Oral
AI: Diagnostic Models
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 08:15 |
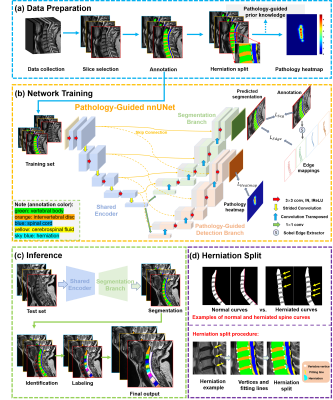 |
0373. Pathology-Guided
AI System for Accurate Segmentation and Diagnosis of Cervical
Spondylosis in MR T2 Images
Q. Zhang, X. Chen, L. Wu, K. Wang, J. Sun, H. Shen
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Impact: This AI-based framework enhances precision and
efficiency in cervical spondylosis diagnosis, reducing
clinician workload and improving diagnostic accuracy, with
PG-nnUNet supporting consistent, automated decision-making.
Future efforts will focus on multimodal imaging for broader
applicability.
|
| 08:27 |
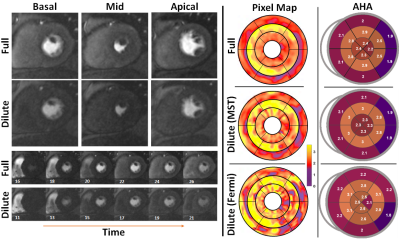 |
0374. Multi-Stage
Deep Learning Enables Accurate Detection of Ischemia in
Myocardial Perfusion MRI with Order-of-magnitude Lower Contrast
Dose
K. Youssef, L. Zamudio, B. Heydari, A. Howarth, B. Sharif
Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, United States
Impact: The MST deep learning method enables accurate
ischemia detection in stress CMR with significantly reduced
gadolinium doses, enhancing patient safety and reducing
costs. This advancement could facilitate safer, more
accessible stress CMR protocols in clinical practice.
|
| 08:39 |
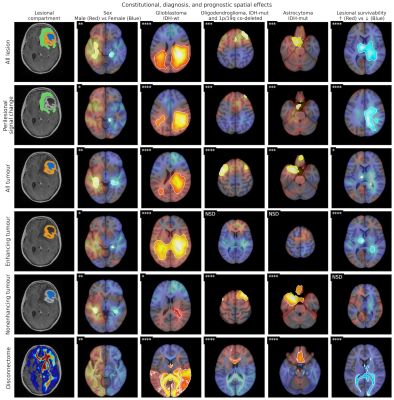 |
0375. The
deep topology of glioma

J. Ruffle, S. Mohinta, R. Gray, C. Foulon, S. Brandner,
H. Hyare, P. Nachev
UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, United Kingdom
Impact: These works illustrate the benefit of
computational modelling across clinical neuro-oncological
imaging data in patient-personalised care, including
diagnostic and outcome prediction, paving the way for future
research and clinical translation.
|
| 08:51 |
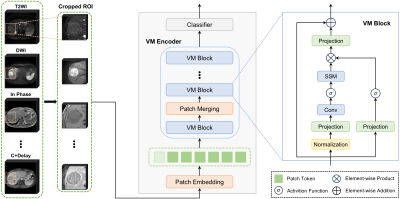 |
0376. Vision
Mamba for Liver Tumor Diagnosis in Multi-phase Magnetic
Resonance Imaging

H. Kang, R. Jiang, J. Xu, Q. Shen, W. Chen
The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Impact: Our proposed deep learning method can diagnose
most primary tumors with high accuracy. It has the potential
to benefit treatment planning and improve patient outcomes.
|
| 09:03 |
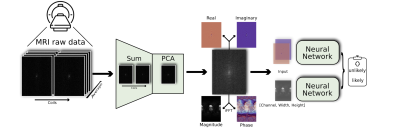 |
0377. Tumor
likelihood estimation on MRI prostate data by utilizing k-Space
information
M. Rempe, F. Hörst, C. Seibold, B. Hadaschik, M. Schlimbach,
J. Egger, K. Kröninger, F. Breuer, M. Blaimer, J. Kleesiek
Institute for AI in medicine, Essen, Germany
Impact: This study enables faster, reliable MRI-based
prostate cancer predictions by utilizing k-Space raw data.
It opens new possibilities for real-time diagnostics and
broader applications of raw MRI data across clinical
imaging.
|
| 09:15 |
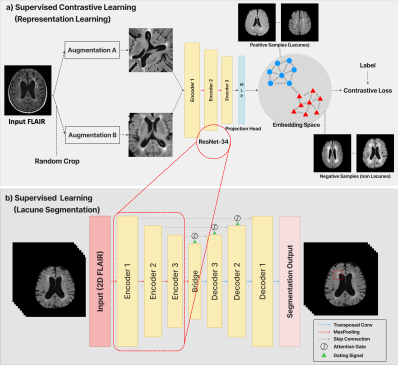 |
0378. Discriminative
Feature Learning for Lacune Detection in 2D T2-FLAIR Images
using Supervised Contrastive Learning
S. H. Kim, C. H. Suh, M. W. Han, W. Jung, S. H. Lee
VUNO Inc., Seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: This work demonstrates an effective encoder
training strategy for distinguishing small lesions like
lacunes in cerebral small vessel disease through enhanced
feature discrimination, potentially reducing both
radiological interpretation time and inter-reader
variability.
|
| 09:27 |
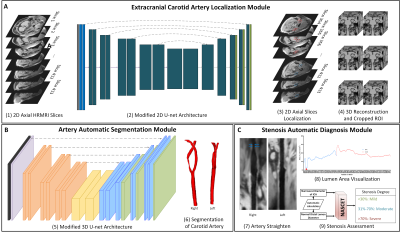 |
0379. Multi-Stage
Deep Learning Architecture for Carotid Artery Segmentation and
Stenosis Degree Evaluation: A Comparative Study with DSA
Z. Zheng, X. Cao, Q. Yang, W. Liu, D. Geng
Academy for Engineering and Technology, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Impact: This pipeline demonstrates high concordance with
DSA and could significantly enhance cardiovascular risk
assessment and atherosclerotic disease diagnosis in a
non-invasive, radiation-free manner. Its clinical
implementation may streamline diagnostic workflows and aid
in the management of carotid artery disease.
|
| 09:39 |
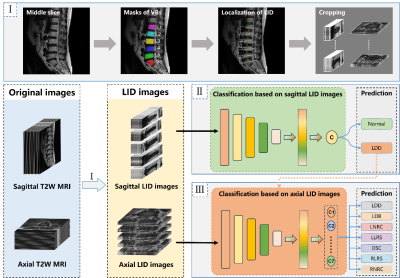 |
0380. Deep
learning-based computer-aided diagnostic system for lumbar
degenerative diseases classification using MRI
Y. Chen, Q. Huang, C. Zhang, J. Li, W. Huang, P. Luo, Q.
Chen, R. Qi, Y. Wan, B. Huang, Z. Gao, X. Lin, S. Wu, X.
Diao
Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (The Fourth Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine), Shenzhen, China
Impact: Our study demonstrates the feasibility of using
deep learning to classify multiple lumbar spine diseases
with strong performance, highlighting the potential of our
CAD system to reduce physician workload in clinical
applications.
|
| 09:51 |
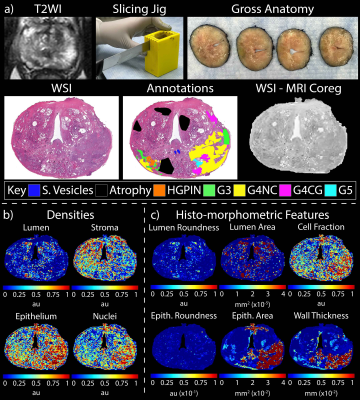 |
0381. Radio-pathomic
maps of histo-morphometric features trained with whole mount
prostate histology distinguish prostate cancer on MP-MRI
S. Duenweg, S. Bobholz, A. Lowman, A. Winiarz, B. Nath, B.
Chao, S. Vincent-Sheldon, K. Bhatt, L. Chaudhary, K. Troy,
K. Iczkowski, K. Jacobsohn, P. LaViolette
Medical College of Wisconsin, Wauwatosa, United States
Impact: This innovative approach uses radio-pathomic
mapping for non-invasive prostate cancer detection, offering
a quantitative alternative to PI-RADS scoring, enhanced
cancer localization, and potentially improving diagnosis,
grading, and treatment planning for prostate cancer
patients.
|
| 10:03 |
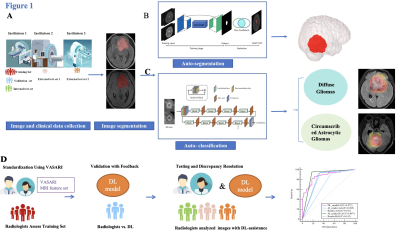 |
0382. A
Fully Automated Deep-Learning Model for Differentiating Diffuse
Gliomas and Circumscribed Astrocytic Gliomas: A Multi-center
Study
S. Li, Q. Yue
West China Hospital of Sichuan university, Chengdu, China
Impact: The integrated deep learning framework
demonstrates robust performance in segmenting and
differentiating diffuse gliomas and circumscribed
astrocytic gliomas across multi-institutional datasets.
Notably, the system significantly enhanced the preoperative
diagnostic performance of radiologists across all experience
levels.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.