Digital Poster
AI for Diagnosis/Prognosis: Body II
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

 |
Computer Number: 33
1405. Prediction
of pathological complete response for breast cancer by
post-treatment multi-phase MRI signatures with automatic
segmentation
H-T Zhu, X-T Li, Y-H Qu, K. Cao, Y-S Sun
Peking University Cancer Hospital, Beijing, China
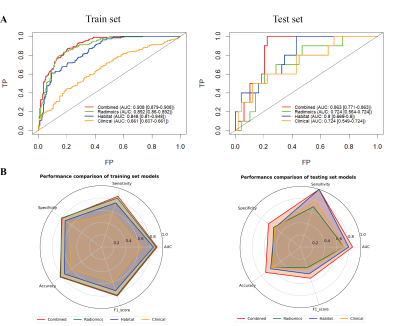
Impact: Post-NAC MRI histogram signature based on
pre-NAC segmentation model can be used to automatically
predict pCR after NAC and assist individualized treatment
for locally advanced breast cancer.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 34
1406. Interpretable
Machine Learning with MRI Habitat Radiomics for Preoperative
Assessment of Microsatellite Instability in Rectal Cancer
Y. Wang, B. Xie, K. Wang, W. Zou, M. Liu, Y. Ma
The First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu, Anhui province, China
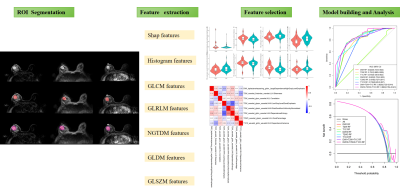
Impact: This study developed and validated a combined
model using multiparametric MRI subregional radiomics,
classical radiomics, and clinical variables for non-invasive
preoperative MSI prediction. SHAP aids personalized
predictions, supporting individualized treatment and
biopsy-targeted decision-making in RC patients.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 35
1407. A
multicenter study on preoperative prediction of TNBC based on
multi-parameter MRI intratumoral combined with peritumoral
radiomics
A. Yang, Y. Cao, M. Cao, X. Liu
青海大学附属医院, 西宁, China
Impact: This model can predict TNBC in a non-invasive
and early manner, which is of great significance to the
treatment and prognosis of patients.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 36
1408. Multiparametric
MRI-based radiomics for predicting the EGFR mutation status in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Y. Zheng, J. Zhang
Lanzhou University Second Hospital, Lanzhou, China
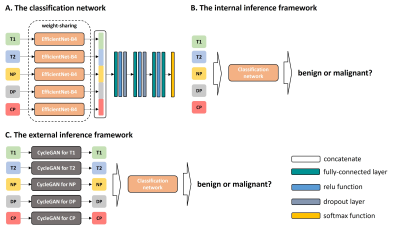
Impact: DWI radiomics signature can be used as a
noninvasive tool for predicting EGFR mutation status in
NSCLC, which is helpful to guide therapeutic strategies.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 37
1409. Investigation
of Deep Learning Models Based on Multiparametric MRI to Diagnose
Solid Small Renal Masses: A Multi-Center Study
Z. Zeng, M. Cui
School of Medical Information Engineering, Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, Jiangxi, China
Impact: Due to overlapping imaging features,
distinguishing benign from malignant SRM is challenging,
leading to unnecessary resection of benign SRM. The DL model
offers an efficient tool for the accurate classification of
SRM.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 38
1410. Assessing
the performance of AI assistance for prostate MRI: a two-center
study involving radiologists with different experience levels
Z. Sun, X. Wang
Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China
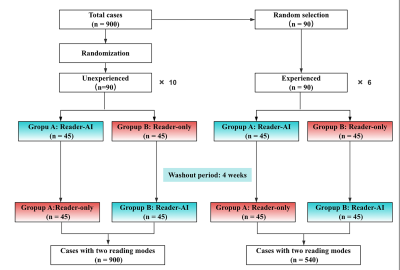
Impact: This research demonstrate how AI can assist
radiologist in interpreting multiparametric prostate mpMRI,
thereby facilitating broader clinical implementation of AI
technologies in routine practice.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 39
1411. Population
based Deep Cardiac Atlas Phenotypes and Application in
Biological Age Prediction
M. Sun, Q. Li, Y. Li, Y. Zhang, L. Sun, Q. Li, C. Wang
Human Phenome Institute, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Impact: Based on cardiac atlases of two key phases,
momenta extracted as deep phenotypes could control
deformation and encode age-related anatomical variations.
Combining these new phenotypes with conventional biomarkers
enables the development of more accurate models for
predicting cardiac biological age.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 40
1412. Development
and validation of an interpretable deep learning radiomics model
using MRI to predict lymph node metastasis in rectal cancer.
Y. Yang, K. Han, H. Zhao, J. Pan, J. Zhang, Z. Xu
The First People’s Hospital of Foshan, Foshan, China
Impact: This DLR model’s accuracy and interpretability
support improved diagnostic confidence in rectal cancer,
aiding clinicians in decision-making. By bridging advanced
imaging and clinical needs, this tool opens new
possibilities for preoperative assessments and personalized
oncology care.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 41
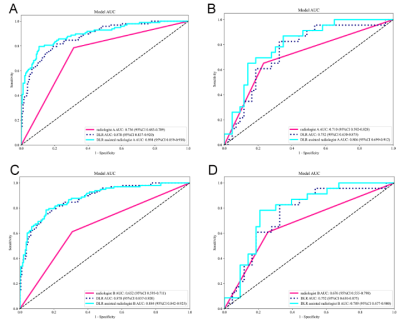
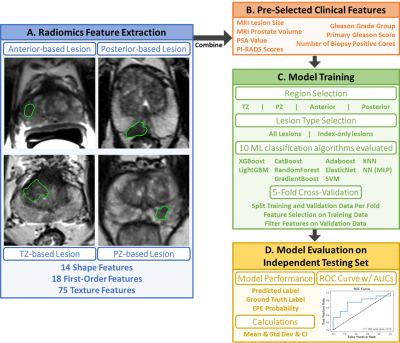
1413. Region-based
Prediction of Extraprostatic Extension Using a Machine Learning
Approach Integrating MRI Radiomics and Clinical Data
S. Naim, H. Zheng, Q. Miao, K. Zhao, R. Yan, S. Raman, H.
Wu, K. Sung
University of California, Los Angeles, Los Angeles, United States
Impact: This study highlights the potential of
incorporating spatial characteristics of csPCa to enhance
EPE prediction through precision imaging, integrating
region-specific mpMRI radiomics features with clinical and
histopathological parameters to guide more precise treatment
decisions and interventions.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 42
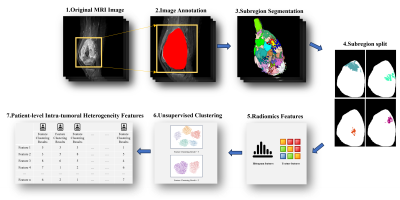
1414. Intratumor
Heterogeneity Features Based on MRI Radiomics for Predicting
Lung Metastasis Risk of Osteosarcoma
Y. Shao, C. Tung, Y. Lin, Z. Xie, X. Chen, X. Chen, Q. Yang,
H. Chen, Y. Zhao
Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Impact: This study presents an MRI-based ITH model,
combined with clinical data, demonstrating significant
potential for non-invasive lung metastasis risk assessment
in osteosarcoma.
|
|
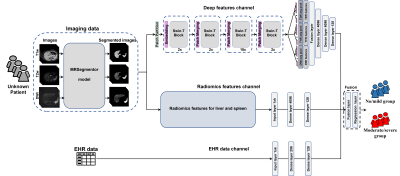 |
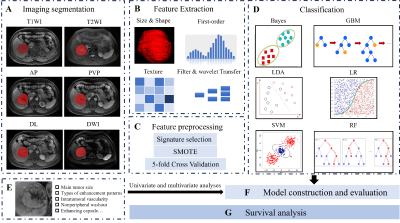
Computer Number: 43
1415. Multiparametric
Deep and Radiomic MRI Features for Liver Stiffness
Classification in Children and Adults with Chronic Liver Disease
R. Ali, H. Li, W. Pan, S. Reeder, D. Harris, W. Masch, A.
Alsam, K. Shanbhogue, N. Parikh, J. Dillman, L. He
Cincinnati children's hospital medical center, Cincinnati, United States
Impact: Our model offers an alternative to conventional
MR elastography, potentially expanding access and improving
care for patients with chronic liver disease.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 44
1416. MRI-based
Radiomics Predict β-catenin Mutation Status and Prognosis in
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multi-Institutional Study
Q. Chen, Y. Zhang, Y. Huang, H. Hu
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
Impact: The radiomics model using DCE-MRI and clinical
factors offers a new tool for personalized treatment.
|
|
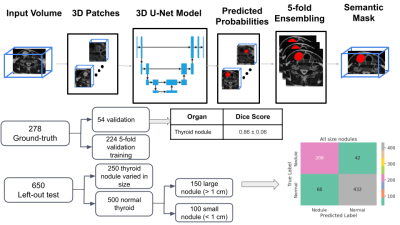 |
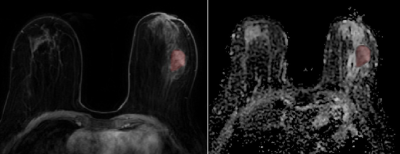
Computer Number: 45
1417. Utilizing
Artificial Intelligence for Enhanced Detection and
Characterization of Thyroid Nodules on T2-Weighted Neck MRI
T-D Nguyen, S. Garg, N. Akbari, S. Lee, M. Datta, S. Basar,
Y. Chodakiewitz, D. Durand, S. Hashemi
Vigilance Health Imaging Network Inc, Vancouver, Canada
Impact: Having the ability to not only automatically
detect thyroid nodules but automatically to characterize
them provides valuable insights as well as saving valuable
time to radiologists in dealing with this condition.
|
|
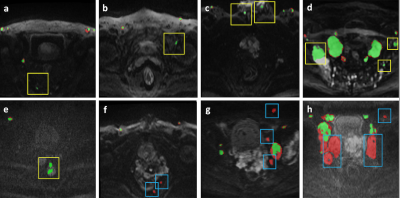 |
Computer Number: 46
1418. Fully
automated detection pelvic lymph nodes in diffusion-weighted
imaging for prostate cancer using deep learning: A multicenter
study
Z. Sun, X. Wang
Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China
Impact: The results confirmed the feasibility of this
method, which could aid in LN staging, quantitative
measurements of tumor burden, and image-guided treatment of
patients with PCa.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 47
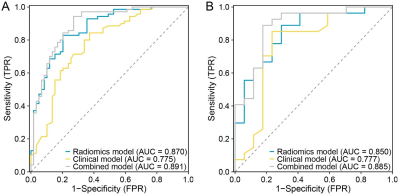
1419. Radiomic
Analysis of Pretreatment DCE-MRI and ADC for Predicting
Pathological Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in
Breast Cancer
X. Tao, T. Liang, L. Wan, Z. Hu, N. Zhang
Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Shenzhen, China
Impact: This study demonstrates the potential of
combining pretreatment DCE-MRI, ADC maps, and clinical
factors in predicting NAC repsponse in breast cancer,
offering a non-invasive approach to guide personalized
treatment strategies, ultimately improving patient outcomes
and reducing unnecessary interventions for non-responders.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 48
1420. Predictive
model for preoperative discerning of tertiary lymphoid
structures in gallbladder cancer using Magnetic Resonance
Imaging
W. Zhi, Y. Xu, S. Wang, L. Xie, F. Ye, X. Zhao
National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
Impact: This MRI-based radiomics predictive model
represents an innovative approach to enhance the accuracy of
preoperative TLS detection in GBC, potentially facilitating
more tailored patient management strategies.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.