Digital Poster
High Field MRI
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

 |
Computer Number: 113
4380. In
Vivo Human Brain MRSI at 10.5 T: Initial Insights
L. Hingerl, B. Strasser, S. Schmidt, K. Eckstein, G.
Genovese, E. Auerbach, A. Grant, M. Waks, A. Wright, P.
Lazen, A. Sadeghi Tarakameh, G. Hangel, F. Niess, Y.
Eryaman, G. Adriany, G. Metzger, W. Bogner, M. Marjańska
HFMR, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
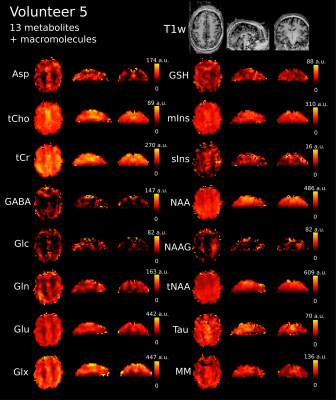
Impact: We have shown for the first time that 1H-FID-MRSI
of the human brain at 10.5 T allows for 3D mapping of up to
13 neurochemicals. This technology could offer a unique view
into the metabolic intricacies of the human brain.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 114
4381. Ultra-high-resolution
imaging of NHP head at 11.7T with a 32-channel Honeycomb modular
receive array
E. Djaballah, P-F Gapais, M. Luong, T. Lilin, M. Roustan, A.
Vignaud, N. Boulant, A. Amadon, Q. Zhu
Cognitive Neuroimaging Unit, INSERM, CEA, Université Paris -Saclay, NeuroSpin Center, Gif-sur-Yvette, France
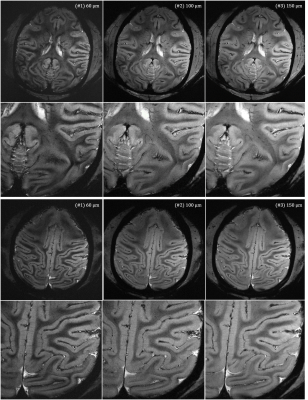
Impact: The modularity of our receivers allows to image
both human and non-human primate brains without the need for
coil retuning. Ultra-high-resolution MRI of whole-head
anesthetized NHP is demonstrated at 11.7T.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 115
4382. Post-Traumatic
Osteoarthritis Progression Over 14 Weeks: MRI Study of Cartilage
Degradation Following a Sub-Critical Impact
A. Singh, Y. Xia, A. Tetmeyer, H. Mantebea
Oakland University, Rochester, United States
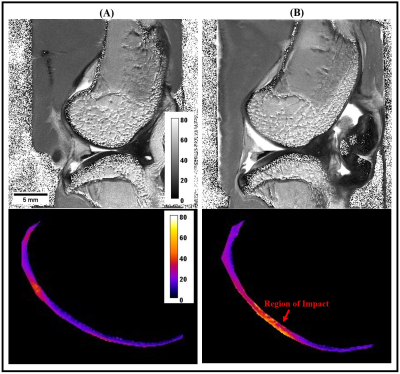
Impact: Without early diagnosis treating PTOA becomes
extremely challenging. This study focuses on PTOA
progression through 14 weeks after a single sub-critical
impact. While risk factors of high-impact injuries are well
known, the effects of low-force impact remain less
understood.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 116
4383. Comparison
of the 60 Tx/32 Rx Tic-Tac-Toe RF head coil to the Nova 1 Tx/32
Rx RF coil in sTx mode at 7T
A. Sajewski, T. Santini, A. DeFranco, W. Salmon, C. Chu, J.
Berardo, J. Berardinelli, H. Jin, J. Li, T. Campos, B. de
Almeida, T. Ibrahim
University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, United States
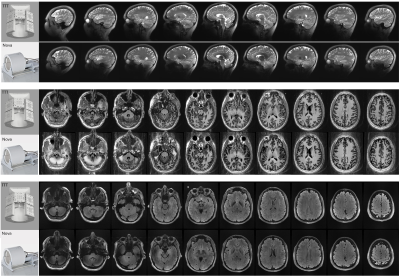
Impact: The 60 Tx/32 Rx Tic-Tac-Toe coil, designed for
sTx mode, exceeds commercial standards for robust and
homogenous imaging across a variety of subjects at 7T.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 117
4384. Computational
EM Simulation of Microscopic Graphene-Based Electrophysiology
Probe at 7T MRI: Acceleration Using a Huygens' Box-Based
Approach
S. Kumar, S. Flaherty, A. Labastida-Ramírez, A. Brunet, B.
Dickie, R. Wykes, K. Kostarelos, L. Lemieux
University College London, London, United Kingdom
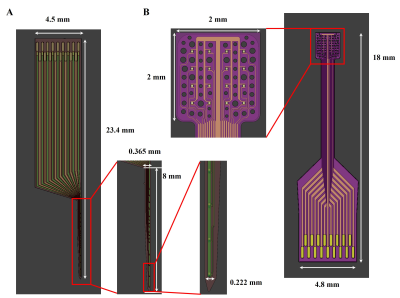
Impact: This study provides evidence on the superior MR
suitability of graphene-based probes compared to the current
technology for concurrent EEG-fMRI acquisitions, offering
the prospect of unprecedented characterization of brain
activity which could lead to better diagnostic and
therapeutic strategies.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 118
4385. Towards
Combined Brain and Cervical Spine Imaging at 7 T with an
8-channel pTx Coil: The Importance of Accurate B1+ Maps for
Dynamic pTx
C. Aigner, M. May, T. Fiedler, S. Kühn, H. Quick, S.
Schmitter
Max Planck Institute for Human Development, Berlin, Germany
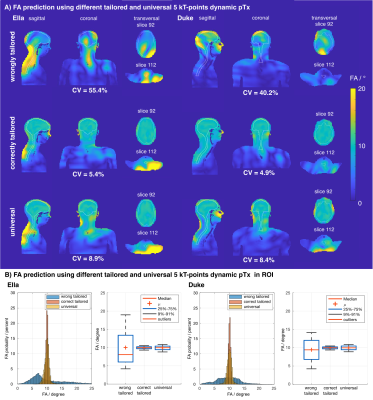
Impact: This simulation study demonstrates feasability
of combined brain and cervical spine MRI at 7 Tesla using an
eight Tx channel dynamic pTx setup. Optimized pTx pulses
result in high FA homogeneity and enable detailed
investigations of both neuroanatomical structures
simultaneously.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 119
4386. Bridging
the gap: 150μm resolution whole brain ex-vivo imaging at 7T with
RF shimming
D. Papp, M. Weigel, M. Rekecki, H. van Loo, M. Cseh, A.
Szum, D. Park, K. Chow, T. Jimenez-Beristain, Z.
Geretovszky, L. Szekely, G. Castelo-Branco, C. Granziera, T.
Granberg, R. Ouellette
Siemens Healthineers, Stockholm, Sweden
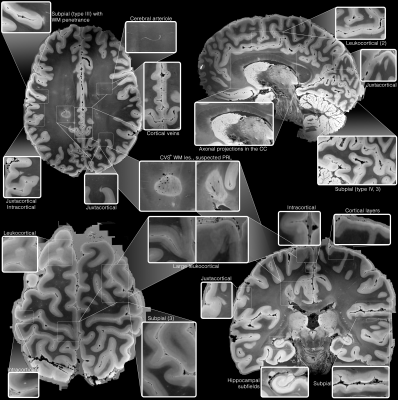
Impact: Using commercial hardware and overnight scan
times, ultra-high resolution MRI at 150μm isotropic voxel
size can be acquired with sufficient SNR and image quality
to detect and differentiate mesoscale structures
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 120
4387. Pushing
human neuroscience past 7T: cerebellar imaging at 9.4T
W. van der Zwaag, D. Tse, B. Poser, N. Priovoulos
Royal Netherlands Academy for Arts and Sciences, Amsterdam, Netherlands
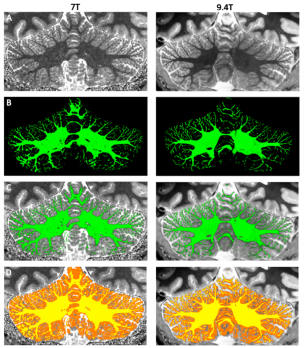
Impact: Reliably visualizing the cerebellum requires
pushing past currently-feasible resolutions with B0=7T or
lower. We demonstrate that neuroscientific experiments can
be performed in the human cerebellum at 9.4T benefitting
from elevated SNR and BOLD sensitivity.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 121
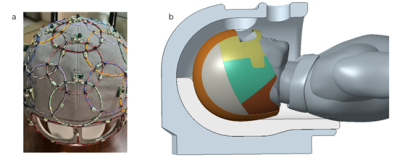
4388. Evaluation
of the coax monopole antenna as a transmit array element for
head imaging at 14T
L. Budé, K. Vat, I. Voogt, I. Zivkovic, A. Raaijmakers
University of Technology Eindhoven, Eindhoven, Netherlands
Impact: The coax monopole antenna would be an excellent
candidate for transmit head coil arrays at 14T MRI, due to
its high SAR efficiency and low coupling. Additionally, its
single-ended design facilitates cable routing, particularly
in a spatially restricted environment.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 122
4389. On
the Reproducibility of Direct Signal Control with Variable
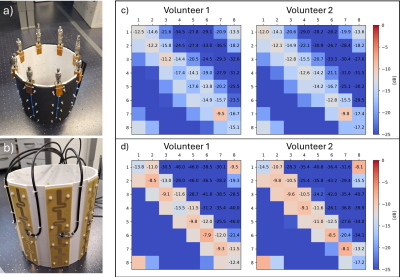
Excitation and Refocusing (DiSCoVER) for TSE Shoulder MRI at 7T
O. Kraff, M. May, L. Wessing, H. Quick
University Duisburg-Essen, Essen, Germany
Impact: Clinically acceptable reproducibility of
currently implemented TSE-DiSCoVER was not achieved over the
full transversal cross-section. Renewing the RF shimming
procedure can improve image quality, even across the whole
slice. A need for improvements in underlying B1+-mapping
and postprocessing is shown.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 123
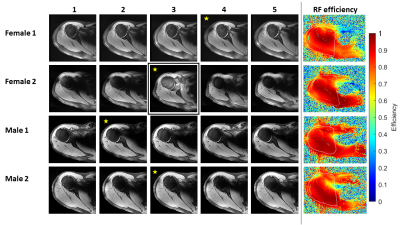
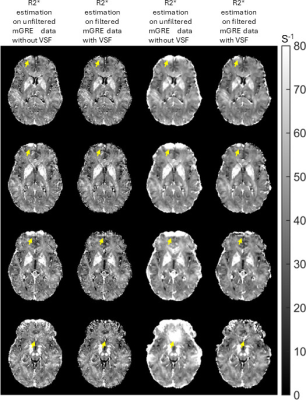
4390. Leveraging
Voxel Spread Function approach to Improve R2* Mapping Accuracy
at 7T MRI
S. V. Kothapalli, J. Pan, F. Paladi, T. Altes, D. Yablonskiy
Washington University in Saint Louis, Saint Louis, United States
Impact: The voxel spread function (VSF) method shows
great promise in correcting macroscopic magnetic field
inhomogeneities in mGRE images, aiding in the accurate
estimation of quantitative mGRE metrics such as R2* and
myelin water fraction at ultra-high field MRI.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 124
4391. A
near-field coupling head coil with 40 elements for 5.0T MRI
Y. Tan, Q. Chen, X. Fan, Y. Ma, B. Wu, X. Zhang, D. Liang,
X. Liu, H. Zheng, Y. Li
Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China
Impact: The novel near-field coupling head
coil represents a significant scholarly contribution to the
field of magnetic resonance technology. This innovative
design promises to enhance imaging performance at ultra-high
field MRI, which will facilitate more accurate diagnostic
assessments and paving the way for new frontiers in MRI
research and clinical practice.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 125
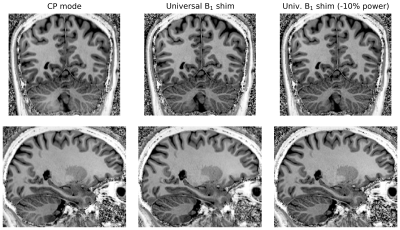
4392. Universal
“MaxTheMin“ B1 Shimming: Robust Adiabatic Pulses at Ultra
High-field
E. Pracht, D. Löwen, P. Ehses, T. Stöcker
German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE), Bonn, Germany
Impact: Universal B1 shimming
improves adiabatic pulse performance by enhancing inversion
efficiency across the brain without increasing scan time or
requiring calibration. This advancement paves the way for
higher-quality, more reproducible imaging at UHF, expanding
its clinical and research applications.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 126
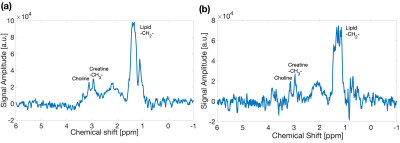
4393. Water-cycled
STEAM cardiac spectroscopy at 7T
E. McConnell Montoya, F. Mozes, D. Tyler, L. Valkovic
University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
Impact: Frequency-aligned spectra from water-suppression
cycled acquisitions enable the quantification of
low-concentration metabolites in the heart at 7T.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 127
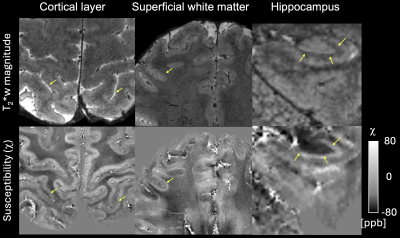
4394. Advancing
mesoscale whole brain T2*-weighted MRI in humans at 10.5 T using
motion-robust multi-echo 3D EPI and RF parallel transmission
S. Qu, J. de Zwart, P. Van Gelderen, J. Duyn, M. Waks, R.
Lagore, A. Bratch, A. Grant, E. Auerbach, L. Delabarre, A.
Tarakameh, Y. Eryaman, G. Adriany, K. Ugurbil, X. Wu, J. Liu
CMRR, Radiology, Medical School, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, United States
Impact: Armed with rapid motion-robust 3D EPI and
parallel transmission, the presented new multi-echo T2*-weighted
imaging strategy will benefit many neuroscience
applications, especially those aiming to investigate fine
scale anatomy in humans at ultrahigh field.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 128
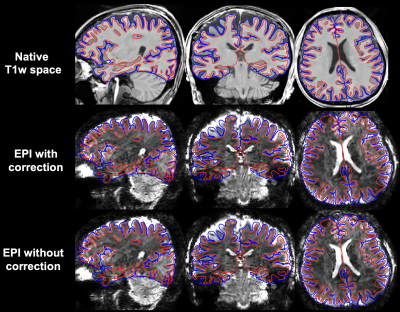
4395. Advancing
whole-brain BOLD fMRI in humans at 10.5 Tesla with motion-robust
3D EPI and RF parallel transmission: initial experience
S. Qu, P. Van Gelderen, J. de Zwart, J. Duyn, M. Waks, R.
Lagore, A. Bratch, A. Grant, E. Auerbach, L. Delabarre, A.
Tarakameh, Y. Eryaman, G. Adriany, K. Ugurbil, J. Liu, X. Wu
CMRR, Radiology, Medical School, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, United States
Impact: Demonstrated useful for whole-brain BOLD fMRI at
10.5 T, our pTx-enabled, motion-robust 3D EPI technique will
have potential to advance ultrahigh resolution fMRI at
ultrahigh field, paving the way for obtaining a better
understanding of brain function and connectivity.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.