Oral
Pulse Sequence Design
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 08:15 |
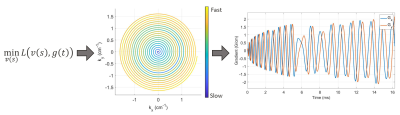 |
1134. Optimized
Gradient Properties through Timing in K-Space (OPTIKS)

M. McCready, X. Cao, C. Liao, K. Setsompop, J. Pauly, A.
Kerr
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: We develop a novel customizable gradient
waveform design method (OPTIKS) capable of optimizing
time-dependent properties while adhering to any specified
trajectory. We apply OPTIKS to design fast-PNS limited
readouts, make imaging quieter, and reduce large prolonged
gradient coil vibrations.
|
| 08:27 |
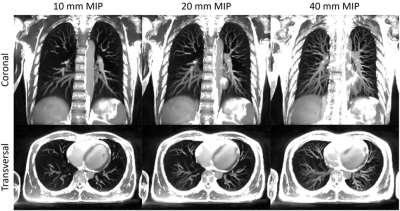 |
1135. Simultaneous
Imaging of the Entire Lung and Heart with Isotropic Resolution
in Free-Breathing
Z. Ding, H. She, Y. Du
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Impact: Comprehensive assessment of the
structures/functions of the cardiopulmonary system and the
cardiopulmonary interaction is feasible using the proposed
technique in a single free-breathing scan.
|
| 08:39 |
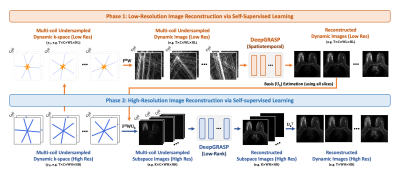 |
1136. Deep
Learning-Optimized GRASP-Pro Reconstruction for
Highly-Accelerated DCE-MRI

H. Pei, L. Feng
New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: The proposed self-supervised learning-optimized
GRASP-Pro enables efficient and reliable 4D MRI
reconstruction. This improves reconstruction quality for
highly-accelerated 4D dynamic MRI, which is useful in
various applications such as DCE-MRI.
|
| 08:51 |
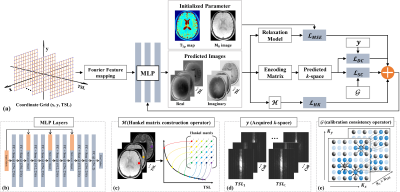 |
1137. Learning
Implicit Neural Representation with Explicit Physical Priors for
Accelerated Quantitative $$$\text{T}_{1\rho}$$$ Mapping
J. Xie, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, Z-X Cui, Q. Zhu, J. Cheng, C. Li,
D. Liang, Y. Zhu
East China Normal University, Shanghai, China
Impact: This study enables accelerated, high-quality
$$$\text {T}_{1\rho}$$$ mapping, improving diagnostic
efficiency and providing a foundation for future
advancements in rapid quantitative imaging, with potential
applications across diverse clinical and research fields.
|
| 09:03 |
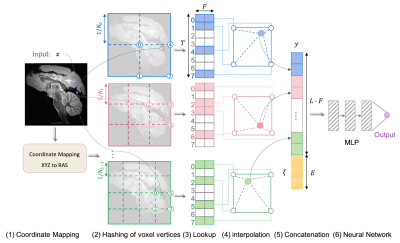 |
1138. Rapid
Whole Brain 180µm Mesoscale In-vivo T2w Imaging
J. Lyu, L. Ning, W. Consagra, Q. Liu, R. J. Rushmore, Y.
Rathi
Harvard Medical School, Boston, United States
Impact: ROVER-MRI with multi-resolution hash encoding
facilitates efficient and seamless MRI super-resolution
reconstruction, achieving rapid 180µm isotropic resolution
while reducing scan time. Our method offers a substantial
leap in acquiring mesoscale whole-brain T2w imaging with
minimal noise and motion artifacts.
|
| 09:15 |
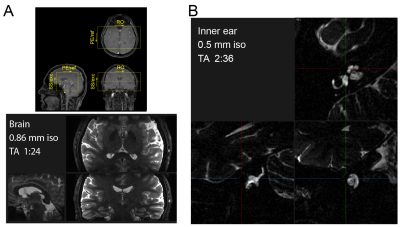 |
1139. 3D
GRASE with Long Echo Trains and Inner Volume Excitation
N. Kobayashi, M. Adams, P. Bolan, G. Metzger
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, United States
Impact: 3D high-resolution FSE acquisitions have been
accelerated by combining GRASE acquisitions, long echo
trains and inner volume excitation, allowing efficient 3D
k-space sampling for rapid high-resolution imaging.
|
| 09:27 |
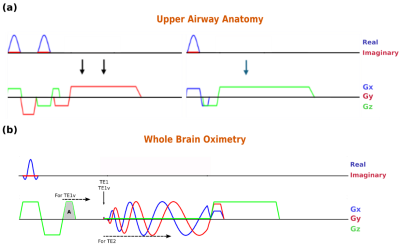 |
1140. Novel
MRI Pulse Sequence to Image Upper Airway Anatomy and Measure
Changes in Neurometabolism During Volitional Model Apneas
J. Dennison, M. Langham, F. Wehrli
University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, United States
Impact: Identifying specific changes in neurometabolism
and upper-airway architecture with an experimental paradigm
validates the proposed approach before applications in a
more challenging naturalistic observation. Experiments in
healthy subjects also helps contextualize the magnitude of
changes noted in natural observations.
|
| 09:39 |
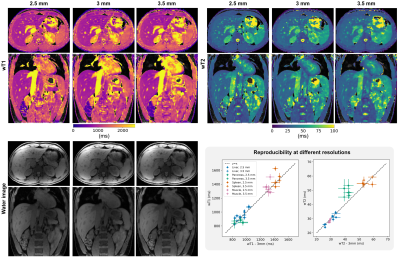 |
1141. 3D
free-breathing water-specific abdominal T1 and T2 mapping using
Cartesian sampling with spiral profile ordering (CASPR)

J. Stelter, K. Weiss, J. Meineke, W. Zhang, B. Kainz, R.
Braren, D. Karampinos
Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany
Impact:
Simultaneous water T1 and T2 mapping is achieved in a scan time of 5min at isotropic resolution of 3mm using a T2-prepared Look-Locker scheme with large-FOV CASPR sampling. This technique may be valuable in assessing diffuse and focal abdominal diseases. |
| 09:51 |
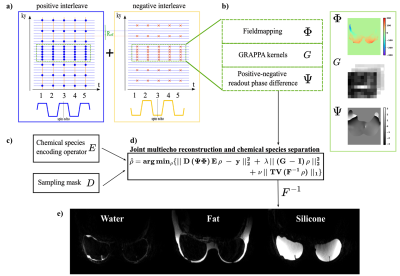 |
1142. Accelerated
T2-weighted imaging of water, fat and silicone with joint
reconstruction and species separation.

A. Nurdinova, X. Zhou, J. Oscanoa, D. Abraham, B.
Daniel, K. Setsompop, B. Hargreaves
Stanford, Stanford, United States
Impact: WFS-separated T2-weighted
imaging with multi-gradient-echo acquisition can be
accelerated ~1.5x by
solving jointly for parallel imaging and species separation
and incoherently undersampling in the ky-TE domain.
|
| 10:03 |
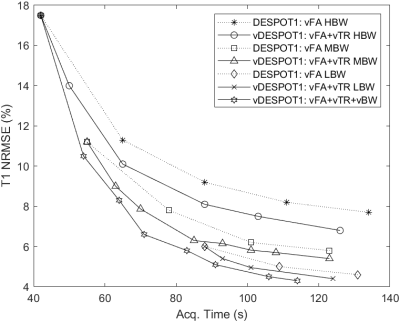 |
1143. Accelerated
DESPOT1 with variable parameters for 3D T1 brain mapping

R. Coronado, C. Besa, R. Botnar, P. Irarrazaval, C.
Prieto
School of Engineering, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
Impact: By using variable TRs, FAs, and BWs with
dictionary-based reconstruction, this research improves
DESPOT1 adaptability and speed, reducing scan time by 40%
for 3D in-vivo T1 brain mapping and promising broader
applications in research and clinical settings.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.