Digital Poster
Imaging of Liver Health
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

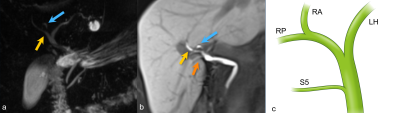 |
Computer Number: 113
2836. Anatomic
Evaluation of Living Liver Donors Using Dual-Contrast MRI and
MRCP: Preliminary Experience
R. Chahine, M. Mendiratta-Lala, N. Parikh, C. Sonnenday, S.
Waits, M. Davenport, H. Hussain, W. Weadock, J. Morehouse,
K. Ali, S. Esch, A. Aslam
University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, United States
Impact: Dual-contrast agent MRI and MRCP can be used as
a one-stop shop for high-quality arterial and biliary
imaging of living liver donors, reducing radiation exposure,
cost and time constraints.
|
|
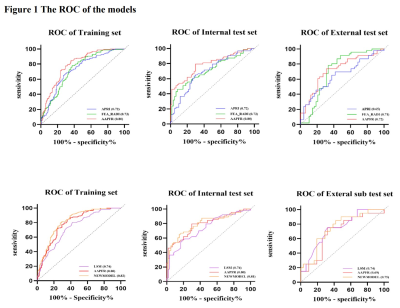 |
Computer Number: 114
2837. Evaluating
the Added Value of MRI in Detecting Significant Hepatic
Histological Changes in Chronic HBV Patients with Normal ALT
Levels
J. Zhong, J. Zha, S. Yang, S. Ju
Department of Radiology, Zhongda Hospital, Medical School of Southeast University, Nanjing, China
Impact: The NEWMODEL exhibited improved diagnostic
efficacy and added value to APRI and FibroScan. This
non-invasive model showed great value of MRI in detecting
SLHC, providing a more precise method to make antiviral
therapy decision for CHB patients with normal ALT.
|
|
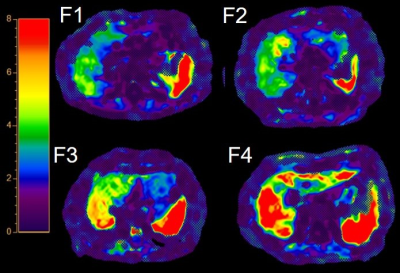 |
Computer Number: 115
2838. Correlation
of MRE-Based Liver and Spleen Stiffness with Platelet Count in
Chronic HBV Infection Patients
H. Zhang, Z. Jiang, X. Zhao, J. Li, B. Zhang, J. Chen
Department of Radiology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Medical School, Nanjing University, Nanjing,Jiangsu, China
Impact: Our study revealed the consistency of changes in
the biomechanical properties of the liver and spleen during
the liver fibrosis progression of chronic HBV infection.
Furthermore, we demonstrated their correlation with
thrombocytopenia.
|
|
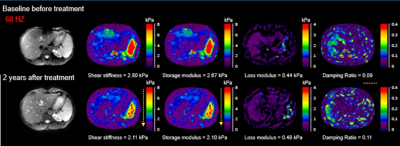 |
Computer Number: 116
2839. Multiparametric
3D-MRE for Longitudinal Monitoring of Disease Progression in CHB
Patients, With or Without Treatment
Y. Wang, Z. Wang, R. Bai, H. Guan, Y. Shi
Department of Radiology, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang,Liaoning, China
Impact: 3D-MRE offers a non-invasive biomarker for
longitudinal monitoring in CHB patients.
|
|
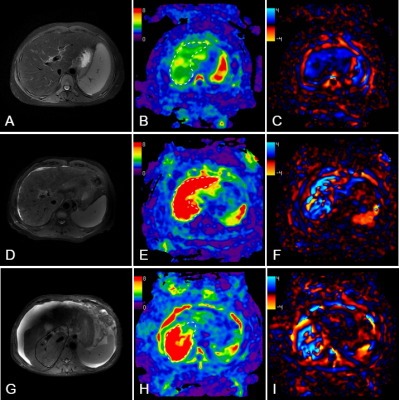 |
Computer Number: 117
2840. Magnetic
Resonance Elastography for Detecting Decompensation in Cirrhotic
Patients with Different Volumes of Ascites
Z. Sun, M. Duan, K. Wang, J. Liu
Department of MR Imaging, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Impact: This study highlights the effectiveness of
magnetic resonance elastography in accurately detecting
decompensation in cirrhotic patients, particularly those
with no or minimal ascites, thereby improving diagnostic
precision and potentially guiding better clinical management
of liver disease.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 118
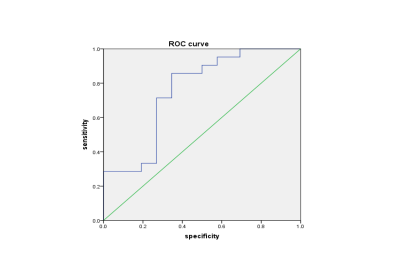
2841. Identification
of early fibrosis stages S1 and S2 in patients with chronic
hepatitis B based on T1 mapping for ECV
L. Huang, T. Liu, W. Liu, J. Tang, W. Zhang, J. Chen
Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Zhuhai,, Zhuhai, China
Impact: Liver ECV quantification through HCT and T1
mapping provides a relatively stable indicator for
distinguishing early liver fibrosis stages S1 and S2. This
non-invasive method offers clinical benefits for patients
with chronic liver disease. Therefore, utilizing HCT and T1
mapping for liver ECV assessment can effectively evaluate
the degree of liver fibrosis and facilitate the
customization of treatment plans for patients.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 119
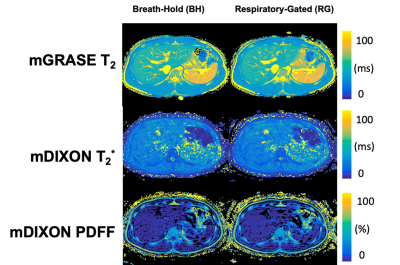
2842. Comparative
Assessment of Hepatic T2, T2*, and PDFF Estimates from
Breath-Hold and Free-Breathing Respiratory-Gated Acquisitions
A. Kilpattu Ramaniharan, J. Kemp, M. Kocaoglu, J. Greer, J.
Tkach, A. Trout, J. Dillman, A. Pednekar, M. K. Manhard
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, United States
Impact: Respiratory-gated mGRASE and mDIXON Quant
acquisitions produced T2, T2*,
and PDFF estimates with excellent agreement to estimates
from breath-hold acquisitions. This approach suggests
applicability for liver assessments in patients with
impaired breath-holding capacity, particularly young
children or patients with comorbidities.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 120
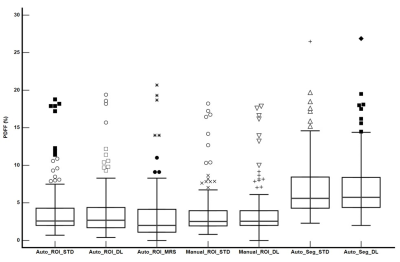
2843. Assessment
of Deep Learning-Accelerated Hepatic Proton Density Fat
Fraction: Linearity and Bias Analysis Against Standard
acquisition
B. Kim, H-S Lee, J-I Choi
Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: DL-accelerated CSE-PDFF showed near perfect
linearity with conventional PDFF and MRS-PDFF while reducing
the scan time to 10 s, highlighting its role in patients
with limited breath-hold capacity and in screening settings
where time efficiency is a priority.
|
|
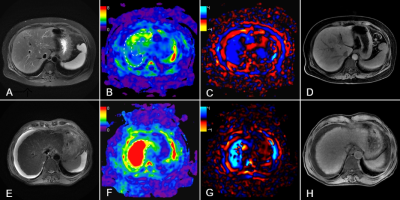 |
Computer Number: 121
2844. Comparative
diagnostic performance of liver shear stiffness and relative
liver enhancement in the detection of decompensated cirrhosis
M. Duan, K. Wang, J. Liu, Z. Sun
Department of MR Imaging, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Impact: In this study, LSS measured by MRE was shown to
be a non-invasive and accurate diagnostic marker for
identifying decompensation in patients with cirrhosis,
without the need for contrast injections.
|
|
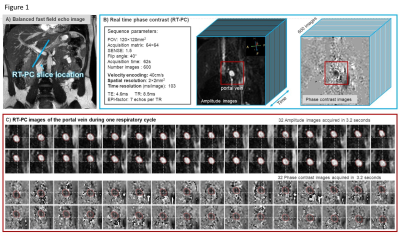 |
Computer Number: 122
2845. Portal
vein flow and motion quantification by Real-Time Phase Contrast
MRI
O. BALEDENT, P. LIU, A. PLANCKE, T. YZET
University Hospital CHU Amiens, Amiens, France
Impact: Real-Time-PCMRI is a simple, rapid, non-invasive
and unsynchronized imaging method to investigate liver
vascularization to establish accurate quantitative
physiological reference values. Dedicated post processing
software should help to use it easily in clinic to better
diagnosis and understanding liver pathologies.
|
|
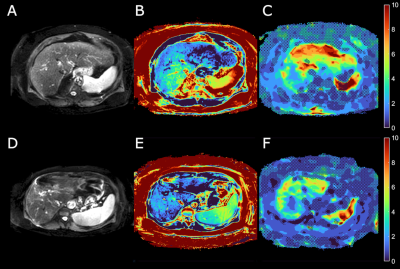 |
Computer Number: 123
2846. Virtual
MRE vs. MRE: Evaluation of vMRE at 3 T for Distinguishing
Fibrosis and Its Sensitivity to Relaxometry Factors
W. Bartholomä, S. Cai, N. Dahlström, J. Tellman, S.
Kachegias, P. Nasr, M. Ekstedt, M. Byenfeldt, P. Lundberg,
J. Kihlberg
Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
Impact: vMRE did not yield results comparable to MRE and
failed to reliably identify hepatic fibrosis. Its high
sensitivity to relaxometry factors, such as intrahepatic fat
or iron, made it susceptible to misestimations of liver
stiffness.
|
|
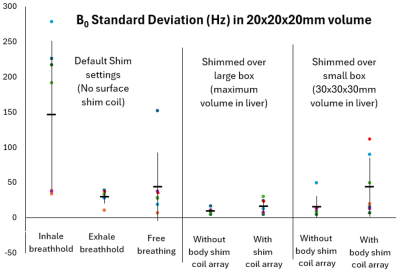 |
Computer Number: 124
2847. Investigating
Liver B0 mapping at 7T: Comparison of respiration phase, shim
volume size and body shim coil arrays
S. Bawden, O. Mougin, A. Spicer, R. Bowtell, S. Francis, P.
Gowland
University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom
Impact: This study provides important information about
the effects of respiration, shim volume size and using body
shim coil arrays in 7T liver MRI/MRS. This data can be used
in future studies to optimize shim routines and improve
spectral line widths.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 125
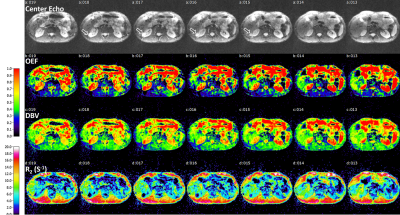
2848. Free-breathing
hepatic Oxygen Extraction Fraction (OEF) mapping using radial
GESSE
K. Zhang, S. Triphan, F. Kurz, C. Ziener, M. Ladd, H-P
Schlemmer, H-U Kauczor, O. Sedlaczek
Heidelberg University Hospital, Heidelberg, Germany
Impact: The feasibility of free-breathing liver OEF
mapping using rGESSE was investigated. Further improvement
of the quantification, possibly using measured macroscopic
field inhomogeneities may be needed.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 126
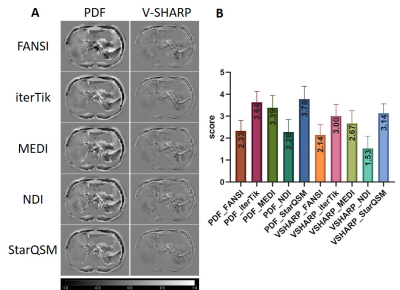
2849. Assessment
of highly repeatable Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping
Processing Pipelines for Abdominal Applications
L. Li, M. Wang, B. Xu, X. Zhao, T. Wu, Y. Xie, Z. Dong, S-t
Feng
The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Impact: Selecting the optimal post-processing method is
crucial for enhancing the reliability of abdominal QSM,
potentially improving clinical diagnostics and patient
outcomes.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 127
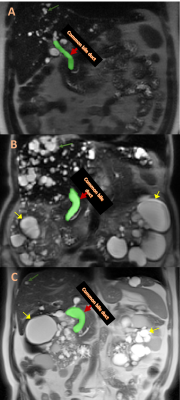
2850. Common
bile duct dilatation on MRI in autosomal dominant polycystic
kidney disease
U. Sattar, Y. Kim, J. Berman, M. Thein, G. Quartin, V.
Bazojoo, C. Zhu, Z. Hu, X. Yin, X. Luo, J. Blumenfeld, M.
Prince
Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: CBD dilatation is more frequent in ADPKD
compared to controls and correlated positively with age and
negatively with serum albumin, a marker of liver
dysfunction. This suggests that CBD dilatation may be
another extra-renal manifestation of ADPKD.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 128
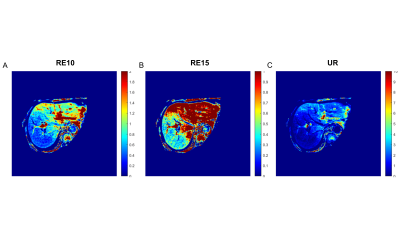
2851. Preoperative
Liver Function Assessment in Biliary Tract Cancer Patients Using
Routine Clinical DCE-MRI: A Prospective Study
X. Lin, M. Xiao, Z. Xu, H. Sun, Y. Wang, S. Yu, C. Xiang, J.
Dong, H. Chen
Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Impact: Our work enhances preoperative risk assessment
in biliary tract cancer by integrating MRI-derived
functional parameters with serum markers, complementing
traditional metrics for more accurate regional liver
function evaluation and improving prediction of
postoperative complications for personalized surgical
planning.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.