accuracy.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 152
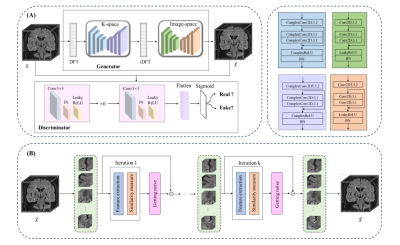
4118. Deep
Learning-Based Composite Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm
Improves High-Resolution MRI Quality of Hippocampus: A
Dual-center Study
X. Zhu, J. Shi, J. Ye, W. Huang, W. Xia, Z. Bao
Northern Jiangsu People's Hospital, Yangzhou, China
Impact: The deep learning-based composite
super-resolution reconstruction method improved 3T MRI
hippocampal resolution, allowing better visualization of
subtle structures crucial for diagnosing conditions like
temporal lobe epilepsy and Alzheimer's disease, without
increasing scan time.
|
|
|
Computer Number:
4119. WITHDRAWN |
||
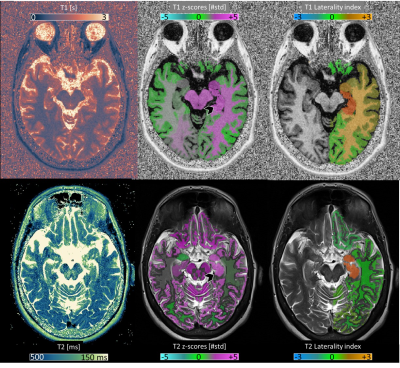 |
Computer Number: 153
4120. Multiparametric
characterization of hippocampal sclerosis using T1 and T2
normative modeling
V. Ravano, M. E. Caligiuri, M. C. Bonacci, T. Di Noto, L.
Bacha, G. F. Piredda, J. Disselhorst, D. Zaca’, N.
Golestani, A. Rampinini, I. Balboni, M. Vaneckova, T. Kober,
T. Hilbert, B. Maréchal
Siemens Healthineers International AG, Lausanne, Switzerland
Impact: The study introduces a novel normative model for
regional T1 and
T2,
enhancing the characterization of brain microstructure. This
approach, assessed on epileptic patients with hippocampal
sclerosis, highlights the clinical relevance of combined T1 and
T2 mapping
and laterality analysis.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 154
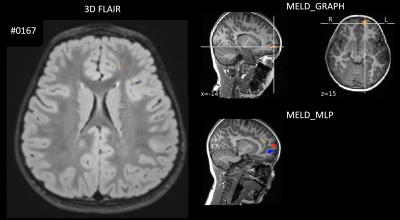
4121. Can
neural networks support identification of epileptogenic foci in
children with suspected focal cortical dysplasia (FCD)?
E. De Vita, M. Ripart, K. Senaurine, A. Knill, Y. J. Li, S.
Pujar, H. Cross, M. Z. Tahir, F. Moeller, S. Sudhakar, P.
Gaur, K. Mankad, A. Biswas, U. Loebel, A. Chari, M. Tisdall,
K. Wagstyl, S. Adler, F. D'Arco
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom
Impact: Clinical validation is essential for AI-based
Focal Cortical Dysplasia lesion-detection algorithms. A
local trade-off between sensitivity and specificity is
necessary when selecting an appropriate decision support
AI/machine-learning tool.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 155
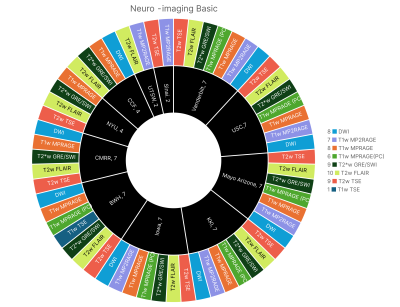
4122. 7T
Translational Alliance of North America (7TANA) Neuroimaging
Protocol Survey – Advancing Best Practices and Toward a Unified
Protocol
D. Wang, Y. Qi, K. Sakaie, S. Jones, M. Lowe, J. Liu, A.
Henning, D. Paech, J. Moore, V. Magnotta, C. Özütemiz, J.
Ellermann, J. Hua, Y. Ge, G. Madelin, S. Chawla, S. Mohan,
A. Seifert, P. Balchandani, J. Cramer, I. Ikuta, Y. Zhou, R.
Menon, J. Pan, M-L Ho, E. Middlebrooks
University of Southern California, Los Angeles, United States
Impact: It is possible to develop a common standard
protocol through consensus of the 7TANA community, despite
the considerable differences across 7T hardware/software
platforms. The protocols will be available on 7TANA website
(www.7TANA.org) to facilitate the clinical translation of 7T
MRI.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 156
4123. Investigating
Neurochemical Alterations in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)
Using 2D Multi-slice MRSI at 3T
D. K. Senapati, H. J. Zöllner, İ. Özdemir, P. B. Barker, D.
Lin
The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, United States
Impact: These findings may help to understand the
underlying pathogenesis of brain involvement in TSC,
including their relationships to neurological symptoms and
cognitive impairment.
|
|
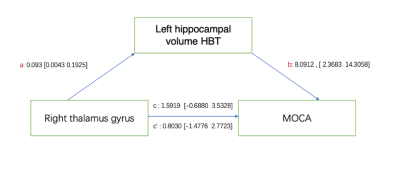 |
Computer Number: 157
4124. The
Relationship Between Hippocampal-Thalamic Volume and Cognition
in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Patients: An Automated Segmentation
Techniques.
j. Li, G. Liu, M. Li, W. Huang, J. Zhang
Lanzhou University, lanzhou, China
Impact: Our study found an association between the
thalamus and cognition, providing a new approach for
understanding the mechanisms of epilepsy and developing
targeted treatment strategies.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 158
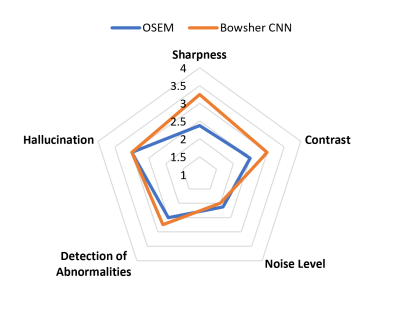
4125. Preliminary
Evaluation of an MR Anatomically Guided PET Reconstruction in
Epilepsy
Y. Wang, C. Ying, J. Cabello, X. Li, D. Faul, M. Ponsio, H.
An
Washington University in St Louis, St Louis, United States
Impact: This study demonstrates that MR
anatomically-guided PET reconstruction using Bowsher CNN
increased image sharpness and contrast. Future investigation
using a larger cohort is needed to examine the potential
clinical utility of MR anatomically-guided PET in diagnosis
and diagnostic confidence.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 159
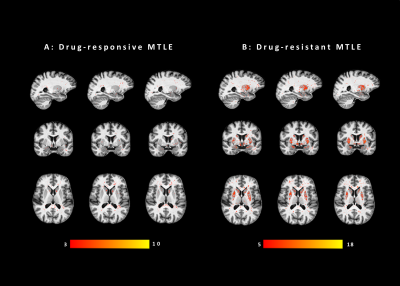
4126. Quantitative
characterization of brain microstructure in Temporal Lobe
Epilepsy: comparison with normative T1 atlas
M. C. Bonacci, V. Ravano, I. Sammarra, G. F. Piredda, A.
Burrus, D. Zacà, B. Marechal, T. Hilbert, T. Kober, A.
Gambardella, M. E. Caligiuri
University Magna Graecia, Catanzaro, Italy, Catanzaro, Italy
Impact: This study provides first evidence in support of
using qMRI alterations as markers of drug-resistance in MTLE.
Analysis using normative atlases accounting for age and sex
allowed the identification of specific changes both at
population and individual level.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.