Oral
Carving AI Currents in Image Synthesis
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 08:15 |
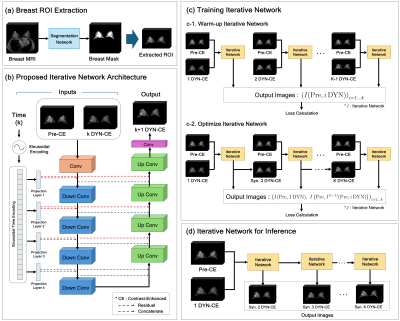 |
1114. Predicting
Delayed Phase Contrast-Enhanced MR Images from Early Phase
Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Using Deep Learning-Based Iterative
Network

W. Chung, J. Kang, G. E. Park, S. H. Kim, Y. Nam
Hankuk University of Foreign Studies, Yongin-si, Korea, Republic of
Impact: By enabling dynamic contrast prediction in
breast MRI, our method aids in the characterization of
enhancement patterns in breast tissue using only early phase
post-contrast images. This approach potentially reduces scan
times for dynamic contrast-enhanced MR applications.
|
| 08:27 |
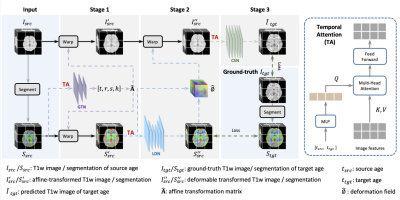 |
1115. A
Deep Learning Approach to Longitudinal Infant MRI Synthesis
Y. Fang, H. Xiong, J. Huang, F. Liu, X. Cai, Z. Shen, H.
Zhang, Q. Wang
ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China
Impact: This framework enables accurate tracking of
infant brain development by filling missing MRI data, aiding
in the creation of developmental atlases, and supporting
early detection of disorders. It may thus advance both
neurodevelopmental research and clinical interventions.
|
| 08:39 |
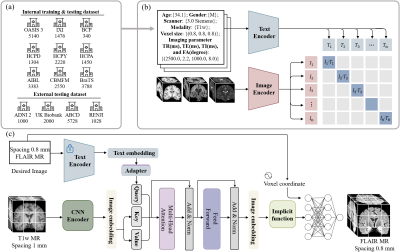 |
1116. Towards
Metadata-customized Brain MR image Synthesis for Disease
Diagnosis
Y. Wang, H. Xiong, K. Sun, S. Bai, Z. Ding, Q. Wang, Q. Liu,
D. Shen
Shanghaitech University, Shanghai, China
Impact: Our general multimodal MRI synthesis foundation
model is capable of quickly and cost-effectively providing
metadata-tailored multiple MR sequences, enabling clinicians
and researchers to customize the desired MR images using
this convenient AI technology, thereby enhancing diagnostic
precision and efficiency.
|
| 08:51 |
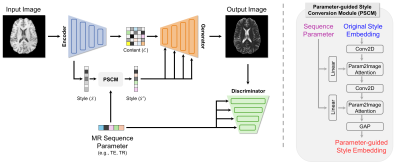 |
1117. Controllable
Magnetic Resonance Image Contrast Adjustment via Sequence
Parameter-Driven Network
H. Jang, H. Kim, Y. Song, D. Hwang
Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: This method adjusts the contrast of MR images
based on MR sequence parameters without requiring additional
scans. This approach has the potential to reduce the scan
time needed to acquire multi-contrast MR images.
|
| 09:03 |
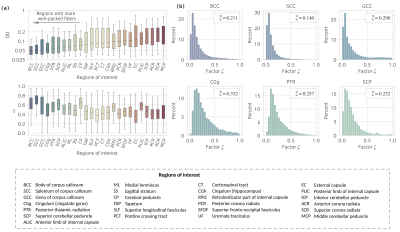 |
1118. Synthesizing
brain-originated realistic diffusion-weighted MRI signal for in
silico experiments
T. Pieciak, S. Aja-Fernández, A. Tristán-Vega
Universidad de Valladolid, Valladolid, Spain
Impact: The proposal models brain-originated
characteristics and enables diffusion-weighted data
synthesis reflecting the observed MRI signal. Compared to
previous solutions, which fix brain characteristics or draw
them randomly, our approach realistically varies signal
properties based on what is observed.
|
| 09:15 |
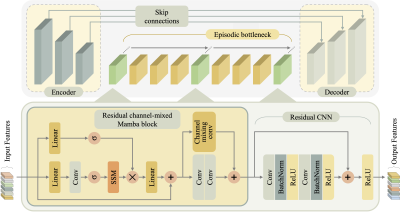 |
1119. Multi-Contrast
MR Image Synthesis with Episodic State-Space Modeling
Ö. Atlı, B. Kabas, F. Arslan, A. Demirtas, M. Yurt, O.
Dalmaz, T. Cukur
Bilkent University, Ankara, Turkey
Impact: The extended scope of multi-contrast protocols
enabled through I2I-Mamba may facilitate comprehensive MRI
exams in numerous applications, including assessment of
pediatric and elderly individuals in need of rapid scans
given limited motor control and vulnerability to toxicity
from contrast agents.
|
| 09:27 |
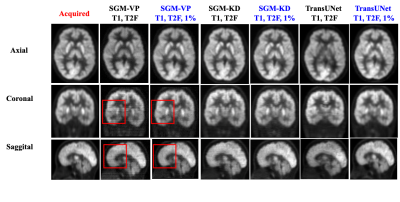 |
1120. Synthesizing
Full-dose FDG Brain PET from MRI With and Without Ultralow-dose
PET using Deep Learning Diffusion Models in Patients with
Epilepsy
J. Wu, J. Ouyang, M. Khalighi, G. Zaharchuk
Stanford University, Stanford, United States
Impact: This study suggests the possibility to use
generative AI approaches to massively reduce dose levels for
FDG PET brain studies. Further work will leverage 3D
patch-based approaches can improve the performance and slice
consistencies.
|
| 09:39 |
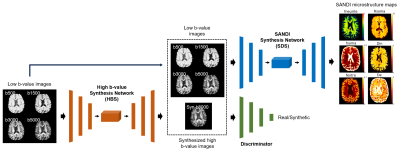 |
1121. Deep
Learning-Based High b-Value Image Synthesis: Application to
SANDI Microstructure Map Prediction
R. Zheng, Y. Li, H. Zhang, B. Zhang, X. Xia, Z. Tang, C.
Wang, Y. Chu, H. Zhang, C. Wang, H. Li, H. Wang
Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Impact: This study explores the feasibility of replacing
real high b-value images with synthesized images generated
by deep learning models, which holds promise for transfer to
other MRI systems with lower gradient performance, thereby
expanding the application scope of SANDI.
|
| 09:51 |
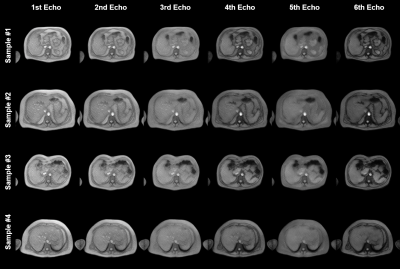 |
1122. Physics-informed
Latent Diffusion Model multi-echo chemical shift-encoded liver
MRI generation
J. Meneses, Y. George, C. Hagemeyer, Z. Chen, S. Uribe
Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Chile
Impact: We successfully generated realistic multi-echo
liver MR images and relevant quantitative maps to train deep
learning models for PDFF estimation. The combination of
limited real samples and numerous synthetic images for
training enabled an improved performance compared to
real-only datasets.
|
| 10:03 |
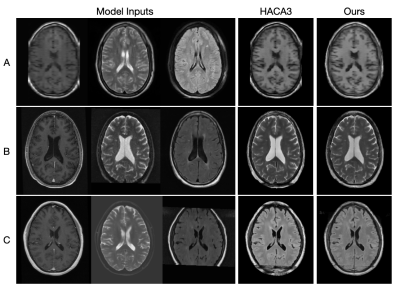 |
1123. Rescuing
Incomplete MR Data: Anatomy Imputation of Restricted Field of
View Images Using Multi-Contrast MR Images
S. Hays, S. Remedios, L. Zuo, J. Zhang, A. Carass, E. Mowry,
S. Newsome, J. Prince, B. Dewey
Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, United States
Impact: Our results impact researchers handling diverse,
inconsistent imaging datasets with variable field-of-view
acquisitions. This approach enables the analysis of
previously unusable data by imputing missing regions using
multi-contrast information, making them suitable for
meaningful clinical or research outcomes.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.