Oral
Towards Foundation Models in MRI
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 15:45 |
Introduction
Anthony Gatti
|
|
| 15:57 |
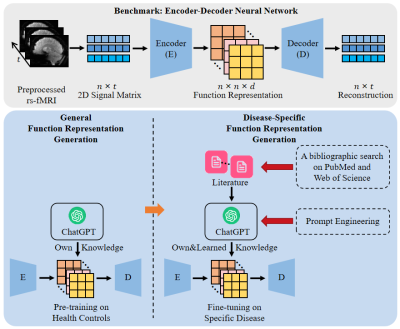 |
0616. Disease-Specific
Brain Function Representation Generation for Diagnosis Using
Large Language Models
M. Liu, L. Zhang, Q. Wang
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Impact: Our findings indicate that general and
disease-specific brain function representations guided with
LLM improve diagnostic accuracy. Additionally, the
framework’s adaptability across different diseases positions
it as a versatile tool in neuroimaging research, with
potential applications in studying various disorders.
|
| 16:09 |
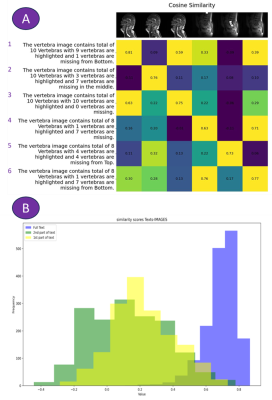 |
0617. Privacy
Preserving Performance Analysis of the AI Model Deployed on the
MRI Scanner with Multimodal Vision-Language Feedback
P. M. Goud, M. G. Reddy, C. Bhushan, D. Shanbhag
GE HealthCare, Bengaluru, India
Impact: We report a privacy preserving mechanism for
monitoring segmentation model performance in terms of simple
text logging, rather than quantitative numbers which might
require re-interpretation to deduce the performance of the
AI model.
|
| 16:21 |
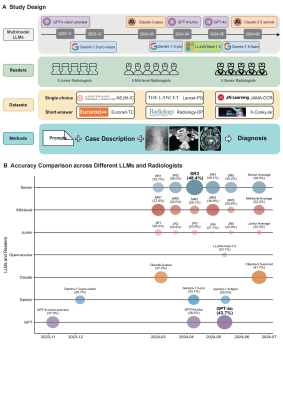 |
0618. Comparison
of Radiologists and Multimodal Large Language Models Responses
to Radiology ImageQuest
Q. Wu, Q. Wu, J. Xue, D. Shen, M. Wang
Henan Provincial People's Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
Impact: Multimodal LLMs show promise in radiology
education and practice, while further research is needed to
validate their impact on real clinical applications
|
| 16:33 |
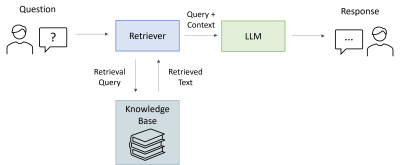 |
0619. Supporting
MRI Technicians: An LLM-Based Troubleshoot Companion for
Operational Assistance
L. Pfaff, B. Geissler, U. Klenke, F. Wagner, R. Schneider,
T. Wuerfl, A. Maier
Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany
Impact: This work enhances MRI troubleshooting by
introducing a context-aware support tool based on LLMs,
improving problem-solving efficiency for technicians. It
highlights the potential of RAG systems in healthcare to
replace traditional keyword-based search methods with more
intelligent solutions.
|
| 16:45 |
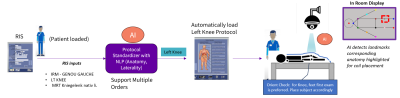 |
0621. Enabling
a one touch MR patient setup using RIS Interpretation and 3D
Camera
D. Anand, S. Gannavarapu, s. Rajamani, M. Patil, S. KS, D.
Shanbhag
GE Healthcare, Bangalore, India
Impact: The trained Coil detection and RIS
interpretation model aids in interpreting the scan intent
thereby enabling proper positioning of patient, coil and
automatic landmarking, saving time and avoiding repeat
scans.
|
| 16:57 |
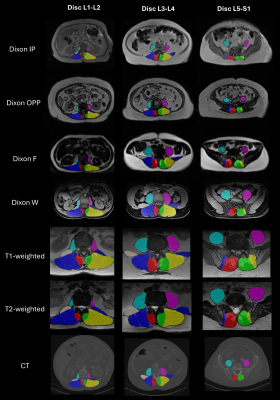 |
0622. Segment-Any-Muscle:
Towards an Open-Source, Contrast-Agnostic Computer-Vision Muscle
Segmentation Model for MRI and CT
E. Wesselink, J. Elliott, M. McKay, E. Martino, N. Caplan,
S. Mackey, J. Cohen-Adad, S. Bédard, B. Leener, E. Naga
Karthik, C. Law, M. Fortin, C. Vleggeert – Lankamp, A. Ieva,
B. Kim, M. Hancock, A. Pool - Goudzwaard, P. Pevenage, K. A.
Weber II
Stanford University, Palo Alto, United States
Impact: This contrast-agnostic computer-vision model can
automatically and accurately assess muscle health from both
MRI and CT. We are expanding this to all muscles to support
multiple clinical and research applications linking muscle
health to overall health and disease.
|
| 17:09 |
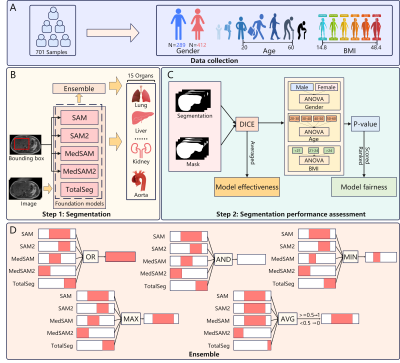 |
0623. Enhancing
organ segmentation performance in foundation models via ensemble
learning

Q. Li, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, Y. Zhang, L. Sun, M. Sun, Q. Li,
Z. Wang, M. Liu, X. Hu, S. Wang, C. Wang
Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Impact: This study integrates the ensemble
learning technique for the first time to enhance the
performance of foundation models, potentially reducing costs
in time and resources. More importantly, it provides an
effective approach for improving foundation model
performance in future applications.
|
| 17:21 |
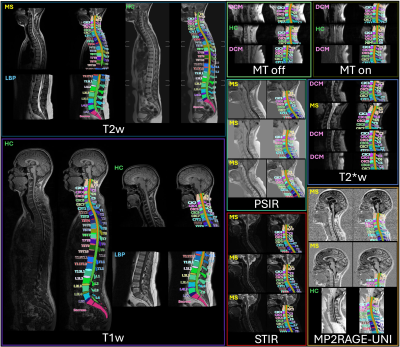 |
0624. TotalSpineSeg:
Robust Spine Segmentation and Labeling Across Multiple MRI
Contrasts
Y. Warszawer, N. Molinier, J. Valosek, E. Shirbint, P-l
Benveniste, T. Granberg, R. Ouellette, C. Tsagkas, V. Callot,
F. Mohamed, J. Bednarik, K. O'Grady, A. Achiron, J. Cohen-Adad
Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel
Impact: TotalSpineSeg could enhance clinical workflows
by providing automatic vertebrae segmentation, improving the
diagnosis of various spinal pathologies and supporting
informed clinical decision-making. It is available on GitHub
(https://github.com/neuropoly/totalspineseg) and in Spinal
Cord Toolbox v.6.514.
|
| 17:33 | 0620. WITHDRAWN |
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.