Oral
Open-Source Sequences & High-Dimensional Imaging
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 13:15 |
 |
1273. Open-Source
Implementation for X-Nuclear and Multi-Site Sequences within the
Pulseq Framework

X. Liu, D. Cui, P. Larson, D. Mayer, J-F Nielsen, R.
Schulte, C. Mu, L. Carvajal, D. Xu, J. Gordon, D.
Vigneron, A. Korzowski, R. Flavell, Z. Wang
University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, United States
Impact: X-nuclear sequence developers can now more
easily transfer their sequences across vendors and software
for multi-site studies.
|
| 13:15 |
 |
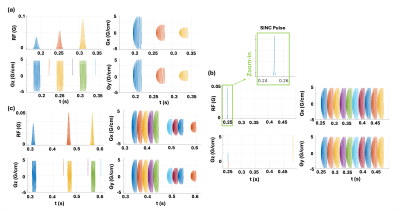
1274. Open
EPTI: pluggable, distortion-free continuous readout developed on
vendor-neutral Pulseq for versatile multi-contrast MR imaging

J. Wu, T. Reese, S. Fujita, B. Bilgic, L. Wald, Z. Dong,
F. Wang
Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, United States
Impact: We developed EPTI into vendor-neutral
sequence/reconstruction frameworks, providing a pluggable,
distortion-free readout for multi-contrast MR imaging. As
proof-of-concept, we demonstrated Pulseq-EPTI readout in
three contrast acquisitions tailored to three different
applications, including quantitative MRI, fMRI, and CEST
imaging.
|
| 13:15 |
 |
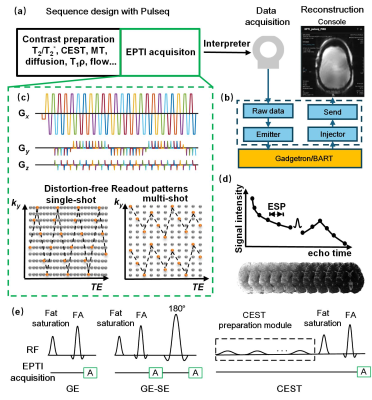
1275. Pulserver:
an open-source Pulseq-based client-server framework for vendor
agnostic, interactive MR sequence design
M. Cencini, K. Wang, S. Huang, R. Schulte, T. Sprenger, D.
Noll, M. Tosetti, J-F Nielsen
INFN, Pisa Division, Pisa, Italy
Impact: Our framework bridges the low-access barrier of
vendor-agnostic design frameworks like Pulseq with the
interactive customizability of native vendor-provided
sequences, enabling faster prototyping and deployment of
novel techniques in clinical workflows.
|
| 13:15 |
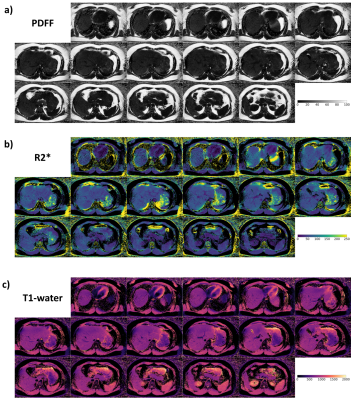 |
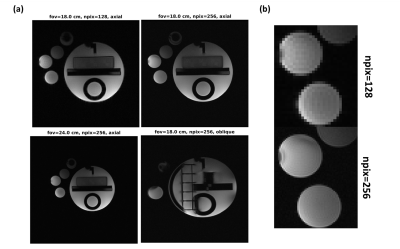
1276. A
Hybrid Multi-Echo Radial Look-Locker (hME-rLL) multi-slice
framework for efficient liver coverage in joint T1-water, PDFF,
and R2* estimation
E. Ahanonu, U. Goerke, B. Toner, K. Johnson, R. Akhbari, G.
Block, D. Martin, V. Deshpande, X. Zhong, H. Wu, A. Bilgin,
M. Altbach
University of Arizona, Tucson, United States
Impact: Joint estimation of T1-water, PDFF, and R2*
would allow for more efficient evaluation of liver condition
for diagnosis and monitor of patients with steatotic liver
disease.
|
| 13:15 |
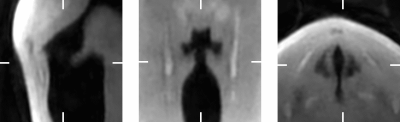 |
1277. Quantification
of the Vocal Fold Oscillations from 3D-isotropic Sub-millimeter
Sub-millisecond MRI

P. Jordan, J. Fischer, F. Stritt, M. Köberlein, L.
Traser, B. Richter, M. Bock
University Medical Center Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany
Impact: VF MRI provides valuable contributions to the
measurement of the VF dynamics in vivo under diverse
physiological conditions. After adaptation, the method might
provide insights into the dynamics of other oscillatory
structures such as the heart valves.
|
| 13:15 |
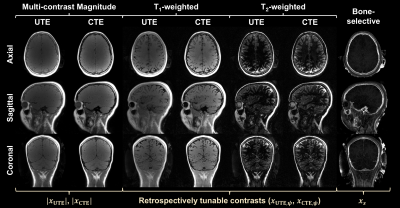 |
1278. DREAMER:
Rapid, high-resolution, and simultaneous multiple-contrast
magnetic resonance imaging of solid and soft tissues
B-T Vu, N. Kamona, F. Wehrli, E. Baccaglini, C. Rajapakse
University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, United States
Impact: DREAMER jointly images solid and soft tissues.
The sequence may enable consolidation of CT and MRI demand
at imaging centers, thereby decreasing patient examination
and wait times, reducing exposure to ionizing radiation, and
simplifying the clinical workflow.
|
| 13:15 |
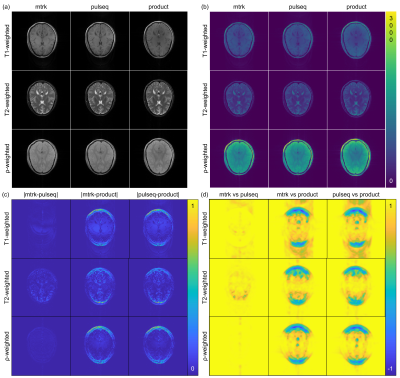 |
1279. Comparison
of mtrk, Pulseq, and vendor sequences using simulated, phantom,
and in-vivo acquisitions

A. Artiges, A. Singh Saimbhi, C. Castillo-Passi, E.
Montin, I. Giannakopoulos, R. Lattanzi, K. Block
New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: mtrk can improve the reproducibility,
accessibility, and dissemination of pulse sequences through
an intuitive development environment. Its human-readable
descriptive language, its compatibility with Pulseq, and its
agreement with vendor sequences make mtrk a powerful
open-source tool for MRI pulse-sequence development.
|
| 13:15 |
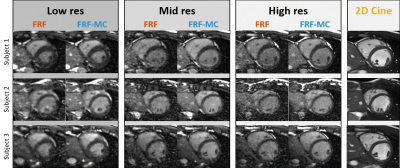 |
1280. Efficient
5D Motion Resolved Imaging: Assessing Spatial Resolutions for
Faster Acquisition Without Compromising LV Ejection Fraction
Accuracy
J. Yerly, A. Ogier, C. Roy, K. Eyre, B. Milani, R. van
Heeswijk, M. Stuber
Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland
Impact: Leveraging inter-bin motion compensation in the
free-running framework with lower spatial resolution enables
rapid, high-quality, free-breathing cardiac MRI in under 2.5
minutes without compromising left ventricular ejection
fraction measurement accuracy. This advancement may enhance
clinical workflows and improve patient comfort.
|
| 13:15 |
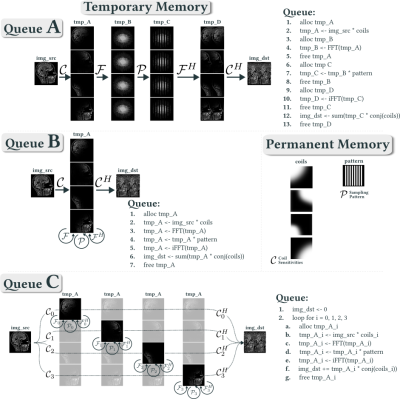 |
1281. Large-scale
High-Dimensional Image Reconstruction via Delayed and
Distributed Computing with BART

M. Blumenthal, M. Uecker
Graz University of Technology, Graz, Austria
Impact: BART is a versatile toolbox for MRI
reconstruction that is widely used due to its flexibility
and performance. It is now more memory-efficient and
supports distributed computing on multiple GPUs and nodes,
allowing researchers to explore even higher-dimensional
datasets.
|
| 13:15 |
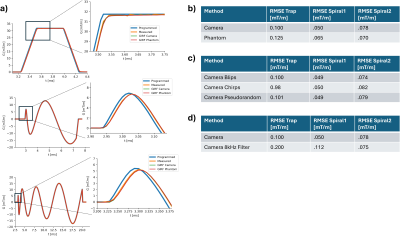 |
1282. Benchmarking
Gradient Impulse Response Function (GIRF) Acquisition Strategies
with Open-Source Measurement Software.
M. Loecher, D. Ennis
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: We developed an open-source package (github.com/mloecher/GIRFbench)
to acquire, process, and benchmark GIRF measurement
strategies to better standardize and understand these
techniques. Estimated GIRFs reduced PC-MRI background
velocity errors to ≤0.4% of VENC and corrected spiral
trajectories to within ∆k=0.31 m-1.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.