Digital Poster
Pediatric Brain Miscellaneous
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

 |
Computer Number: 145
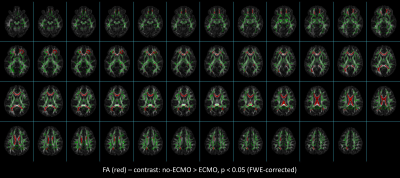
2245. White
Matter Integrity Differences in Children Treated with
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Tract-Based Spatial
Statistics Analysis
M. Ruttorf, T. Schaible, M. Weis, F. Zoellner
Heidelberg University, Mannheim, Germany
Impact:
Analysing diffusion measures can help to detect early microstructural changes in the brain of children treated with ECMO as neonates making it a promising tool for focused screening to support therapeutic strategies or targeted training to mitigate neurodevelopmental deficits.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 146
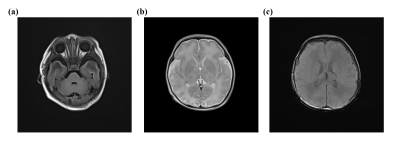
2246. Neonatal
brain MR imaging using a dedicated 32-channel semiflexible
receive coil array at 3T
F. Du, N. Li, D. Fang, Y. Zhang, X. Meng, S. Wen, X. Zhang,
H. Zeng, Y. Li
Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China
Impact: A 32-channel semiflexible receive coil array
dedicated for brain MRI in neonates within 12 months at 3T
was developed. The acquired high SNR and high-spatial
resolution MR images indicated the potentiality for the
application in neonatal clinical diagnosis.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 147
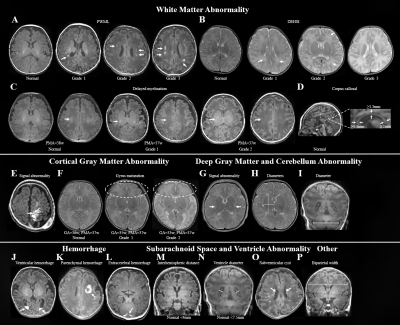
2247. Predicting
adverse developmental outcomes in infants with mild to moderate
white matter injury; A prospective cohort study with
conventional MRI
P. Bai, M. Wang, C. Liu, C. Liu, C. Da, Z. Li, X. Huang, X.
Li, J. Yang
Department of Diagnostic Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, P.R. China, Xi'an, China
Impact: The model is a relatively reliable tool to
predict adverse developmental outcomes in infants with mild
to moderate WMI.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 148
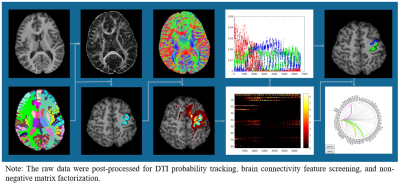
2248. Structural
connectivity changes of primary motor cortex after TMS in
cerebral palsy assessed by DTI and non-negative matrix
factorization
Y. Bian, Z. Wei, Z. Jia, L. Wu, T. Chen, J. Yang, X. Li
The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China
Impact: This study demonstrates that TMS induces
structural reorganization in the precentral gyrus of
children with spastic cerebral palsy, offering insights into
its potential as a targeted neuroplasticity-driven
therapeutic approach for motor function improvement.
|
|
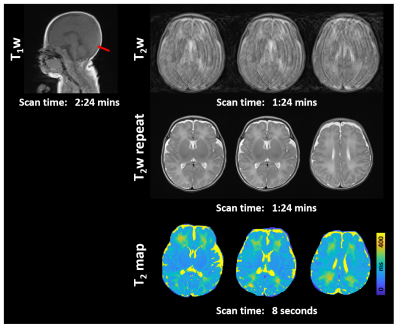 |
Computer Number: 149
2249. Ultrafast
and motion-robust quantitative MRI for awake infants with brain
injury using multiple overlapping-echo detachment imaging
N. Ge, Q. Yang, J. Bao, Z. Chen, C. Cai, S. Cai
Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
Impact: Due to its ultrafast quantification nature,
MOLED makes it possible to quantitatively track brain
development in infants affected by postnatal brain injuries,
which has previously been challenging.
|
|
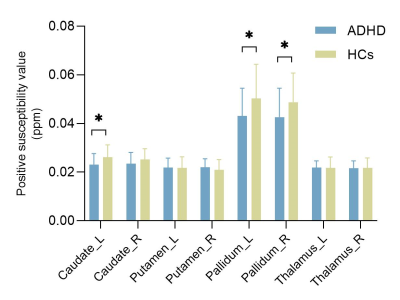 |
Computer Number: 150
2250. Brain
iron deficiency in children with attention deficit hyperactivity
disorder using APART-QSM
Y. Li, B. Xu, Y. Chen
The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Impact: The advanced approach to separate paramagnetic
and diamagnetic substances susceptibility shows the ability
to reveal brain iron deficiency in ADHD, and provides a
potential biomarker for early diagnosis and a better
understanding the pathological mechanism of ADHD.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 151
2251. Neurovascular
Coupling Alterations in Language and Visual Processing Regions
in Children with Spastic Cerebral Palsy: An rs-fMRI and ASL
Study
H. Yu, Y. Luo, C. Zhao, L. Nie, Y. Peng, D. Luo, Y. Yin, H.
Ran, H. Liu
Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, China
Impact: This study identifies distinct NVC patterns in
SCP, providing potential biomarkers for assessing disease
severity and guiding targeted interventions for SCP-related
impairments.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 152
2252. Comparison
of quantitative susceptibility mapping with source separation in
full-term, moderate-to-late preterm, and very preterm brains
M. Jang, A. Dimov, G. Chiang, E. Mallack, Y. Wang, T.
Nguyen, Z. Zun
Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: This study demonstrated significant differences
in positive and negative susceptibilities between very
preterm and full-term born infants, suggesting that
quantitative susceptibility mapping with source separation
may help early detection of iron deficiency and delayed
myelination in preterm-born infants.
|
|
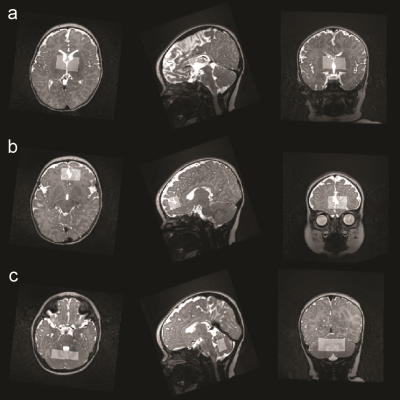 |
Computer Number: 153
2253. Brain
metabolite concentrations in neonates of mothers with COVID-19
exposure during pregnancy: a case-control study
S. Hui, J. Ngwa, K. Kapse, N. Andescavage, C. Limperopoulos
Children's National Hospital, Washington, United States
Impact: Neonates of COVID-19 infected mothers during
pregnancy may have their neurodevelopment altered. Research
focusing on neurodevelopment protection, including a dietary
supplement of choline and close monitoring of the neonates’
cognitive development, could benefit this cohort.
|
|
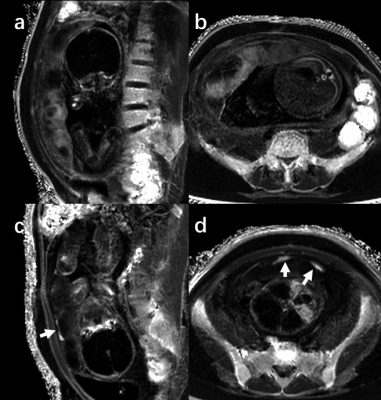 |
Computer Number: 154
2254. Effective
R2* Mapping based on Multi-Echo DIXON sequence: A Promising Tool
for Supporting Prenatal Diagnosis
Z. Meng, Z. Yijia, X. Jiaxiang
Department of Radiology, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, 济南, China
Impact: Quantitative R2* mapping derived from the
multi-echo DIXON sequence effectively aiding prenatal
diagnosis.
|
|
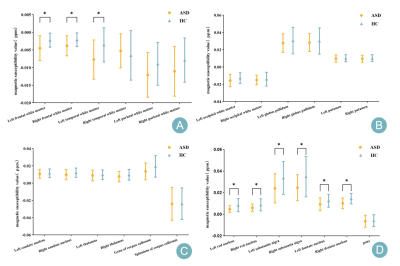 |
Computer Number: 155
2255. Exploring
Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping in Preschool Children with
Autism Spectrum Disorder: Correlations with Clinical Symptoms
Y. Lu, S. Li, S. Liu, K. Wang, L. Feng, X. zhang, C. Wang,
L. Zhang, X. Zhao
The Third Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Impact: ASD has a high prevalence among children, and
diagnosis primarily depends on clinical assessment due to
its unknown pathogenesis. This study may enhance the
understanding of autism's neurobiology and inform diagnostic
and treatment strategies using new imaging markers.
|
|
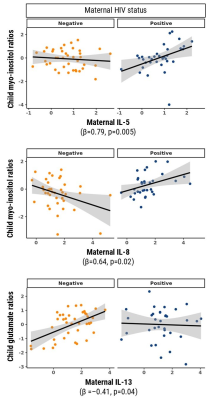 |
Computer Number: 156
2256. Maternal
immune activation is associated with neuroinflammation in
children who are HIV-exposed and uninfected: a South African
birth cohort
C. Bertran Cobo, F. Robertson, T. Kangwa, J. Annandale, S.
Subramoney, K. Narr, S. Joshi, N. Hoffman, H. Zar, D. Stein,
K. Donald, C. Wedderburn, P. Naudé
University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa
Impact: This study elucidates novel immunological
pathways through which maternal HIV infection may influence
neurometabolic development in children, underscoring the
potential for future research on prognostic tools and early
interventions to mitigate neurodevelopmental risks in
HIV-exposed uninfected children.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 157
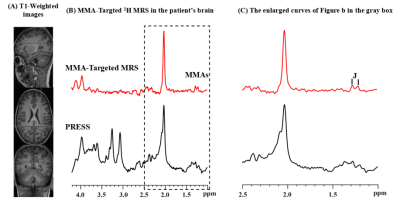
2257. The
Targeted 1H MRS of Methylmalonic Acid and Lactate In Vivo
M. Zhuo, Y. Yun, J. Xin, Y. Chen, Y. Zhao, T. Gong, X. Xing,
F. Liu, Y. Li, Y. Zou, G. Wang
Shandong University, Jinan, China
Impact: We successfully detected methylmalonic acid and
Lac signals in MMA patients, providing crucial support for
exploring MMA metabolic pathways in vivo.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 158
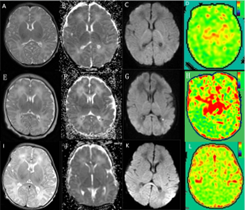
2258. Evaluation
of 3DASL in early diagnosis and short-term prognosis of
full-term neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)
T. Wang, C. Liu, Y. Liu, Y. Zhang
The First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China
Impact: We observed significant group differences
between HIE neonates with good and adverse outcomes and
healthy controls. 3DASL could reflect abnormal changes of
cerebral perfusion in HIE infants and demonstrated the
clinical value for early diagnosis and diagnosis of HIE.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 159
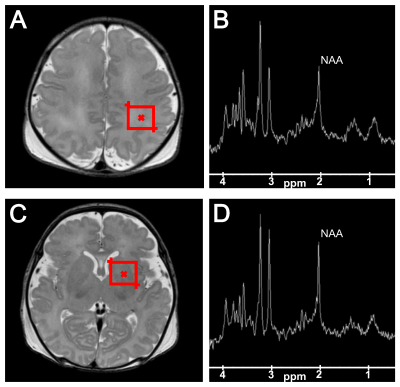
2259. White
matter brain temperatures are associated with neurodevelopmental
outcome following neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)
L. Malina, B. Brotschi, R. Heule, R. Kottke, C. Hagmann, B.
Latal, R. O'Gorman Tuura
University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Impact: In infants with HIE, WM brain temperatures from
MRS correlate with motor, cognitive, and language outcomes
at 2 years. WM brain temperatures represent a promising
marker for outcome, aiding parent counselling and early
identification of patients needing additional support.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 160
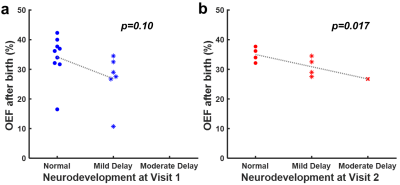
2260. Prediction
of long-term neurodevelopmental delay using cerebral oxygen
extraction fraction in neonates with hypoxic ischemic
encephalopathy
P. Liu, F. Aycan, B. Hussey-Gardner, D. Jiang, Y. Pan, S.
Chen, E. Cho, D. El-Metwally
University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, United States
Impact: This study demonstrated that global OEF,
measured by TRUST MRI non-invasively in 1.2 minutes, can be
an effective biomarker for predicting long-term
neurodevelopmental outcomes in neonates with HIE, assisting
clinical decisions on early initiation of adequate
therapies.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.