Oral
The Perfect Wave: AI-Powered Advances in Image Segmentation
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 16:00 |
Introduction
Esin Ozturk-Isik
|
|
| 16:12 |
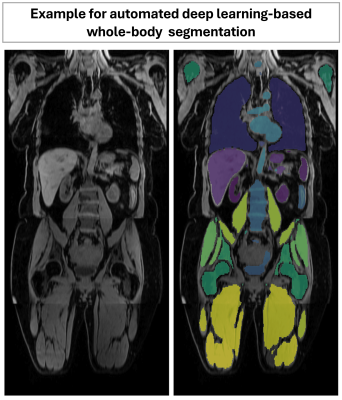 |
0254. Exploration
of Whole-Body Anatomy in the German National Cohort (NAKO): 3D
Segmentation of 55 Structures in 28,969 MRI Scans
L. Fay, Q. Wang, B. Yang, T. Kuestner, S. Gatidis
Medical Image and Data Analysis (MIDAS.lab), Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University Hospital of Tuebingen, Tuebingen, Germany
Impact: This study validates deep learning-based
segmentation of the TotalSegmentator model for large-scale
MRI analysis (28,969 subjects), showing precise, scalable
results. Automated and quality-controlled segmentations
demonstrate strong agreement, highlighting its potential to
advance research on anatomical structures and health
outcomes.
|
| 16:24 |
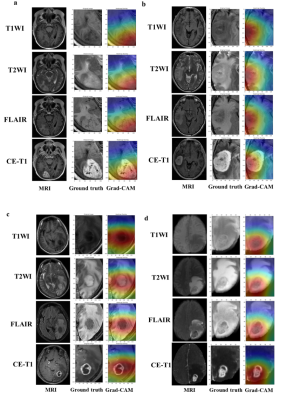 |
0255. Automatic
segmentation and classification of GBM and SBM using a 3D deep
learning model on multiparametric MRI: a multi-center study
M. Wu, J. Luan, H. Wang, X. Wang, X. Liang, C. Zhang, Y.
Zhao
The Second Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin, China
Impact: Reading with 3D DL model improves the diagnostic
accuracy of radiologists, thereby enhancing patient
treatment and prognosis potentially. Considering its
promising performance, it is recommended for routine
clinical application.
|
| 16:36 |
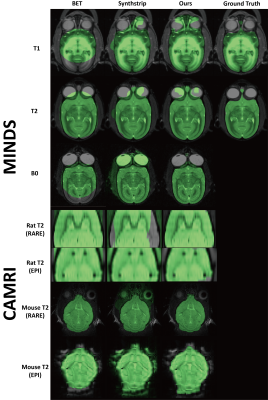 |
0256. Multimodal,
Multispecies and Pathology Invariant Skullstripping
J. S. Park, J. Ha, S. Tahkur, S. Bakas, E. Garyfallidis
Indiana University, Bloomington, Bloomington, United States
Impact: This is the first demonstration of a multimodal,
multispecies and pathology invariant skullstripping model,
only trained on synthetic data with minimal assumptions.
Results suggest that with correct assumptions, a single
model could be all we need for any skullstripping task.
|
| 16:48 |
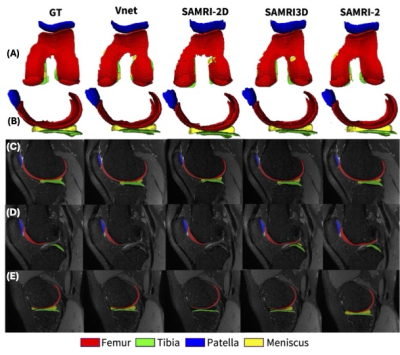 |
0257. On
Memory-Based Interactive Deep Learning Models for Cartilage
Segmentation in 3D MRIs of the Knee Joint
D. Lopes Ferreira, B. Nunes, X. Zhang, L. Carretero, M.
Fung, R. Soni, G. Avinash
GE Healthcare, San Ramon, United States
Impact: By leveraging memory-based 3D-VFM for
morphometric assessment of cartilage through 3DMRIs, we
significantly enhance the accuracy and generalizability of
the challenging knee soft tissue segmentation, paving the
way for more precise measurements of osteoarthritis
progression.
|
| 17:00 |
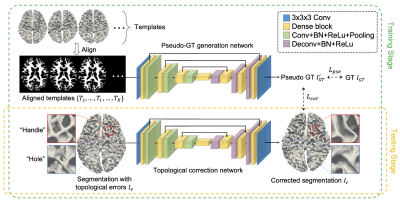 |
0258. Semi-Supervised
Topological Correction
Y. Sun, L. Wang, W. Lin, G. Li, L. Wang
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, United States
Impact: The proposed semi-supervised framework addresses
topological defects in the segmentation of the brain’s
complex folds, providing improved accuracy in cortical
analysis and surpassing existing correction methods. This
advancement has the potential to enhance studies of
neurodevelopmental, neurodegenerative, and psychological
disorders.
|
| 17:12 |
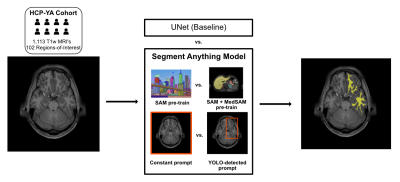 |
0259. Evaluating
a Deep Learning Foundation Model for Neuroimaging Segmentation
in the Data-Rich and Data-Constrained Settings
K. Nair, Y. Lui, N. Razavian
NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: While foundation models such as MedSAM have
potential for medical segmentation, they currently may not
surpass traditional models when using sufficient data. In
the data-limited setting, however, they can be useful when
extremely little labeled data is available.
|
| 17:24 |
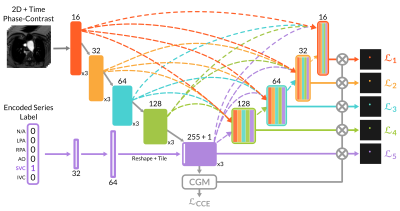 |
0260. MultiFlowSeg:
Unified deep learning model for multi-vessel classification and
segmentation of phase-contrast MRI in single ventricle patients
T. Yao, N. St. Clair, G. Miller, A. Zoubian, J. Steeden, R.
Rathod, V. Muthurangu
University College London, London, United Kingdom
Impact: We have developed a pipeline that uses our novel
MultiFlowSeg model to automate the extraction,
classification, and segmentation of phase-contrast MRI
images. It enables rapid, accurate flow quantification for
five blood vessels in a single ventricle registry without
manual input.
|
| 17:36 |
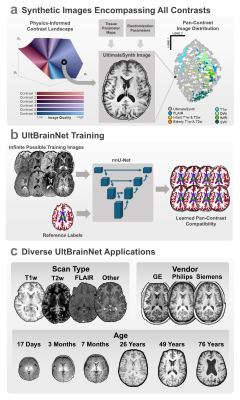 |
0261. Pan-Contrast
Learning of MRI Segmentation for Healthy and Anomaly Cases:
Faithful to Tissue Properties and MR Physics

R. Adams, W. Zhao, S. Hu, W. Lyu, K. Huynh, S. Ahmad, D.
Ma, P-T Yap
Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, United States
Impact: UBN offers a comprehensive solution for
consistent segmentation across all MR image contrasts,
vendors, resolutions, sites, preprocessing methods, and age
groups.
|
| 17:48 |
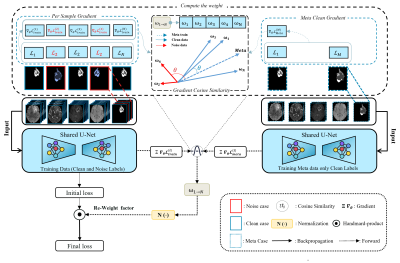 |
0262. Meta-Learning
for Robust Medical Image Segmentation: A Gradient-Similarity
Reweighting Approach to Mitigate Noisy Labels
A. Al-Fakih, A. Rezk, A. Shazly, K. Ryu, M. A. Al-masni
Sejong University, seoul, Korea, Republic of
Impact: This advancement addresses noisy data and
limited data availability in medical image segmentation,
enabling more accurate and reliable predictions.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.