Oral
AI-Enhanced Imaging: Redefining Clarity & Precision
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 08:15 |
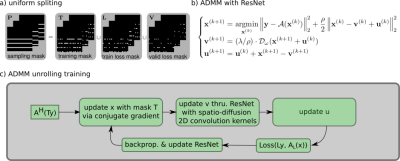 |
0743. Self-gated
self-supervised ADMM unrolling enables mesoscale high-resolution
motion-robust diffusion-weighted imaging
Z. Tan, P. Liebig, A. Hofmann, M. Jaroszewicz, Y. Jiang, V.
Gulani, F. Laun, F. Knoll
University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, United States
Impact: Our
proposed ADMM unrolling enables whole brain DWI of 21
volumes at 0.7 mm isotropic resolution and 10 minutes scan,
and shows higher signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), clearer tissue
delineation, and improved motion robustness, which make it
plausible for clinical translation.
|
| 08:27 |
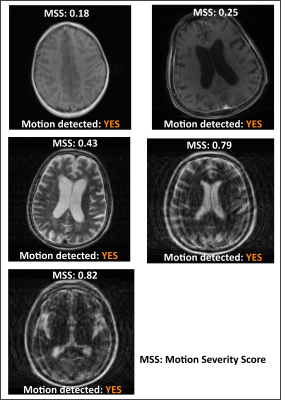 |
0744. An
Explainable AI-based Motion Detection approach for MR images
without requirement of motion annotated ground truth data
S. Banerjee, D. Shanbhag, S. Chatterjee
GE HealthCare, Bengaluru, India
Impact: Reliable motion alert for MRI scans shall enable
technologists to re-scan the subjects while in the scanning
room. This will help in reducing the patient recalls due to
motion artifact and hence reduce burden on the healthcare
system.
|
| 08:39 |
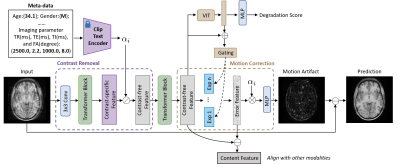 |
0745. Unified
Motion Correction Model for Multi-modal MRI
H. Xiong, F. Li, J. Cai, Q. Wang
School of Biomedical Engineering & State Key Laboratory of Advanced Medical Materials and Devices, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China, Shanghai, China
Impact: This framework enhances multi-modal MRI by
effectively correcting motion artifacts, leading to improved
image quality and diagnostic confidence. It holds potential
for widespread clinical adoption, benefiting patient care
and advancing research involving diverse MRI.
|
| 08:51 |
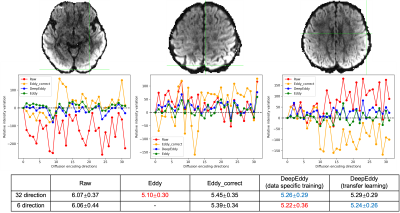 |
0746. DeepEddy:
high-quality fast eddy current and bulk motion correction using
deep learning-based image synthesis and co-registration

J. Zhang, F. Lange, J. Andersson, J. Zheng, Y. Jing, H.
Yang, M. Liu, Z. Li, W. Wu, Q. Tian, Z. Li
University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
Impact: DeepEddy enables eddy current and bulk motion
correction for diffusion data with any number of diffusion
directions, showing the promise to benefit clinical
applications where scan time is extremely limited.
|
| 09:03 |
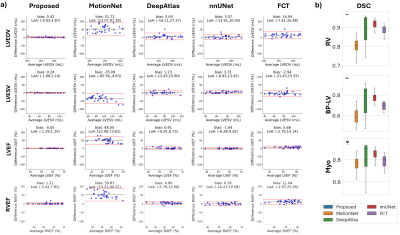 |
0747. Registration-Guided
Cardiac Functional Assessment from Limited Annotations in a
Single Breath-hold Cine

A. Ghoul, P. Cassal Paulson, K. Hammernik, P. Krumm, D.
Rueckert, S. Gatidis, T. Küstner
University Hospital of Tübingen, Tuebingen, Germany
Impact: Our framework enables automated cardiac function
assessment, even for highly accelerated single breath-hold
scans. We improve CMR accessibility for studies with limited
subjects and sparse manual annotations. Results indicate
reliable motion estimation, ventricular function measures
and myocardial strain analysis.
|
| 09:15 |
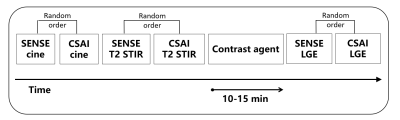 |
0748. Deep
Learning Super-Resolution reconstruction for fast cardiac MRI
protocol:A Comparative Study with Conventional cardiac MR
Y. Hua, H. Lu, X. Yue, F. Du, N. Zhang, H. Jin, M. Zeng
Zhongshan hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China
Impact: This study demonstrates that CSAI-CMR improves image quality
and significantly reduces scan time, enhancing patient
comfort and clinical efficiency, it supports advancing
cardiac MRI toward more precise, efficient, and
patient-friendly practices, potentially increasing its
clinical adoption.
|
| 09:27 |
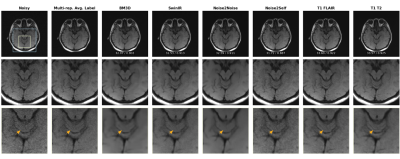 |
0749. An
Ambient Denoising Score Matching Based Self-supervised Denoising
Approach for Multicontrast Low-Field MRI
J. Tu, Y. Shi, F. Lam
University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, United States
Impact: Our method represents a new approach for
self-supervised multicontrast MRI denoising. It may offer
better trade-offs in SNR, resolution, and speed to benefit
many low-field applications.
|
| 09:39 |
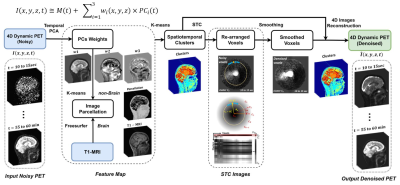 |
0750. NUCLIDE:
A Novel Unsupervised Clustering-based Image Denoising and
Enhancement for 4D Dynamic PET/MRI Data
H. Yousefi, M. Hamdi, R. Laforest, M. Brier, T. Benzinger,
Y. Chen, H. An
Washington University in St.Louis, Creve Coeur, United States
Impact: Our method enables robust, unsupervised
denoising for PET/MRI, preserving critical TACs and
structural information. This method has applications in
clinical settings and is adaptable to multimodal imaging.
|
| 09:51 |
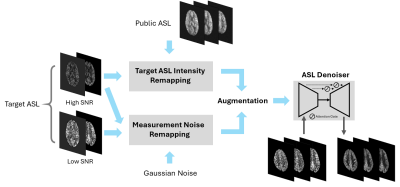 |
0751. Denoising
ASL Images Using Distribution Remapping-Based Deep Learning
Z. Xu, R. Guo, Z. Ke, Y. Li, Y. Zhao, W. Jin, Z. Meng, Y.
Li, Z-P Liang
University of Illinois, Urbana Champaign, Urbana, United States
Impact: Our proposed method addresses the issue of
limited target ASL training datasets for deep learning-based
ASL denoising and demonstrates excellent denoising
performance. It can be generalized for the practical utility
in both research and clinical applications.
|
| 10:03 |
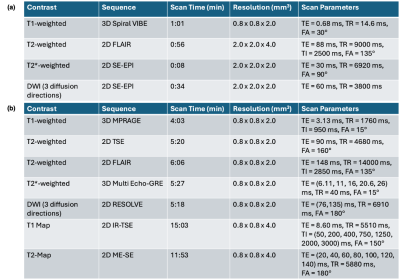 |
0752. Ultra-fast
High-Resolution Multi-Contrast Qualitative and Quantitative MRI
of the Entire Brain in 3 minutes

B. Alyuz, S. Qiu, H-L Lee, C. Gao, S. Madhusoodhanan, N.
Sicotte, P. Sati, Y. Xie, D. Li
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, United States
Impact: The proposed approach enables high-resolution
multi-contrast MRI and quantitative mapping of the entire
brain in 3 minutes. It can improve and facilitate diagnosis
and monitoring of neurological diseases like MS by making
detailed brain imaging feasible in time-sensitive clinical
settings.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.