Oral
Transformative Diffusion Models for MRI
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 13:30 |
Introduction |
|
| 13:42 |
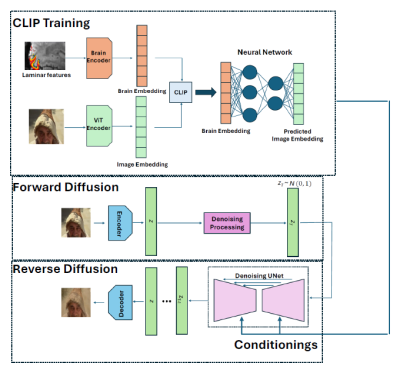 |
0928. Face
Decoding and Reconstruction from 7T Laminar fMRI Data using A
Diffusion Generative Model

N. Huynh, G. Deshpande
Auburn University, Auburn, United States
Impact: Brain disorders, like stroke and prosopagnosia,
can impair brain regions for facial processing, making face
perception difficult. By understanding the neural circuitry
involved in face perception, researchers may identify
pathways that could be targeted to alleviate symptoms in
these conditions
|
| 13:54 |
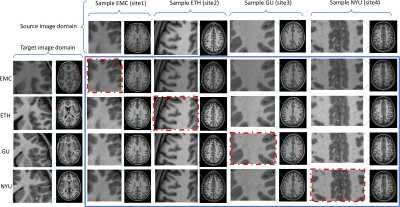 |
0929. Diffusion
based multi-domain neuroimaging harmonization method with
preservation of anatomical details
H. Lan, B. Varghese, N. Sheikh-Bahaei, F. Sepehrband, A.
Toga, J. Choupan
University of Southern California, Los Angeles, United States
Impact: This work showed efficacy of using diffusion
model to tackle neuroimaging harmonization problem with the
preservation of anatomical and biological details. It is
specifically evaluated to harmonize the imaging texture
heterogeneity present in the large cohorts of multi-center
dataset.
|
| 14:06 |
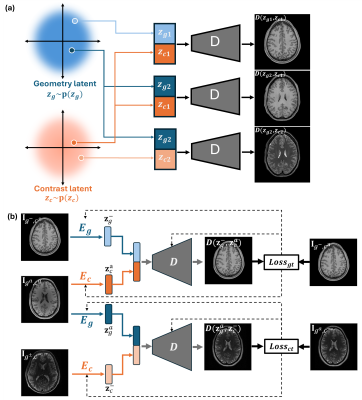 |
0930. Multidimensional
MR Image Reconstruction Using A Disentangled Representation
R. Zhao, F. Lam
University of illinois, Urbana Chamapign, Champaign, United States
Impact: The proposed method may provide a new
perspective for learning-based, high-dimensional MRI
reconstruction, for which small or even no data are
available problem-specific supervised training.
|
| 14:18 |
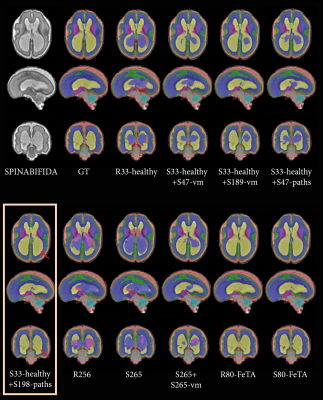 |
0931. Enhancing
Pathological Fetal MRI Segmentation through Generative AI: A
Novel Approach to Synthetic Pathological Data Generation
M. Kaandorp, H. Asma-ull, H-G Kim, D. Agbelese, K. Payette,
A. Jakab
University Children’s Hospital Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Impact: Our approach overcomes challenges of limited
annotated pathological MRI datasets, facilitating the
training of robust segmentation models without the need for
pathological data. This advancement is an important step
towards addressing privacy issues while improving
segmentation performance in prenatal imaging.
|
| 14:30 |
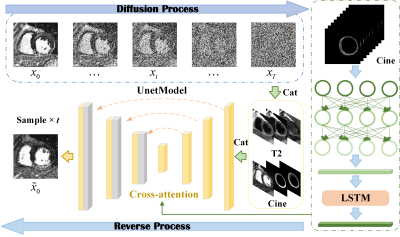 |
0932. LGEDiffusion:
A Multi-Sequence Guided Diffusion Model for Virtual
Contrast-Free LGE Generation in Myocardial Infarction
J. Qi, X. Yue, M. Hu, J. Li, T. Li, K. He
Medical Innovation Research Department, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
Impact: This study highlights the potential of denoising
diffusion probabilistic models for multi-sequence-guided MRI
translation, emphasizing the value of virtual LGE as a
viable contrast-free imaging alternative for myocardial
infarction assessment.
|
| 14:42 |
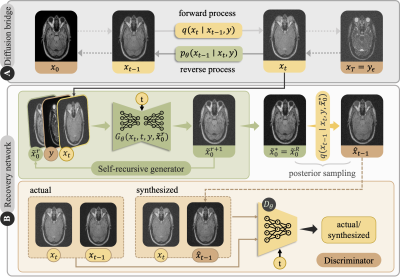 |
0933. A
Self-Consistent Diffusion Schrodinger Bridge for Multi-Modal
Medical Image Translation

F. Arslan, B. Kabas, O. Dalmaz, M. Ozbey, T. Cukur
Bilkent University, Ankara, Turkey
Impact: The enhanced image fidelity in multi-modal
protocols achieved by SelfRDB can extend the scope of
imaging-based assessments, while maintaining relatively low
scan budgets and minimizing exposure to invasive agents or
radiation, particularly benefiting at-risk pediatric and
elderly populations.
|
| 14:54 |
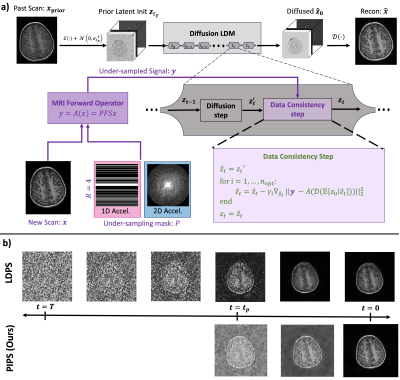 |
0934. Accelerating
Longitudinal MRI using Prior Informed Latent Posterior Sampling
(PIPS)

Z. Shah, Y. Urman, A. Kumar, B. Soares, K. Setsompop
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: We propose an unsupervised prior conditioning
method to further accelerate MRI for longitudinal studies.
Our method is both scalable and generalizable, as it does
not require sequential k-space for training and enforces
data consistency throughout the reconstruction.
|
| 15:06 |
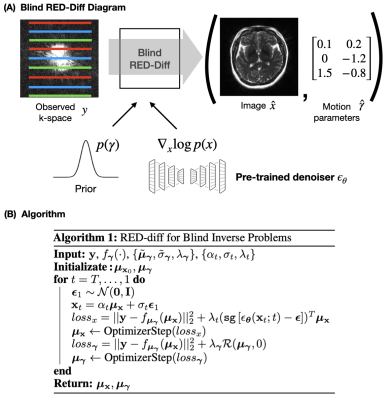 |
0935. Variational
Diffusion Models for Motion Correction: Comprehensive Evaluation

J. Oscanoa, C. Alkan, A. Nurdinova, D. Abraham, K.
Setsompop, M. Mardani, D. Ennis, J. Pauly, S. Vasanawala
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: We demonstrate the value of our blind inverse
problem framework based on diffusion models. Our method
outperforms state-of-the-art methods for reconstruction with
motion correction in both retrospectively and prospectively
corrupted data.
|
| 15:18 |
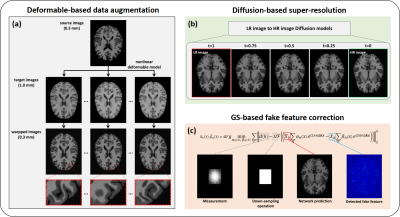 |
0936. AI-powered
0.3 mm Ultrahigh Resolution MR Brain Imaging
Z. Ke, Z. Xu, H. Zhuang, W. Tang, Y. Li, Z-P Liang
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, United States
Impact: Conventional MRI scans of the brain are
typically done at 1 mm resolution. Ultrahigh-resolution MRI
will open up many opportunities for research and clinical
applications. The proposed approach may also be useful for
solving other imaging and processing problems.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.