Digital Poster
Hyperpolarization (Gas)
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

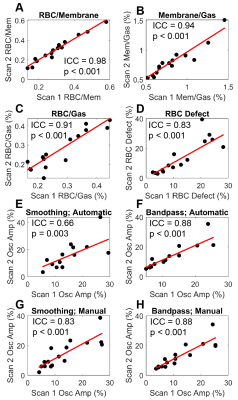 |
Computer Number: 49
4634. Optimizing
Repeatability of RBC Signal Oscillation Measures from
Hyperpolarized 129Xe MRI
I. Mali, B. Frizzell, S. Haworth, P. Niedbalski
University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, United States
Impact:
Hyperpolarized 129Xe oscillation imaging is a noninvasive technique to assess pulmonary microvascular function. By optimizing the technique for repeatability, it has potential to provide a new means to interrogate pulmonary vascular diseases. |
|
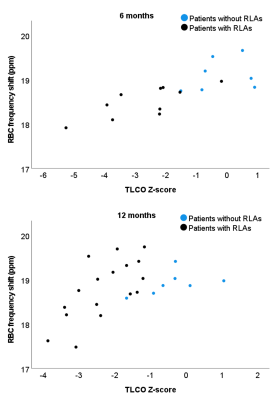 |
Computer Number: 50
4635. 129Xe
red blood cell chemical shift and T2* in patients hospitalised
due to COVID-19 with and without residual lung abnormalities
seen on CT
L. Saunders, G. Collier, G. Norquay, L. Smith, P. Hughes, S.
Strikland, L. Gustafsson, T. Newman, M. Plowright, J.
Watson, Z. Gabriel, P. Wade, J. Meiring, J. Grist, K. L. Ng,
A. Harrison, J. Eaden, J. Bray, H. Marshall, D. Capener, M.
Brook, A. Biancardi, J. Ball, N. Stewart, K. Johnson, A.
Swift, S. Rajaram, L. Watson, P. Collini, G. Mills, R.
Lawson, J. Brooke, P. Molyneaux, A. Goodwin, I. Stewart, L-P
Ho, J. Jacob, T. Meersman, G. Pavlovskaya, F. Gleeson, I.
Hall, R. G. Jenkins, A. A. R. Thompson, J. Wild
The University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom
Impact: RBC chemical shift is sensitive to
alveolar-capillary diffusion abnormalities in patients with
residual lung abnormalities following COVID-19 and may
enable more sensitive monitoring of gas transfer
abnormalities in these patients.
|
|
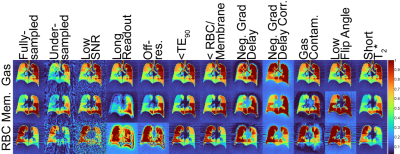 |
Computer Number: 51
4636. Assessment
of Sequence and Assumption Imperfections on 1-point Dixon 129Xe
Gas Exchange MRI Metrics
M. Willmering, A. Matheson, P. Niedbalski, Z. Cleveland, L.
Walkup, J. Woods
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, United States
Impact: Hyperpolarized 129Xe gas exchange imaging
metrics are sensitive to imaging parameters and assumptions.
More advanced acquisitions and reconstructions will improve
the accuracy and robustness of regional gas exchange
metrics.
|
|
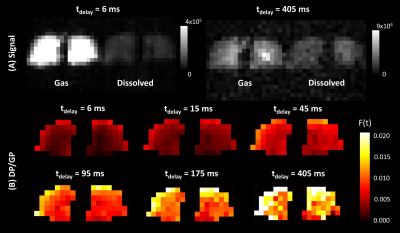 |
Computer Number: 52
4637. Measuring
Pulmonary Gas Exchange with Hyperpolarized 129Xe Chemical Shift
Saturation Recovery Spectroscopy and Imaging
J. Pilgrim-Morris, G. Norquay, L. Saunders, R. Thompson, G.
Collier, N. Stewart, J. Wild
University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom
Impact: Error quantification of CSSR parameters is
important for clinical utility and interpretation. Dynamic
CSSR gas uptake imaging allows for regional quantification
of alveolar septal thickness, which could help identify
fibrosis in heterogeneous lung disease.
|
|
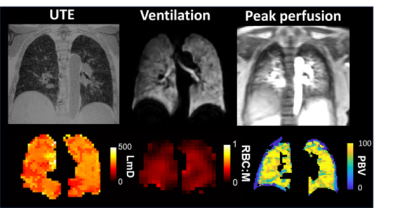 |
Computer Number: 53
4638. 129Xe
MRI is sensitive to pulmonary hemodynamics in systemic sclerosis
patients with suspected pulmonary arterial hypertension
L. Saunders, S. Strikland, G. Collier, P. Hughes, I. Smith,
L. Smith, G. Norquay, N. Stewart, J. Pilgrim-Morris, H.
Marshall, A. Biancardi, F. Hitchcock, A. Swift, A. Rothman,
D. Kiely, R. Condliffe, J. Wild, A. A. R. Thompson
The University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom
Impact: 129Xe
red blood cell oscillation amplitude is a promising,
non-invasive MRI marker of elevated pulmonary arterial
pressure in patients with systemic sclerosis. 1H
and 129Xe
MRI provide clinically relevant and complementary
information on pulmonary function in this population.
|
|
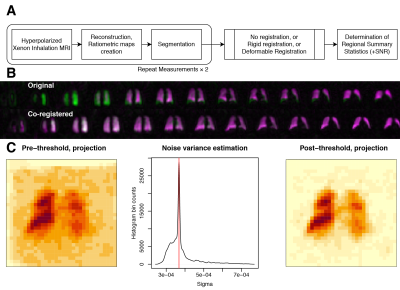 |
Computer Number: 54
4639. Regional
Reproducibility of Dissolved-Phase Hyperpolarised 129Xe MR Gas
Imaging
M. Kristensen, M. Væggemose, E. Hansen, N. Bøgh, U.
Kjærgaard, M. Aastrup, J. Agergaard, B.
Schiøttz-Christensen, L. Østergaard, E. Bendstrup, J.
Miller, C. Laustsen
Aarhus Universitet, Aarhus, Denmark
Impact: Regional 129Xe MRI measurements show excellent
repeatability across all lung regions, validating its use
for detecting localized pathology. This first comprehensive
regional repeatability study establishes quantitative bounds
for clinical interpretation of regional lung function
measurements.
|
|
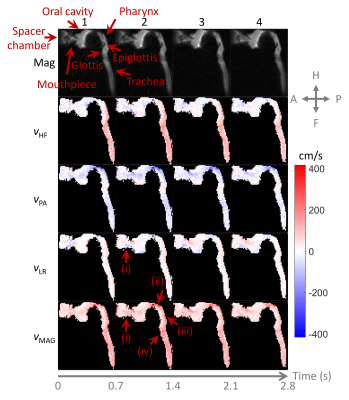 |
Computer Number: 55
4640. Hyperpolarized
xenon-129 phase-contrast velocimetry in an inhaler spacer and
the upper airways using direction-specific aliasing velocities
J. Ball, G. Collier, N. Stewart, R. Munro, G. Norquay, H.
Elphick, J. Wild
University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom
Impact:
The results demonstrate the feasibility of phase-contrast velocimetry MRI of inhaled xenon-129 within an inhaler spacer and the upper airways. This will improve validation of computational fluid dynamics to improve inhaled therapy delivery and understanding of upper airways diseases. |
|
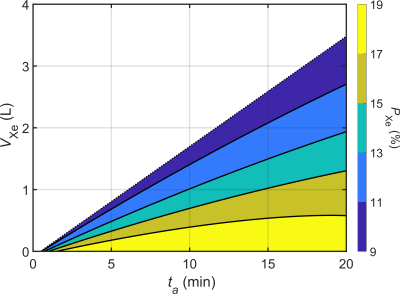 |
Computer Number: 56
4641. Rapid
polarization of 1 liter of xenon-129 to 10% in 6 minutes with a
continuous-flow spin-exchange optical pumping polarizer
J. Ball, R. Munro, O. Rodgers, J. Wild, G. Norquay
University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom
Impact:
The results demonstrate the ability to produce rapid on-demand hyperpolarized xenon-129 doses in large volumes, which will improve clinical workflows for hyperpolarized gas MRI studies. |
|
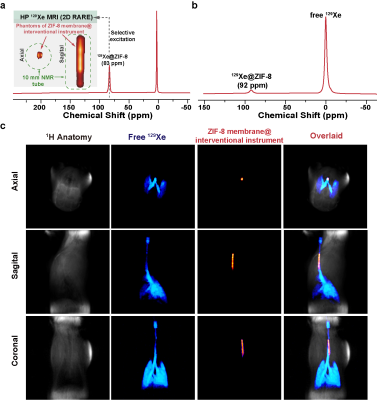 |
Computer Number: 57
4642. Hyperpolarized
129Xe MRI : a new option for navigating respiratory
interventions
X. Yang, J. Zhu, Q. Guo, Q. Zeng, X. Zhao, H. Li, X. Zhou
Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences , Wuhan, China
Impact: We demonstrate a method for the localization and
navigation of interventional instruments within the airway
on 129Xe MRI scanners, i.e., using ZIF-8 membranes as
imaging markers, and preliminarily validate the possibility
of 129Xe MRI as a respiratory interventional navigation
technique.
|
|
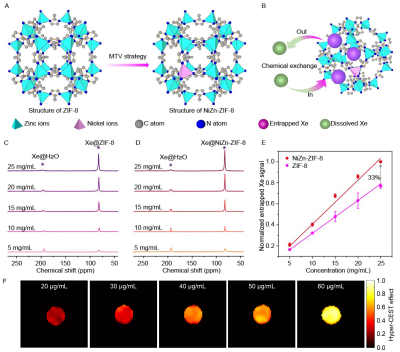 |
Computer Number: 58
4643. Enhancing
the Hyperpolarized Xenon NMR Signal through Multivariate
Metal-organic Framework
Q. Zeng, Q. Yue, Q. Guo, X. Zhou
Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, China
Impact: We develop a MOF for efficiently entrapping
xenon atoms and provide a general method for enhancing the
129Xe NMR signal and facilitating the application of
hyperpolarized 129Xe molecular imaging in vivo.
|
|
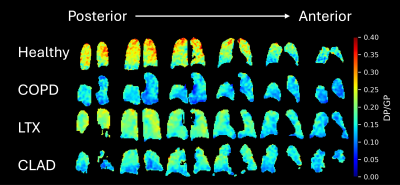 |
Computer Number: 59
4644. Assessment
of Post-Transplant Lung Function Alterations Using
Free-Breathing Hyperpolarized Xenon MRI
M. Ismail, H. Hamedani, L. Loza, S. Kadlecek, C. Bermudez,
M. Crespo, A. Courtwright, J. Diamond, P. Gregorio, E.
Cantu, C. Jiawei, M. Gorora, J. Park, A. Gurevich, K.
Ruppert, R. Rizi
University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, United States
Impact: The findings suggest that dynamic HP-Xe MRI is a
sensitive tool for detecting early pulmonary function
alterations in lung transplant recipients that traditional
imaging methods might miss. This could enable earlier
diagnosis and intervention of CLAD, potentially improving
long-term survival.
|
|
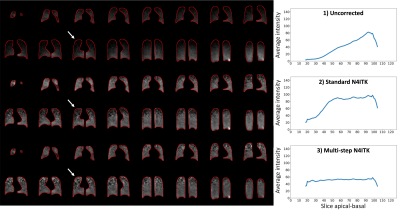 |
Computer Number: 60
4645. A
Reader Study to Compare Multi-step vs. Standard N4ITK bias field
Correction Methods in Xenon MRI
S. Leewiwatwong, M. Willmering, D. Mummy, A. Costelle, D.
Clements, H. Qin, F. Li, B. Driehuys
Duke University, DURHAM, United States
Impact: This study provides valuable insights into the
effectiveness of different bias field correction methods in
reducing variability and improving quantification accuracy
in 129Xe
ventilation MRI across multiple imaging centers.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 61
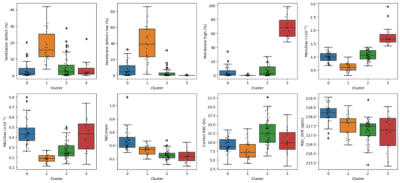
4646. Classification
of COPD and ILD Subtypes Using 129Xe MRI/MRS with Unsupervised
Cluster Analysis
F. Li, D. Mummy, S. Leewiwatwong, A. Costelle, H. Qin, B.
Driehuys
Duke University, DURHAM, United States
Impact: This study offers a pathway for designing future
prospective clinical trials that could validate non-invasive
129Xe MRI/MRS metrics of gas exchange by demonstrating that
certain patterns distinguish between lung disease subtypes
with high accuracy.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 62
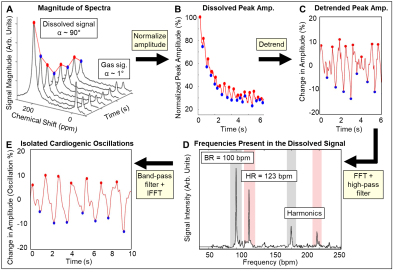
4647. Hyperpolarized
129Xe Gas Exchange MRS in Mice: Impact of Heart Rate,
Ventilation Pressure, and a Paralytic on Cardiogenic Signal
Oscillations
M. Costa, E. Fugate, S. Soderlund, N. Chatterjee, D.
Lindquist, Z. Cleveland
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, United States
Impact: 129Xe
dissolved into tissue displays one peak in mouse lungs.
Despite lacking a unique RBC peak, cardiogenic oscillations
are observed via MRS. Oscillation amplitude is sensitive to
lung hemodynamics and represents a promising means to
noninvasively assess pathology in mice.
|
|
 |
Computer Number: 63
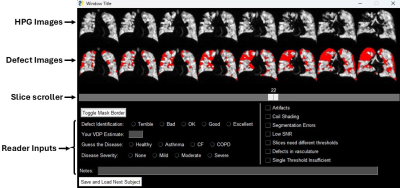
4648. Assessment
of Hyperpolarized Gas Ventilation Defect Percentage via
User-defined Defect Thresholds
G. Garcia Delgado, C. Thornburgh, U. A. Shammi, J. Mugler
III, J. Mata, M. He, W. Miller, T. Altes, R. Thomen
University of Missouri, Columbia, United States
Impact: Single-threshold VDP methods are often
discordant with human reader selection of defect thresholds.
The extent to which defect mis-labeling is acceptable
differs substantially between researchers and radiologists.
Defect maps should always be evaluated visually and mis-labeled
voxels corrected if necessary.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.