ISMRT Poster Presentations
ISMRT Clinical Posters
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 00:00 |
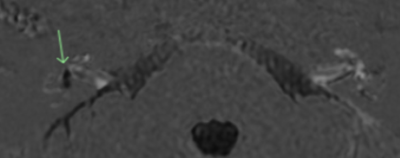 |
5307. HYDROPS:
MRI Technique and Pitfalls in the assessment of Meniere’s
Disease
N. Kularatne
South Coast Radiology (IDX), Brisbane, Australia
Impact: Delayed gadolinium-enhanced HYDROPS MRI is an
emerging technique that can be used in clinical practice to
aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of Meniere’s disease,
ultimately supporting improved patient care.
|
| 00:00 |
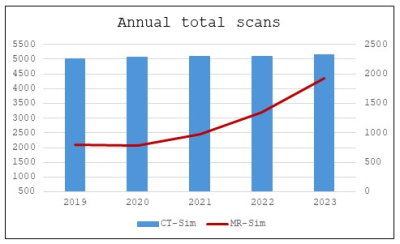 |
5308. Understanding
the resource implications of MRI utilization and complexity for
radiation therapy planning and dose delivery
A. Simeonov, C. Robertson, T. Rosewall, J. Seuntjens
Princess Margaret Cancer Center, Toronto, Canada
Impact: The results have prompted the hiring of
additional MR technologists, an increase in hours of
operation, and investment to increase the MRI capabilities
in the department. MRI is considered essential for
personalized radiation treatment planning, guidance and
delivery.
|
| 00:00 |
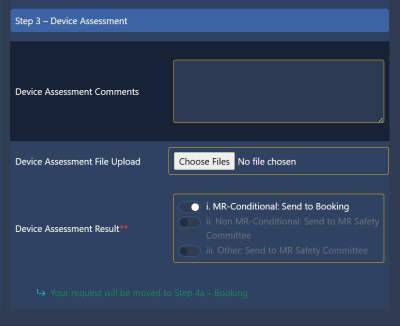 |
5309. Implant
Clearance Tracker –Improving Efficiency in Clearing Patients
with Implants for MRI
N. Talbot, B. Wintersperger, K. Eyers, T. Chen
University Health Network, Toronto, Canada
Impact: The tool creates a method for ensuring that
patients are not delayed in their implant review, thereby
ensuring that MRI exams are performed in a more timely
manner.
|
| 00:00 |
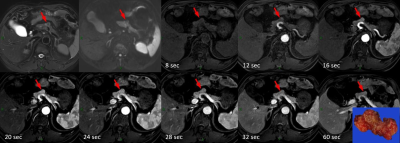 |
5310. Compressed
Sensing High Temporal Resolution (HTR) Dynamic Contrast-enhanced
MR Imaging in Detecting Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor
Y. Li, X. L. Geng, L. Wang, X. H. Gong, W. Liu, J. Cai, D.
J. Liu, X. Y. Wu, Z. Zhao, L. J. Qian
Ren ji Hospital,Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
Impact: HTR MRI extends the temporal window for
identifying pNET hyperenhancement, enhancing diagnostic
accuracy.
|
| 00:00 |
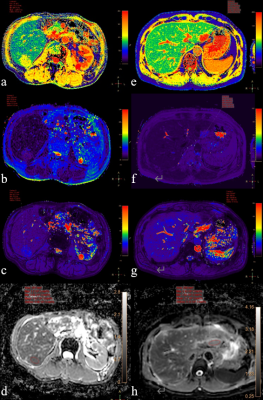 |
5311. Effect
of Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Technique In Differentiating
Benign And Malignant Tumors in Liver
D. Wang, L. Han, S. Ye, Z. Lin, S. Fu, Y. Zhang
Ningbo Medical Center Lihuili Hospital, NingBo, China
Impact: This study shows that Mapping techniques of T1
and T2 represents attractive and promising new tools in
differential diagnosis of liver benign and malignant tumors.
T2* Mapping is not reliable.
|
| 00:00 |
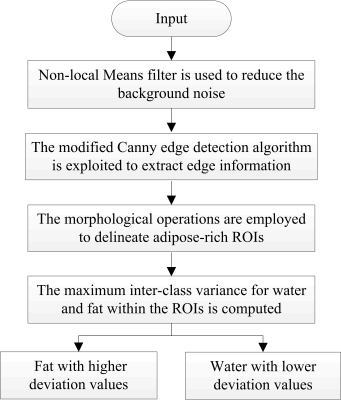 |
5312. Rapid
and Robust Automated MRI Dixon Water and Fat Image
Classification
J. Cheng, C. Wang, Z. Xu, Y. Cui, Q. Fu, Y. Zhang, W. Chen,
Y. Feng, J. Cheng
The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Impact: Misclassification of water-fat in clinical MRI
examinations can lead to diagnostic ambiguity, potentially
impacting clinical decision-making and increasing the risk
of medical disputes. This paper proposes a rapid and robust
automated water-fat image classification method to address
this issue.
|
| 00:00 |
5313. A
Nursing Support Model for Fetal Magnetic Resonance Examination:
The Appreciative Inquiry Method
w. Mou
Southwest Hospitai, Chongqing, China
Impact: This study has the potential to revolutionize
the work of obstetricians, prenatal care physicians, and
magnetic resonance engineers. It can foster new
collaborative models, present novel directions for research
related to fetuses, and inspire further exploration.
|
|
| 00:00 |
5314. Feasibility
of Shoulder MRI Protocol Using Deep Learning - assisted
Iterative Algorithm Protocols: Comparison with Standard MRI
Protocols
m. xiao
Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine, zhuhai, China
Impact: Shoulder MRI images using DLIA protocol could
shorten the scanning time while maintaining comparable image
quality and diagnostic capability.
|
|
| 00:00 |
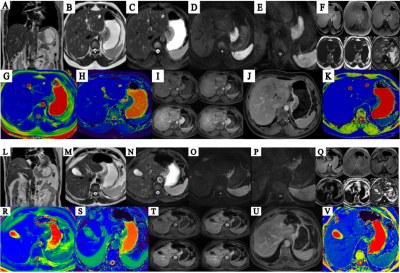 |
5315. A
simple and efficient method of preparing patients with gastric
cancer for abdominal MRI examination
x. huan, w. xueqin, z. letian
Army Medical Center of PLA, Chongqing, China, China
Impact: This strategy aimed to improve both the physical
and mental states of the patients, enabling better
cooperation during training and MR scans.
|
| 00:00 |
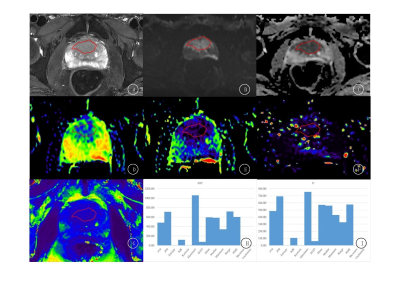 |
5316. Histogram
analysis of quantitative parameters for prostate cancer and
prostatic hyperplasia: A Preliminary 5.0 T MRI Study
c. zheng, s. xing, x. liu, w. zeng, s. xiang, h. ma, z.
feng, y. xiong
Graduate School of Jinzhou Medical University, ,Jinzhou City, China
Impact: This study demonstrates that 5.0T MRI, with
advanced histogram analysis, offers a reliable and
non-invasive method for distinguishing prostate cancer from
benign prostatic hyperplasia, enabling more accurate early
diagnoses and reducing unnecessary biopsies in clinical
settings.
|
| 00:00 |
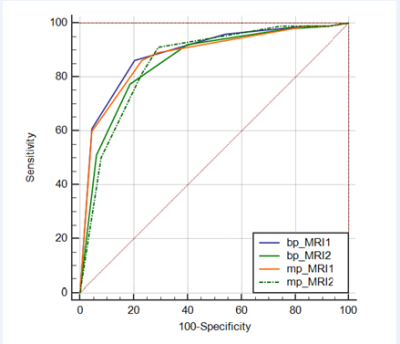 |
5317. To
Study the Application of MRI Report combined with VI-RADS
Dual-parameter and Multi-parameter Scoring System in Bladder
Cancer
H. Xu, Y. Chen, L. Ye
westchina hospital of Sichuan university, Chengdu, China
Impact: It improves the efficiency of MR examination for
patients with bladder cancer, and helps patients who cannot
cooperate with the examination for long time. To provide
more magnetic resonance imaging methods for patients with
renal dysfunction and contrast agent allergy.
|
| 00:00 |
5318. Differences
in amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation in patients with
chronic schizophrenia treated with different antipsychotics
X. Chen, L. Liu
Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China
Impact: Differences in functional brain activity in the
right caudate nucleus of chronic schizophrenic patients
treated with different antipsychotic drugs.
|
|
| 00:00 |
5319. Gray
Matter Volume and Cognitive Function in Adolescents with NSSI
R. Yu, N. Liu
Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, Sichuan Province, China, China
Impact: 为 NSSI 发病机制提供证据,促进临床干预和研究。
|
|
| 00:00 |
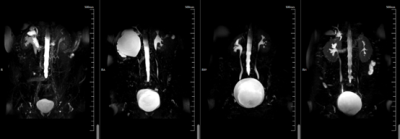 |
5320. Rapid
Breath-Hold 3D GRASE MR Urography: Examining Parameter Effects
on Image Quality.
J. Chun, Y. Zhu
The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiao Tong University, Xi'an City, Shaanxi Province, China
Impact: BH-GRASE
MRU reduces scan time to 19 seconds without impacting
diagnostic accuracy, benefiting patients unable to sustain
long breath-holds. This improvement broadens MRU
accessibility.
|
| 00:00 |
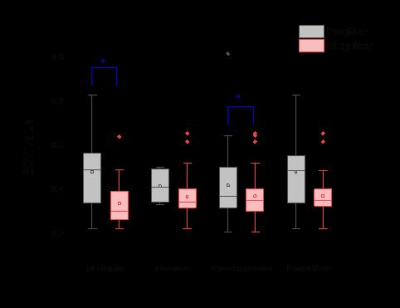 |
5321. The
preliminary application value of extracellular volume fraction
in rectal cancer.
H. Zhang, M. Zhou, P. Wu
Department of Radiology, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, China
Impact: Extracellular volume fraction has application
value in rectal cancer.
|
| 00:00 |
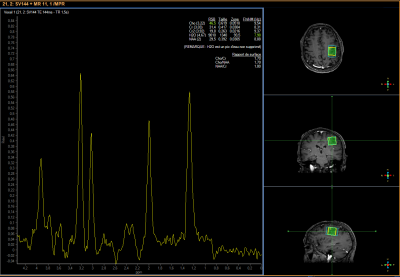 |
5322. Spectroscopy
in Neuroradiology: A Practical Guide
v. g. julien, v. marion, p. lisa, d. helena
chu amiens picardie, amiens, France
Impact: This study aims to democratize the use of MRS in
neuroradiology by providing technicians with a practical
guide to improve spectrum quality, thereby facilitating
result interpretation and enhancing patient care.
|
| 00:00 |
5323. MRI
Safety : speaking the same language !
J. BOINET
NORMEDIS RADIOLOGIE, MONCEAUX EN BESSIN, France
Impact: MRI is a complex technique, the specifics of
which you need to know, and there are several sources of
danger. Simple but effective steps can be taken to make this
imaging technique safe for everyone.
|
|
| 00:00 |
5324. Advancing
Psychosis Diagnosis in LMICs through Functional MRI Techniques
J. Armo
Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital , Kumasi , Ghana
Impact: This systematic review highlights the urgent
need for investment in neuroimaging infrastructure and
training within LMICs to facilitate the integration of fMRI
into clinical practice. Collaborative efforts between
researchers, clinicians, and policymakers are essential to
overcome barriers and improve mental health diagnostics for
vulnerable populations.
|
|
| 00:00 |
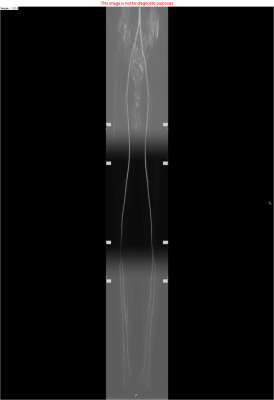 |
5325. Peripheral
Angiogram in Renal Impairment: The Triggered Angiography Non
Contrast Enhanced (TRANCE) Approach
D. Atawone
International Maritime Hospital, Tema, Ghana
Impact: The TRANCE approach enables safe, effective
peripheral angiogram studies for renal impaired patients
without the need for contrast agents. Its compatibility with
standard MRI systems and non-invasive nature make it an
ideal diagnostic tool for at-risk patients, minimizing
nephrotoxicity.
|
| 00:00 |
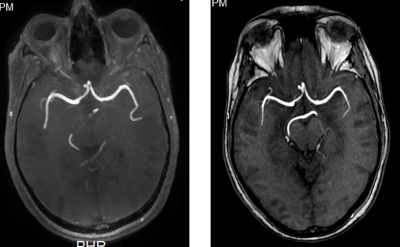 |
5326. Advancing
MR Angiography: Overcoming Time Constraints in Pathologies
requiring assessment of Intracranial Large Vessels Using
LAVA-Flex
P. RAJU
Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology, THIRUVANANTHAPURAM, India
Impact: LAVA- Flex is a useful non-invasive inflow
related sequence to assess large vessels in pathologies
acute ischemic stroke, intracranial aneurysm, parasellar and
skull base lesions. Scan time of MRA using LAVA-Flex is
about one-fifth that of 3D-TOF MRA with HyperSense.
|
| 00:00 |
 |
5327. Enhancing
MRI Safety by Identifying High-Risk Tasks and Implementing
Electronic Screening
M. KAWAMATA, H. TAKIMOTO, A. MASAOKA, A. WATANABE, Y.
YAMANE, K. NAKANISHI
Osaka International Cancer Institution, Osaka, Japan
Impact: By pinpointing and addressing specific high-risk
tasks in the MRI process, we significantly enhanced patient
safety. The electronic screening system integrated with EMRs
ensures accurate identification of patients with metal
implants, reducing the risk of adverse events. This approach
provides a practical model for other medical imaging
departments aiming to improve safety protocols and patient
care worldwide.
|
| 00:00 |
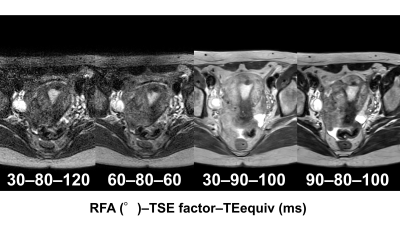 |
5328. Proposal
for Improving the Image Quality of 3D T2-weighted MRI of the
Female Pelvis
Y. Takatsu, A. Ikemoto, T. Yamashiro, T. Miyati
Fujita Health University, Toyoake, Japan
Impact: LC-VRFA enhances 3D T2-weighted MRI of the
female pelvis, yielding sharper images with fewer artifacts.
The proposed parameter settings can improve diagnostic
accuracy and streamline protocols, benefiting clinicians and
patients by reducing scan time while maintaining image
quality.
|
| 00:00 |
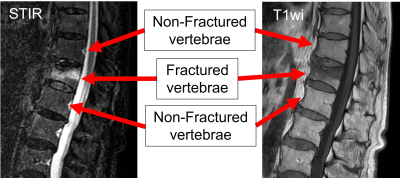 |
5329. Assessment
of IVIM-Derived Microcapillary Perfusion in Osteoporotic
Vertebral Fractures
H. Takashima, R. Imamura, Y. Abe, T. Morita, R. Fukushi, Y.
Akatsuka, T. Takebayashi
Faculty of Health Sciences, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan
Impact: This study establishes IVIM as a reliable,
non-invasive tool for assessing perfusion in osteoporotic
vertebral fractures, providing baseline data for prognostic
use. Findings may support early interventions, improving
outcomes and potentially reducing long-term care needs in
elderly populations.
|
| 00:00 |
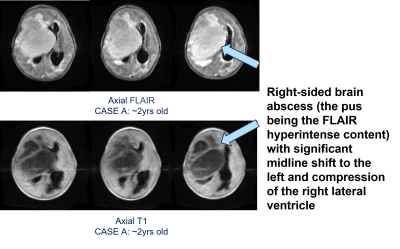 |
5330. A
Clinical Case Study of Brain Abscess in a 23-month Old Child
From a Rural Malawian Setting
C. Chilingulo
Blantyre Malaria Project, Blantyre, Malawi
Impact:
Using the low-field MRI scanner, we saved the life of a 23-year old child who had a large brain abscess whose presentation mimicked a stroke. Questions on how long the residual pus will dissolve still remain unanswered |
| 00:00 |
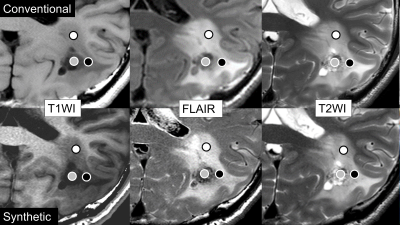 |
5331. Advancing
Brain Imaging: Synthetic MRI’s Potential for Enhanced Contrast
in Tumors and Surrounding Tissues
Y. Takatsu, S. Harada, K. Murayama, T. Miyati
Fujita Health University, Toyoake, Japan
Impact: The findings could transform clinical practices
by improving tumor visualization and differentiation,
leading to more accurate diagnoses. This research prompts
new questions on optimizing synthetic MRI and underscores
its value in advancing neuroimaging for better patient
outcomes.
|
| 00:00 |
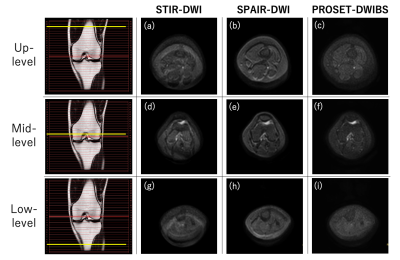 |
5332. Enhanced
Fat Suppression Effect in Off-Center Knee Imaging by Integrating
DWIBS with PROSET.
S. Takano, K. Watanabe, N. Konta, R. Iwasaki, T. Horie, M.
Honda, K. Yasumoto, M. Obara
Department of Radiology, Tokai University Hospital, Kanagawa, Japan
Impact: By reducing chemical shift artifacts caused by
Methylene, PROSET-DWIBS has the potential to improve
diagnostic clarity.
|
| 00:00 |
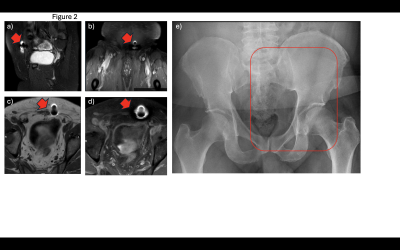 |
5333. Mystery
in the MRI: A case study of an uncharacteristic artifact
J. Thairu, C. Mokua, I. Ohuma, P. Kung'u, S. Farquharson
Sonar Imaging Centre, Nairobi, Kenya
Impact: This study emphasizes the challenges of
identifying elusive MRI artifacts, impacting radiologists
and MRI technologists by highlighting areas where diagnostic
accuracy can be improved. Developing a framework for
investigating rare artifacts could significantly enhance
diagnostic precision and patient care.
|
| 00:00 | 5334. WITHDRAWN | |
| 00:00 |
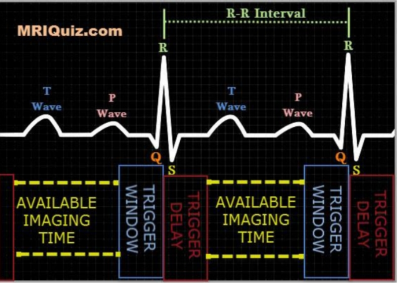 |
5335. Enhancing
Image Quality in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance: The Impact
of Patient Preparation and Scan Protocol Adjustments
C. MUCHUKI, P. GITHINJI
KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL, NAIROBI, Kenya
Impact: Increased Diagnostic Confidence by providing
clearer visualization of cardiac structures and functions.
|
| 00:00 | 5336. WITHDRAWN | |
| 00:00 |
 |
5337. The
portable ultra-low field Magnetic Resonance Imaging device,
wherever it's needed.
C. Kroesbergen
LUMC, Leiden, Netherlands
Impact: The pMRI scanner is a portable, ultra-low-field
scanner for brain imaging that can be used in any
in-hospital room to save valuable time, hospital resources
and reduce risks for ICU or ER patients.
|
| 00:00 |
 |
5338. Sneak
Peek: Preparing Children for MRI Scans
S. Eigenbrood-Lensen
Leids Universitair Medisch Centrum , Leiden, Netherlands
Impact: The "Sneak Peek" app reduces anxiety for
children during medical exams by providing educational
content. This boosts their confidence and improves
parent-child interaction, leading to smoother examinations
and better health outcomes. Future research could explore
broader applications in healthcare.
|
| 00:00 |
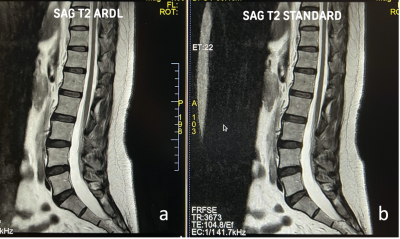 |
5339. Optimising
Spine Imaging with AIR Recon DL (ARDL): Enhancing Patient Care
through Improved Efficiency and Diagnostic Value
J. H. Wong, E. E. Kyaw, Y. Y. Sitoh, W-Y Yu, E. Ng Geok
Ling, H. P. Oh
National Neuroscience Insitute, Singapore, Singapore
Impact: The results demonstrate that ARDL can
significantly reduce MRI scan times while improving image
quality, enhancing patient comfort and clinical workflow.
This study enables further exploration into AI-driven
imaging techniques and their broader implications for
patient care and diagnostic accuracy.
|
| 00:00 |
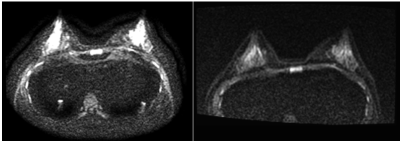 |
5340. Clinical
Comparison of Conventional DWI STIR and Focus DWI FS for Breast
Cancer Evaluation
M. Ahmad
National University Health System (NUHS), Singapore, Singapore
Impact: FOCUS DWI is more superior to conventional DWI.
A shorter readout time enables a reduction of FOV, reducing
off-resonance induced artifacts and physiological image
blurring. CHESS fat-signal technique improves spatial
resolution and SNR when utilized with proper ROI imaging.
|
| 00:00 |
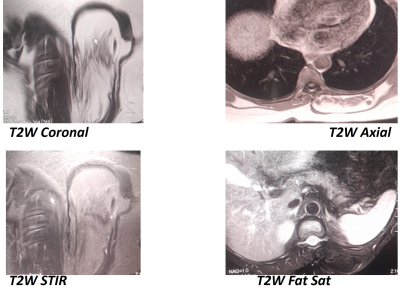 |
5341. MRI
Features Of Thoracic Intramuscular Lipoma Using The Stir and Fat
suppression In Different planes: A Case Report.
K. Mnisi, K. Motiang
Sefako Makgatho Health Sciences University, Pretoria, South Africa
Impact: study highlights MRI’s role in accurately
detecting intramuscular lipomas, allowing targeted imaging
to enhance diagnostic precision. It supports faster,
non-invasive decision-making, reducing biopsy reliance and
aiding effective management of benign lesions for improved
patient outcomes.
|
| 00:00 | 5342. WITHDRAWN | |
| 00:00 |
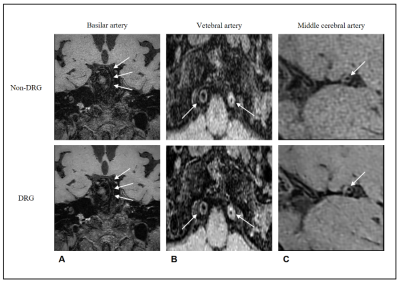 |
5343. Deep
Learning-Based 3D-T1 SPACE Vessel Wall MRI Reconstruction Using
Deep Resolve Gain for Enhanced Image Quality
Y. JEONG, S. KIM, E. SEO, D. SON, C. DAE
Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea, Republic of
Impact: DRG-denoised 3D T1 SPACE MRI enhances vessel
wall imaging precision, enabling earlier and more accurate
detection of vascular diseases. This advancement supports
clinicians in identifying high-risk vascular features,
improving diagnostic accuracy and facilitating timely
appropriate treatment for the respective patient.
|
| 00:00 |
5344. Safety
challenges associated with in vivo studies for HDBS trajectory
planning conducted on sedated miniature pigs in 7T ultra-high
field MRI.
I. Kampman, B. Hansson, L. Wennberg, D. Törnquist, K.
Markenroth Bloch, R. in 't Zandt, H. Bjartmarz, J. Thelin,
J. Schouenborg
Lund University hospital, Lund, Sweden
Impact: The methods outlined here are particularly
valuable for other 7T research sites planning to initiate
similar studies, offering crucial insights into managing
safety and welfare in such specialized settings.
|
|
| 00:00 |
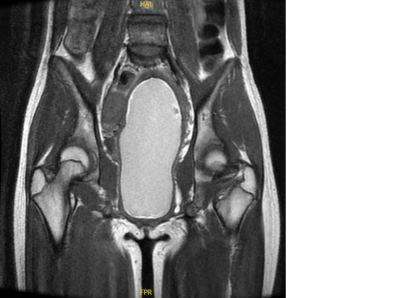 |
5345. A
Young Girl With Bilateral Buttock Pain Accidentally Finding of
Imperforate Hymen - A Case Report
Y. Chang, Y. Lin, C. Hung, W. Chai
Linkou Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan
Impact: The diagnosis of imperforate hymen is often
missed in clinical because its low incidence. So
radiographer should according to the patient's condition and
inform to the radiologist. Make the good suggestion could
help patients.
|
| 00:00 |
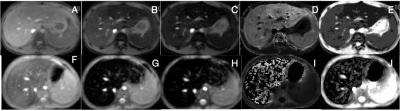 |
5346. Estimation
of Hepatic Iron Concentration (HIC) on Patients with High Iron
Burden
M. Smith, L. Martin, B. Bryan, J. Storrs, M. Rees
Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, United States
Impact: R2*/T2* maps generated from multi-echo GRE scans
are used to quantify hepatic iron concentration (HIC), but
these maps are prone to failure in patients with high HIC.
Manual calculation of hepatic T2* may be necessary for these
patients.
|
| 00:00 |
 |
5347. New
Signs Created to Help Control Access to the MR System Room
S. Valencerina, F. Shellock
Keck Medical Center of USC, Los Angeles, United States
Impact: New signs were created that are designed for the
door and the floor leading to the MR system room.
|
| 00:00 |
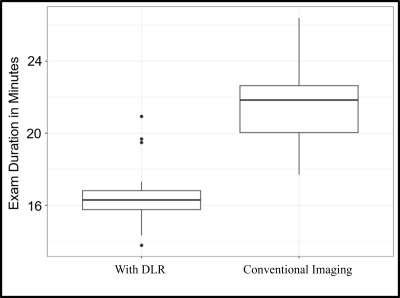 |
5348. Clinical
Impact of Deep Learning Reconstruction in MRI Knee and Patient
Throughput
T. Kryzer, H. Hu, C. Strickland, J. Korf, G. Bosma, J.
Selan, A. Merkle
UCHealth , Highlands Ranch, United States
Impact: Deep Resolve Sharp & Gain deep learning
reconstruction software is a clinically useful tool to
significantly reduce MR knee exams times without
compromising image quality at 3.0 Tesla.
|
| 00:00 |
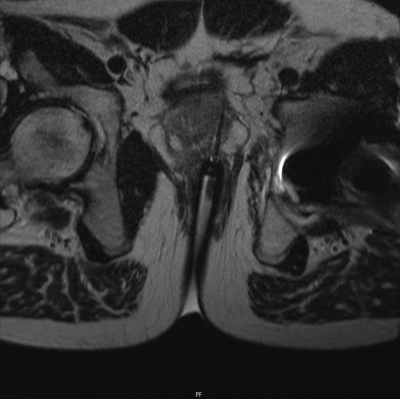 |
5349. Low-field
MR-Guided Prostate Biopsy: Low and Steady Wins the Race
J. Morehouse, S. Esch
Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, United States
Impact: Low-field MR-guided biopsy is an effective
method for patients with unique challenges, especially those
with implanted hip arthroplasty. Advancements in MR
applications over the years make possible a creative and
interesting means to improve the practice.
|
| 00:00 |
 |
5350. A
unique workflow to improve visualization and speed of the
“Swallow Tail” appearance in the Substantia Nigra
M. Bruno, M. Keerthivasan, T. Shepherd
Department of Radiology, New York University Center for Advanced Imaging Innovation and Research (CAI2R), Department of Radiology, New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York , United States
Impact: We created a robust imaging workflow to
delineate the substantia nigra in healthy volunteers. The
visualization of the swallow tail appearance or lack of can
be an imaging biomarker allowing for earlier detection of
pathological changes associated with Parkinson's disease.
|
| 00:00 |
 |
5351. Multi-Sensory
Approach to Alleviate MRI Claustrophobia
Y. Zhu, G. Verma, X. Xu, C. Cannistraci, P. Balchandani
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, United States
Impact: This multi-sensory approach enhances patient
comfort during MRI scans, reduces anxiety-related
cancellations, and improves diagnostic accuracy. It offers a
scalable, cost-effective solution that can be widely
implemented across all clinical settings, benefiting
patients and clinicians.
|
| 00:00 |
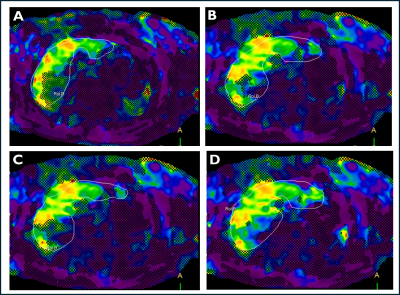 |
5352. Impact
of denoising levels in compressed sensing accelerated MR
Elastography on liver stiffness measurement in clinical patients
S. Hipko, G. White, N. Ali, D. Akselrod, J. Zhang
University of Vermont, Burlinton, United States
Impact: csMRE shorten breath-hold duration significantly
but underestimate the stiffness at higher fibrosis stages. A
calibration curve is needed for csMRE to improve accuracy of
fibrosis staging. The medium denoising level have a good
balance between confident area and LS accuracy.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.