Oral
Artifacts & Correction: Motion & Acquisition
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 15:45 |
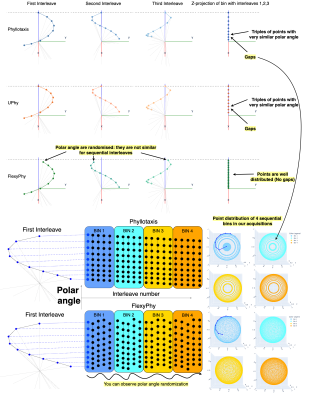 |
0635. Polar
Angles Randomisation Overcomes Binning-Introduced Artefacts in
3D Radial Phyllotaxis GRE

M. Leidi, E. Peper, J. Délitroz, J-B Ledoux, L. Romanin,
J. Bastiaansen, J. Schneider, B. Franceschiello
HES-SO, Sion, Switzerland
Impact: The flexyPhy trajectory improves 3D spiral
phyllotaxis by enhancing sampling uniformity, binning
flexibility, and image quality. It has potential to improve
motion estimation in sequential binning applications, such
as fMRI, and boost uniformity in motion-resolved techniques
like cardiac MRI.
|
| 15:57 |
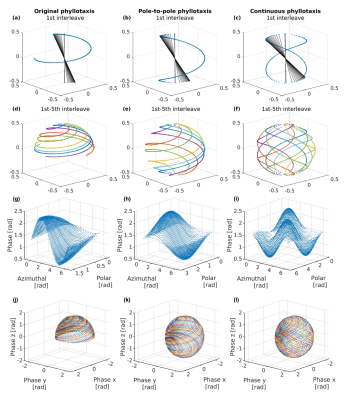 |
0636. Evaluation
of 3D Radial Phyllotaxis Trajectories for Artifact-Free Imaging
and Parametric Mapping
E. Peper, G. Bauman, B. Açikgöz, N. Plähn, A. Mackowiak, Y.
Safarkhanlo, D. Piccini, L. Feng, C. Roy, O. Bieri, J.
Bastiaansen
Inselspital, Bern University Hospital, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
Impact: The proposed 3D radial phyllotaxis trajectory
designs reduce artifacts and improve T1,T2 mapping accuracy,
enhancing image quality for researchers using 3D radial
imaging across MRI sequences, including bSSFP. These designs
enable accurate radial imaging in both research and clinical
applications.
|
| 16:09 |
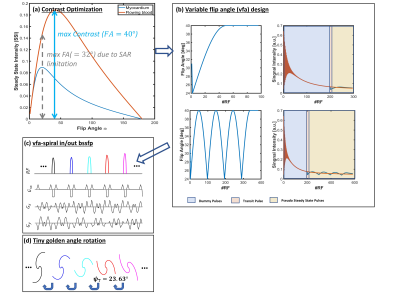 |
0637. Optimization
of free-breathing spiral cardiac cine imaging at 3T with
variable flip angle scheme and region-optimized virtual coils
(ROVir)

K. Yan, Q. Dou, Z. Wang, X. Feng, C. Meyer
University of Virginia, Charlottesville, United States
Impact: Reduced image contrast, along with interference
artifacts can restrict the clinical use of free-breathing
spiral cardiac cine imaging at 3T. The optimizations
presented here offer significant potential to broaden the
clinical applicability of this technique at 3T.
|
| 16:21 |
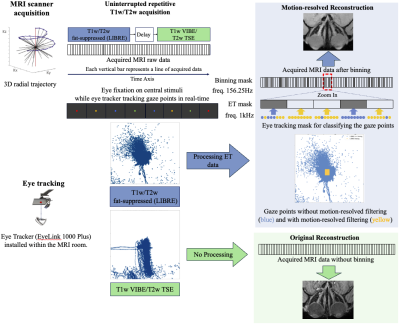 |
0639. MR-Eye:
A High-Resolution Motion-Resolved MRI Protocol for Anatomical
Imaging of the Human Eye

Y. Jia, B. Milani, O. Esteban, E. Fornari, J-B Ledoux,
H. Vitali, J. Bastiaansen, B. Franceschiello
Institute of Systems Engineering, School of Engineering, HES-SO Valais-Wallis, Sion, Switzerland
Impact: Current MRI protocols for diagnosing orbital
inflammation and tumors are prone to motion artifacts. Our
motion-resolved protocol enhances structural detail and
image quality in terms of quantitative metrics, advancing
MRI’s diagnostic capabilities in ophthalmology.
|
| 16:33 |
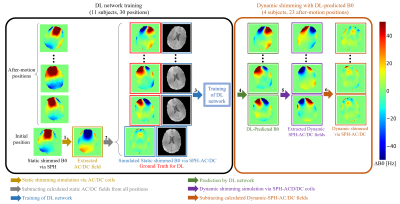 |
0638. Correcting
motion-related B0 Inhomogeneities via Combined Spherical
Harmonics and AC/DC Matrix Coils Using AI-based Prediction
M. Khosravi, B. Bachrata, W. Bogner, B. Strasser, J.
Stockmann, G. Grabner, S. Motyka
Department of Medical Engineering, Carinthia University of Applied Sciences, Klagenfurt, Austria
Impact: Dynamic shimming with spherical harmonics and
AC/DC matrix coils based on AI-prediction of motion-related
B0 inhomogeneities is shown feasible. This offers a
promising approach for dynamic shimming that could
potentially replace volumetric navigators while maintaining
motion-related B0 stability.
|
| 16:45 |
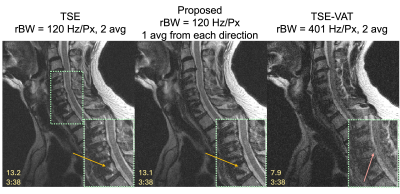 |
0640. Distortion
Correction in TSE Near Metal Implants at 0.55T Using Model-Based
Iterative Reconstruction and Opposite Readout Acquisitions

B. Li, N. Lee, K. Keskin, D. Yoon, A. Toews, J. Acharya,
J. Gross, B. Hargreaves, K. Nayak
University of Southern California, Los Angeles, United States
Impact: This method enhances SNR without blurring for
MRI near metal implants at 0.55T, benefiting low-SNR regions
such as the spine and disc, while avoiding the prolonged
scan times associated with VAT methods that require multiple
averages for SNR improvement.
|
| 16:57 |
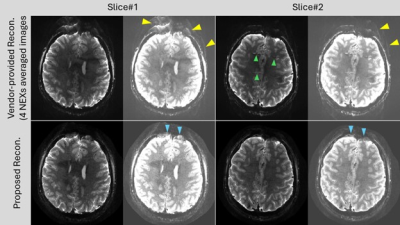 |
0641. An
Efficient Signal Averaging with Model-Based Reconstruction for
Meso-scale Resolution T2*W GRE-EPI at 7T with High-Performance
Gradients
U. Yarach, S. Akrasirakul, F. Godenschweger, H. Mattern, Y-H
Tung, O. Speck
Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
Impact: This advanced imaging technique enables rapid,
ultra-high-resolution brain scans with reduced artifacts,
enhancing structural detail and diagnostic quality. It
provides a promising alternative to conventional methods,
potentially advancing clinical neuroimaging and expanding
applications of 7T MRI in research.
|
| 17:09 |
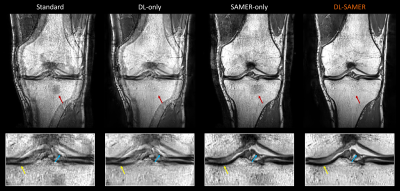 |
0642. Towards
Fast and Motion-Robust Foot and Knee MRI: Application of SAMER
Retrospective Motion Correction with Deep Learning for 2D TSE
and 3D SPACE
D. Polak, E. Raithel, R. Andujar Lugo, A. Fischer, D. N.
Splitthoff, B. Clifford, E. Gabler, W-C Lo, L. L. Wald, S.
Cauley
Siemens Healthineers AG, Forchheim, Germany
Impact: SAMER retrospective motion correction was
applied to knee and foot imaging and integrated with a deep
learning reconstruction to facilitate fast and motion-robust
2D and 3D MSK imaging. This could enhance clinical
diagnostics and improve patient outcomes in musculoskeletal
MRI.
|
| 17:21 |
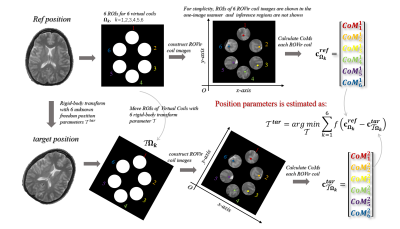 |
0643. Head
Motion Sensing and Estimation in 3D Radial MRI using
Region-Optimized Virtual Coil
E. Lin, F. Calakli, S. Warfiled
Computational Radiology Laboratory, Bostion Children's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, United States
Impact: This research offers a groundbreaking approach
to high-temporal motion sensing in MRI, enhancing image
quality through accurate position estimation. It opens
avenues for future investigations into motion compensation
techniques, ultimately benefiting clinical applications in
brain imaging and diagnostics.
|
| 17:33 |
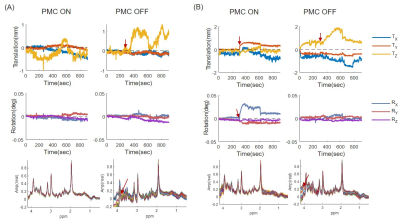 |
0644. Markerless
prospective motion correction assisted functional MRS during
motor activation using PRESS sequence at 3T

Y. Liu, Y. Wei, Y. Yang, X. Zhang, J. Zhao, P. Lee, A.
Tal, H. Chen, Z. Zhang
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Impact: With the assistance of a markerless prospective
motion correction system, fMRS at 3T with a clinically
feasible protocol is capable of detecting small changes of a
few percent in Glx concentrations during functional
activation.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.