Digital Poster
Large Language Models in MRI
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

 |
Computer Number: 33
3376. Designing
MR Exams Using an Autonomous Multi-Agent Large Language Model
System
A. Sharma, W. Grissom, M. Griswold
Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, United States
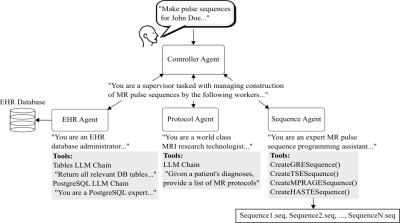
Impact: MR exam delivery is challenged by a worldwide
shortage of radiology staff. We demonstrate that a
multi-agent LLM system shows promise in automating MR exams
by accessing a patient’s health record and designing the
protocol and sequences to be acquired.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 34
3377. Using
Large Language Models and Retrieval-Augmented Generation in MRI
Protocol Selection: Balancing Accuracy and Privacy
C-H TANG, P-C LIANG, Y-H YANG, Y-H YANG, S-S WU, J-Y GAO,
I-L CHUNG, J-C HSU, W-D HUANG
NTU BioMedical Park Hospital, Hsinchu County,, Taiwan
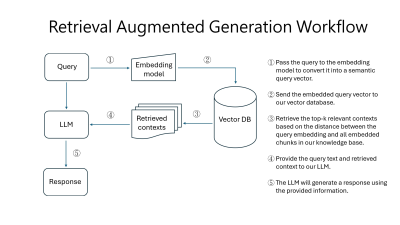
Impact: We've proven that RAG-based LLMs are feasible
for early MRI decision-making, offering a new tool for
learning and error prevention. Cloud-based LLMs and local
LLMs each have their strengths in accuracy and privacy, but
neither is perfect just yet.
|
|
|
Computer Number:
3378. WITHDRAWN |
||
 |
Computer Number: 35
3379. Text-Enhanced
Vision-Language Motion Correction (VLM-MoCo) for Mitigating
Severe Motion Artifacts in MRI Scans
M. Safari, S. Wang, R. L. Liu, C-W Chang, D. S. Yu, H. Mao,
X. Yang
Emory University, Atlanta, United States
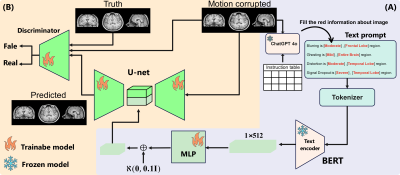
Impact: By integrating text descriptions into deep
learning models, this method significantly enhances
collaboration between clinicians and AI systems to remove
MRI motion artifacts. It especially benefits patients prone
to involuntary movements and transforms clinician-AI
collaboration in medical imaging.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 36
3380. AI-Driven
Scribble-Based Foundation Model for Left Ventricular Scar
Quantification on cardiac MRI
N. Tavakoli, A. A. Rahsepar, B. Benefield, D. Shen, S.
López-Tapia, F. Schiffers, E. Wu, A. Katsaggelos, D. Lee, D.
Kim
Northwestern University, Chicago, United States
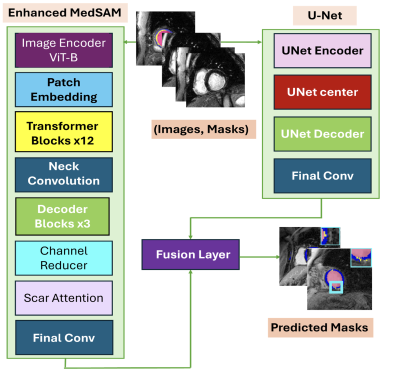
Impact: Our foundation model offers a significant
advancement in automated LV scar assessment, improving
reliability, reducing manual workload, and enhancing
consistency in clinical cardiac imaging, which can lead to
better patient outcomes through timely and accurate
diagnosis.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 37
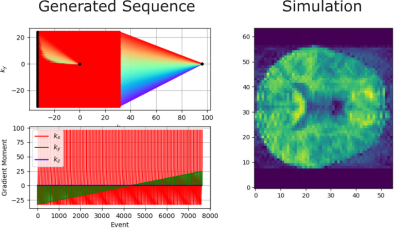
3381. SeqGPT:
Training a Large Language Model to Generate MRI Pulse Sequences
S. Hussain, J. Huber, M. Günther, D. Hoinkiss
Fraunhofer MEVIS, Bremen, Germany
Impact: This shows the capability of LLMs to generate
MRI sequences. Which then can be fine-tuned with a
differentiable simulator to adjust the sequence towards
desired imaging objectives.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 38
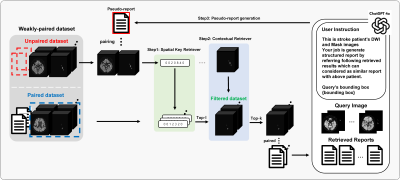
3382. Boosting
Vision Language Segmentation via Pseudo-Report Generation in
Weakly Paired Stroke Datasets
H. Eum, J. Lee, K. S. Choi
Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: Our pseudo-report generation approach maximizes
VLSM potential in report-limited environments without
additional training, enhancing efficiency. Notably, with
only 10% of reports available, it outperforms image-only
models and more effectively reduces false positives,
providing practical clinical benefits.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 39
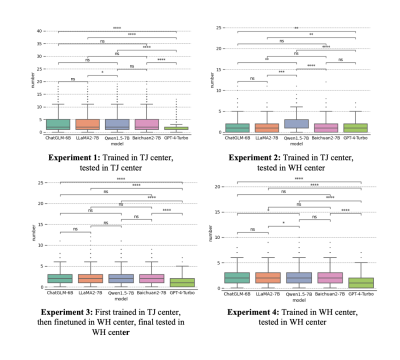
3383. Automatic
Generation of Impressions from Brain MRI Report Findings using
Large Language Models: A Multi-centers Retrospective Analysis
C. Chai, Z. Liu, M. Zhang, C. Liu, Y. Yu, H. Wang, W. Shen,
S. Xia
Department of Radiology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin Medical Imaging Institute, School of Medicine, NankaiUniversity, Tianjin, China, Tianjin, China
Impact: we find that while LLMs can correct some
diagnostic errors, they also introduce inaccuracies,
underscoring the critical role of radiologist oversight. We
believe these findings demonstrate the potential of LLMs as
a valuable quality improvement tool in radiology.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 40
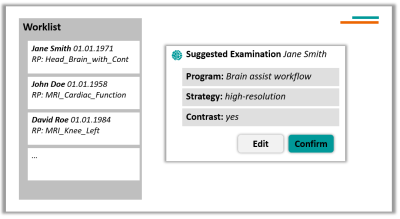
3384. Language
Models Can Assist Technicians Choosing a Patient-Tailored MRI
Scan Protocol
F. Wagner, R. Thangaraj, R. Schneider, L. Pfaff, J. Gühring,
J. Wohlers
Siemens Healthineers AG, Forchheim, Germany
Impact: This work streamlines MRI scan protocol
selection using a context-aware, RAG-based pipeline. By
minimizing manual input and training needs, it demonstrates
potential for enhancing workflow efficiency and
patient-adapted imaging based on available patient
information.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 41
3385. Utilizing
ChatGPT for the responses assessment of brain tumors treated
with immunotherapy based on multiple RNAO criteria: a validation
study
G. Tan, M. Cai, A. Liu, W. Liu, X. Liu
The Affiliated Yuebei People's Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shaoguan, Guangdong Province, China, Shaoguan, China
Impact: Our study is the first application of ChatGPT in
deeper understanding of complex iRABT criteria from multiple
RANO criteria, which is critical useful for improved
clinical management. Better performance of ChatGPT 4o may
suggest optimal selection of LLM tools.
|
|
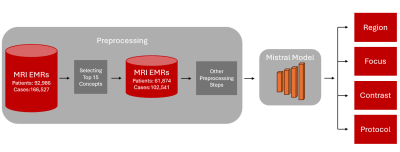 |
Computer Number: 42
3386. Predicting
MRI Protocol Using an Adapted Large Language Model
P. Shokrollahi, A. Li, I. Zare Estakhraji, A. Chaudhari, A.
Loening
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: The proposed system would offer radiologists a
privacy-preserving decision-support tool, potentially
reducing protocol mismatches, enhancing diagnostic accuracy,
and optimizing workflow. Streamlining MRI protocoling aims
to enhance diagnostic quality, safeguard patient health,
expedite treatment, and lower healthcare costs.
|
|
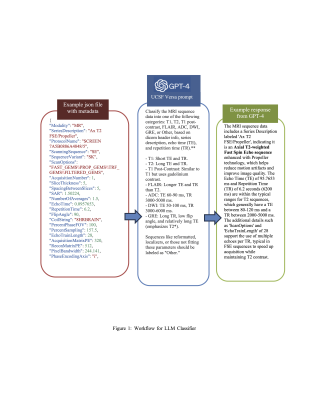 |
Computer Number: 43
3387. Large
Language Model Based Identification of Brain MRI Sequences
R. Bhalerao, H. Kukreja, A. Rauschecker
UC Berkeley and UCSF, Berkeley, United States
Impact: LLMs provide a more accurate and interpretable
approach for MRI sequence classification, offering
clinicians and researchers a more reliable tool. This could
enhance research workflows, reduce manual labeling time, and
allow for more robust deep learning models in medical
imaging.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 44
3388. Foundation
Models for Multimodal MRI Synthesis with Language Guidance
M. Yurt, X. Cao, Z. Zhou, K. Setsompop, S. Vasanawala, J.
Pauly
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: Conventional synthesis models rely on
image-to-image translation with just visual inputs and often
show limited generalizability. We demonstrate a foundation
model with language guidance that leverages textual inputs
for improved adaptability to new modalities.
|
|
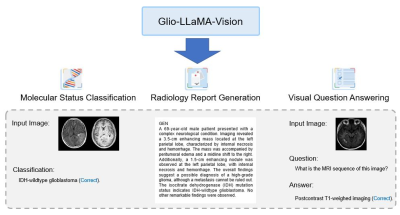 |
Computer Number: 45
3389. Glio-LLaMA-Vision:
A Vision-Language Model for Molecular Prediction, Radiology
Report Generation, and VQA in Adult-type Diffuse Gliomas
Y. W. Park, M. Kang, S. H. Park, S. S. Ahn
Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: Glio-LLaMA-Vision shows promising performance in
molecular subtype prediction, radiology report generation,
and VQA in adult-type diffuse gliomas. Notably, our current
study provides a practical paradigm of adapting general
domain LLMs to applications in a specific medical domain.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.