Oral
Motion-Robust MRI: Reconstruction & Motion Correction
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 08:15 |
Introduction
Jingjia Chen
|
|
| 08:27 |
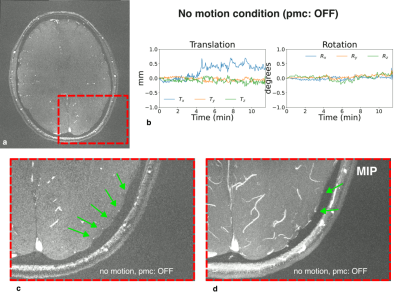 |
0027. High-resolution
0.16-mm time-of-flight angiography at 7 T with volumetric
navigators for prospective motion correction
D. Haenelt, J. Polimeni, Y. Chang, S. Bollmann, D. Gomez, S.
Abbasi-Rad, A. Van der Kouwe, R. Frost
Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, United States
Impact: We show that slab-selective isotropic 0.16-mm
TOF-MRA is feasible with whole-brain volumetric navigators
for prospective head motion correction, enabling robust in
vivo imaging of the human vasculature at an unprecedented
scale.
|
| 08:39 |
 |
0028. Automatic
respiratory and bulk patient motion corrected (ACROBATIC)
free-running whole-heart 5D MRI

R. Ferincz, L. Romanin, M. Prša, E. Tenisch, T. Rutz, J.
Yerly, M. Stuber, C. Roy
Department of Radiology, Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV) and University of Lausanne (UNIL), Switzerland, Lausanne, Switzerland
Impact: Bulk motion correction in ferumoxytol-enhanced
free-running 5D whole-heart MRI enhances image quality in
patients, moving during the acquisition, by accounting for
respiratory displacement and rigid bulk motion while
rejecting outliers. This could reduce the need for
sedation, particularly in pediatrics.
|
| 08:51 |
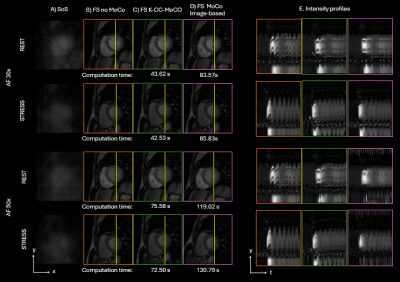 |
0029. K-CC-MoCo:
A fast respiratory motion correction in coil-compressed K-space
for highly accelerated first-pass perfusion cardiac MRI

E. Moya-Sáez, R-M Menchón-Lara, J. Sanchez-Gonzalez, R.
Nunes, C. Real, C. Galán-Arriola, B. Ibanez, T. Correia,
C. Alberola-López
University of Valladolid, Valladolid, Spain
Impact: The k-space-based motion correction outperforms
image-based correction in free-breathing FPP-CMR
acquisitions accelerated up to 50x. This method can
estimate/correct respiratory motion in k-space without an
initial reconstruction, thereby enabling its use for
model-based and/or deep-learning reconstructions from highly
accelerated scans.
|
| 09:03 |
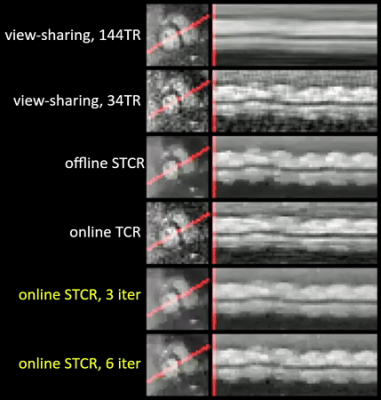 |
0030. Online
spatiotemporally constrained reconstruction for real-time
interactive MRI

D. Le, P. Kumar, E. Yagiz, Y. Tian, K. Nayak
University of Southern California, Los Angeles, United States
Impact: We demonstrate low-latency reconstruction for 2D
real-time MRI with spatial resolution 1.5/2.25mm2,
temporal resolution 25.2/31.8ms, and FOV 240×240/320×320mm,
improving visual recognition of rapidly moving boundaries.
|
| 09:15 |
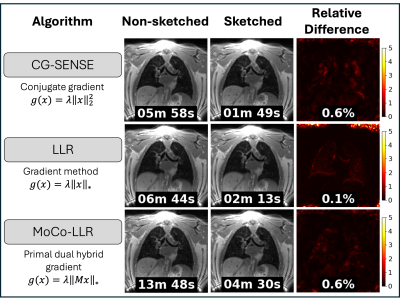 |
0031. Coil
sketching for fast and efficient 4D lung MRI reconstruction
J. Plummer, P. Daudé, R. Ramasawmy, A. Javed, A.
Tsakirellis, J. Moss, A. Campbell-Washburn
National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, United States
Impact: 4D coil sketching enables <5 minute
reconstructions for high-resolution respiratory-resolved
lung imaging, without the need for server-grade GPUs. This
approach is ideal for free-breathing lung MRI applications,
like phase-resolved functional-lung (PREFUL) MRI, that
demand extensive oversampling and high temporal resolution.
|
| 09:27 |
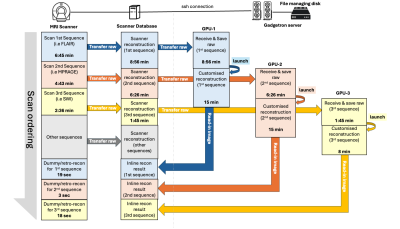 |
0032. A
Framework for Inline Parallel Multi-Sequence Reconstructions: A
Head Motion Correction Application

Z. Ning, S. McElroy, S. Neves Silva, Y. Brackenier, R.
Thornley, L. Canas, A. Price, J. Cleary, L. Grande, D.
Tournier, J. Verdera, J. Hutter, P. Bridgen, P. Cio, M.
Cleri, M. Modat, C. Steves, J. Hajnal
King's College London, London, United Kingdom
Impact: This generalized inline framework enables
advanced but time-consuming, customised multi-sequence
reconstructions within an MR examination without acquisition
or scanner-reconstruction delays. It demonstrated high
robustness and is extensible for future integration of
customised methods across scanners via centralized servers.
|
| 09:39 |
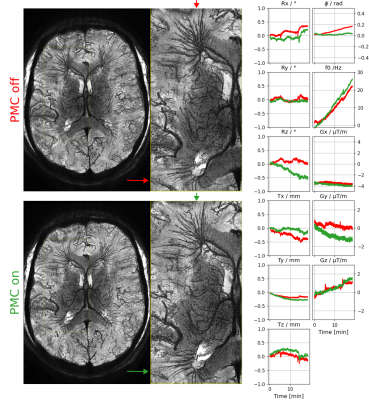 |
0033. Motion-
and field-robust ultra-high-resolution whole-brain imaging
enabled by servo navigation

M. Serger, R. Stirnberg, P. Ehses, M. Riedel, T. Ulrich,
M. Zaitsev, N. Boulant, K. Pruessmann, T. Stoecker
German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE), Bonn, Germany
Impact: Improvements in visibility of small vessels
demonstrate the capability of servo navigators to correct
for small motions and field changes during
ultra-high-resolution T2*-weighted whole-brain imaging
(0.25mm isotropic) using 3D-EPI.
|
| 09:51 |
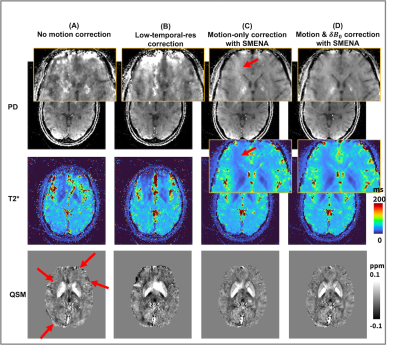 |
0034. Scout-based
Multi-Echo NAvigating (SMENA) for high temporal resolution
motion and B0 estimation: applications to EPTI and multi-echo
GRE

N. Wang, Y. Brackenier, A. Nurdinova, Z. Zhou, D.
Abraham, Y. Lin, X. Cao, C. Liao, K. Setsompop
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: SMENA was developed for joint estimation of
motion and δB0 at
high temporal resolution. It can be flexibly applied to
different sequences, providing accurate
high-temporal-resolution motion and δB0 tracking,
and potentially unleashing the power of MRI on
motion-subject populations
|
| 10:03 |
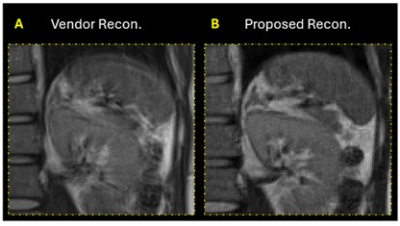 |
0035. Improving
T2-Weighted TGSE-BLADE Liver Imaging via Model-Based
Reconstruction with Self-Breathing Motion Correction
U. Yarach, S. Akrasirakul, H. Mattern, O. Speck
Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
Impact: This reconstruction method improves liver MRI by
effectively managing breathing motion artifacts, enhancing
diagnostic accuracy. It provides radiologists with clearer
images, potentially reducing repeat scans and benefiting
patients by minimizing the need for breath-hold techniques
in routine imaging.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.