Digital Poster
Physics & Engineering: Low to High Field
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

 |
Computer Number: 113
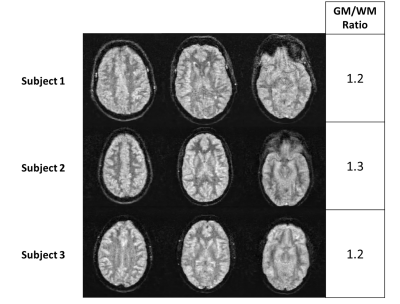
4238. Optimizing
the white matter/grey matter contrast on a portable 46 mT MRI
scanner
B. Lena, C. Najac, T. O'Reilly, R. van den Broek, A. Webb
Leids Universitair Medisch Centrum, Leiden, Netherlands
Impact: This study demonstrates that a T1-weighted
sequence with optimized inversion time effectively enhances
grey-to-white matter contrast in low-field MRI, offering
reliable tissue differentiation for different subjects and
resolutions.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 114
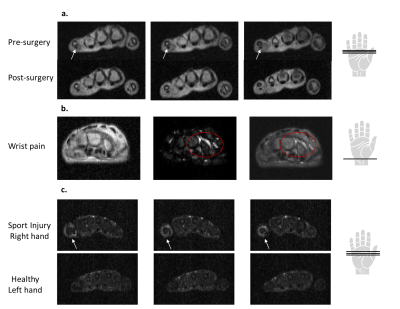
4239. A
fluid-sensitive MRI protocol for the small joints of the hand
using a portable 46 mT scanner
B. Lena, J. Parsa, S. van Griethuysen, D. Ton, Y. Dong, A.
van der Helm -van Mil, A. Webb
Leids Universitair Medisch Centrum, Leiden, Netherlands
Impact: In this study, we developed a fluid-sensitive
MRI protocol for a portable 46 mT system. This method allows
to capture both anatomical structures and fluid details,
while ensuring comfortable scanning, showing potential for
affordable, accessible joint inflammation detection.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 115
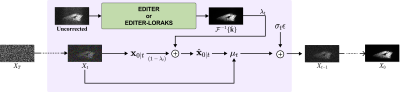
4240. Electromagnetic
Interference Removal in Low-Field MRI via EDITER, Structured
Low-Rank Modeling, and Denoising Diffusion Model
G. S. Jhun, H. J. Yook, J. H. Cho, S. Srinivas, C. Cooley,
B. Bilgic, T. H. Kim
Hongik University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: We propose a novel framework for enhanced
low-field MRI by integrating LORAKS and DDNM into EDITER,
which effectively eliminates electromagnetic interference
(EMI) and improves SNR. The proposed method substantially
improves low-field MRI, overcoming limitations of existing
methods.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 116
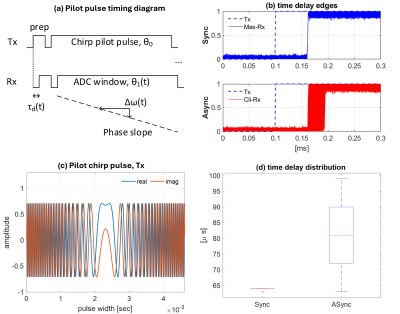
4241. Signal
distortion characterization and correction using pilot chirp
pulse train for free-running clock synchronization
W. Lee, D. Abraham, S. Vasanawala, J. Pauly, S. Greig
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: Pilot chirp can improve the usability of
tracking and correcting offset distortions associated with
asynchronous free-running receivers.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 117
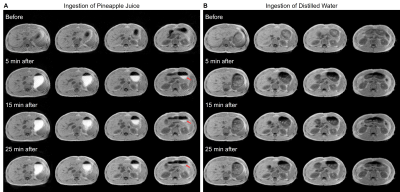
4242. Ultra-low-field
Abdominal MRI Using Pineapple Juice as Oral Contrast Agent: A
Preliminary Study
Y. Zhao, S. Su, Y. Ding, J. Zhang, X. Lin, J. Hu, A. T. L.
Leong, E. X. Wu
The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Impact: We evaluate the initial feasibility of using
pineapple juice as a natural oral contrast agent for 0.05T
abdominal MRI. The developments can advance ultra-low-field
abdominal MRI, potentially offering a more accessible,
cost-effective and patient-friendly approach to address
numerous clinical needs.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 118
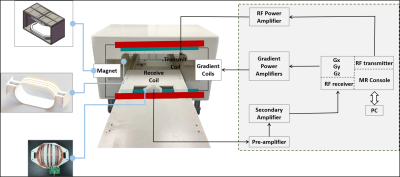
4243. A
50 mT portable MRI scanner for breast imaging: proof-of-concept
imaging implementation
Z. Wu, X. Hu, X. Jiang, Z. Ni, H. Yi, R. Lu
Southeast University, Nanjing, China
Impact: The constructed 50 mT portable breast MRI
prototype has the potential to be used in early screening of
breast disease in the future.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 119
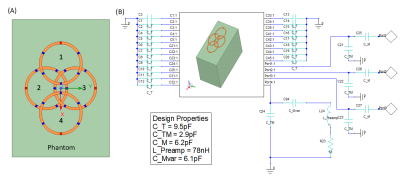
4244. Improving
Preamp Decoupling Accuracy in Multi-Channel MRI Coils: A
Comparison of Measurement Techniques
M. Shrestha, M. Mahmutovic, S-L Hansen, A. Ghotra, B. Keil
TH Mittelhessen - University of Applied Sciences, Giessen, Germany
Impact: Direct impedance measurement for preamplifier decoupling provides a more accurate method than traditional techniques, reducing coil coupling, improving signal quality and enabling further developments in
multi-channel MRI coil design for high-resolution,
parallel imaging.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 120
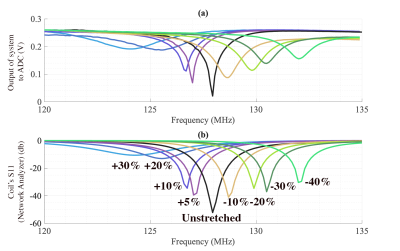
4245. In-Bore,
Non-Magnetic Detection of Stretchable Coils’ Resonance Frequency
F. Narongrit, T. Ramesh, J. Rispoli
Purdue University, West Lafayette, United States
Impact: This resonance detection system enables in-bore,
adaptable frequency monitoring and retuning for flexible MRI
coils without ferromagnetic components. It facilitates
future wireless, multi-coil, and multi-nuclei applications,
reducing equipment limitations and improving coil
performance in high-field MRI environments.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 121
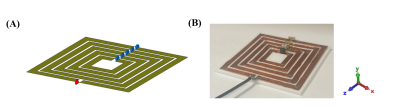
4246. Design
and evaluation of multimodal concentric surface coils for 3T MR
imaging
Y. Zhao, A. Bhosale, X. Zhang
State University of New York at Buffalo, Buffalo, United States
Impact: The proposed multimodal concentric coil
demonstrates superior B1 field efficiency and reduced SAR
compared to conventional surface coils. These improvements
can significantly enhance image quality and patient safety
in 3T MRI, paving the way for better clinical outcomes.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 122
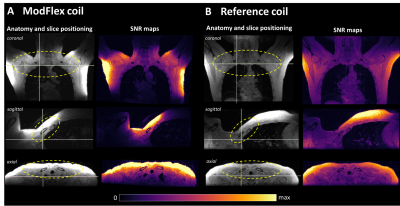
4247. Improved
thoracic outlet syndrome MRI assessment with a modular flexible
coil at 3 T
L. Nohava, B. Assabah, R. Gillet, G. Drouot, E. Laistler, J.
Felblinger, K. Isaieva
High Field MR Center, Center for Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Impact: A novel modular flexible coil significantly
improves MRI imaging for thoracic outlet syndrome, enhancing
SNR and patient comfort. This proof-of-concept study
promises more accurate diagnoses and shorter exam times,
potentially improving clinical practice for TOS assessment.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 123
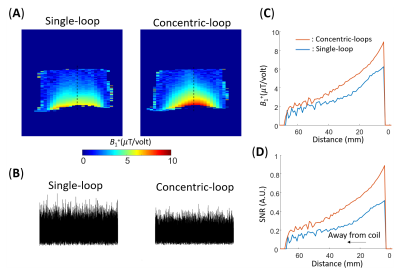
4248. Concentric-loops
coil reducing imaging noise and enhancing imaging SNR compared
to traditional single-loop coil
X. Li, X-H Zhu, W. Chen
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, United States
Impact: This simple novel coil can be optimized and
adapted for a broad range of MRS and MRI imaging
applications with largely reduced imaging noise, improved
coil sensitivity and approximately doubled imaging SNR as
compared to the traditional single-loop coil.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 124
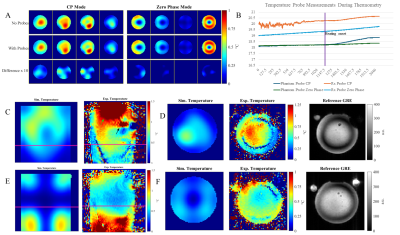
4249. Embedding
Dynamic Field Probes in 7T RF Array Coils Enables Concurrent
Field Monitoring Without Degrading Coil Performance
S. Williams, C. Mirkes, P. McElhinney, B. Ding, S. Gross, K.
Pine, R. Müller, N. Weiskopf, H. Möller, S. Gunamony
University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom
Impact: Incorporating dynamic field probes in
parallel-transmit RF coils with high receive channel counts
can help mitigate increased B1+ and B0 at
ultra-high fields. We explore the effects on RF coils with
integrated probes by evaluating performance with and without
probes.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 125
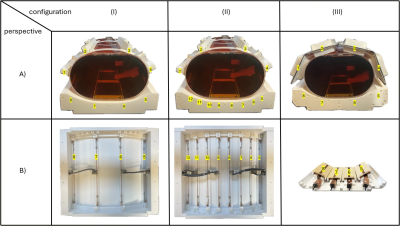
4250. Characterization
of Coaxial-End Dipoles and Comparison with Meander
Stripline-Elements for Prostate Imaging at 7T
C. Stevens, O. Kraff, G. Solomakha, K. Scheffler, N.
Avdievich, H. Quick, M. May
Department of Physical Engineering, Westphalian University of Applied Sciences, Gelsenkirchen, Germany
Impact: The coaxial-end dipole array demonstrated
superior transmission efficiency over meander stripline
elements. Due to the higher channel count increases in SNR
and receive performance are possible. However, the dipoles
were more sensitive to loading than meander stripline
elements.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 126
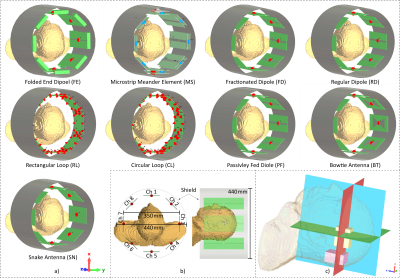
4251. Simulation
of the RF Shimming Performance of 8 Channel Arrays for 7T
Head-Imaging with a Large Diameter Transmit Coil
M. J. Hubmann, R. Kowal, S. Orzada, O. Speck, H. Maune
Otto-von-Guericke University, Magdeburg, Germany
Impact:
This work demonstrates the potential of different large diameter Tx coil arrays and should help other researchers who want to build a large diameter Tx coil to decide on a suitable coil type. |
|
 |
Computer Number: 127
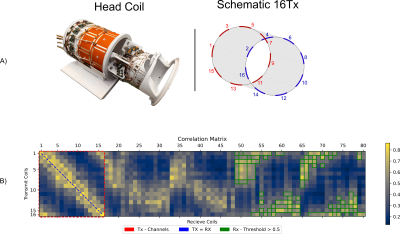
4252. Higher
Fields, Deeper Insights: DL-based $$$B_{1}^{+}$$$ prediction at
10.5T
K. Hadjikiriakos, F. Zimmermann, F. Krüger, C. Aigner, M.
Marjanska, S. Schmidt, Y. W. Park, G. J. Metzger, S.
Schmitter
Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB), Braunschweig and Berlin, Germany
Impact: The study suggests that training a neural
network to predict $$$B_{1}^{+}$$$-maps for a 16Tx/80Rx head
coil at 10.5T might not require all coil elements,
highlighting methods to identify redundant elements to
optimize training speed and specific applications.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 128
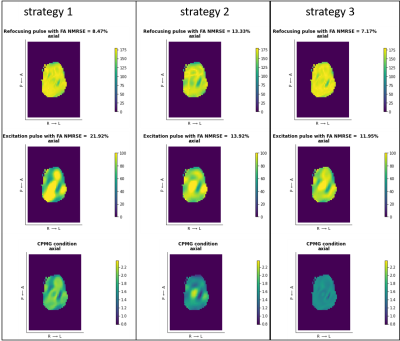
4253. Joint
design of a 90° - 180° spokes pulse in pTX for 2D TSE imaging at
11.7 Tesla
J. Brégeat, A. Massire, N. Boulant, V. Gras, F. Mauconduit
Paris-Saclay University, CEA, CNRS, BAOBAB, NeuroSpin, Gif-sur-Yvette, France
Impact: The joint design appears to be a promising
strategy, enabling the generation of excitation and
refocusing pulses while enforcing the respect of CPMG
condition. This is a key step toward enabling 2D TSE
sequences at ultra-high fields.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.