Oral
State-of-the-Art Lung MR Imaging II
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 13:30 |
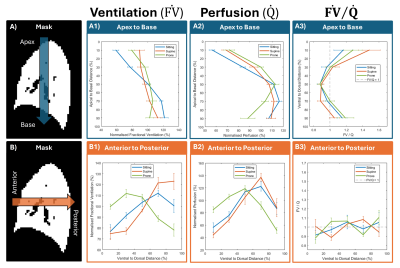 |
0908. Quantitative
Assessment of Pulmonary Function Distribution in the Sitting,
Supine, and Prone Postures Using PREFUL MRI with an Open Scanner
A. Harrison, T. Meersmann, G. Pavlovskaya, P. Gowland, J.
Paul, R. Sobhan, O. Mougin
University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom
Impact: A deeper understanding of lung function
variability in response to postural changes will enhance
clinical decision-making in pulmonary medicine.
Additionally, posture dependent lung function could serve as
a marker for lung disease and support stratified treatment
approaches.
|
| 13:42 |
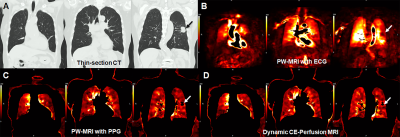 |
0909. Comparison
of Capabilities for Regional Perfusion and Functional Changes
among ECG- and PPG-Gated PREFUL MRIs and Dynamic CE-Perfusion
MRI
Y. Ohno, A. Palomar-García, M. Yui, B. Triaire, M. Ozaki, K.
Yamamoto, Y. Sano, M. Ikedo, H. Nagata, T. Ueda, M. Nomura,
T. Yoshikawa, D. Takenaka, Y. Ozawa
Fujita Health University School of Medicine, Toyoake, Japan
Impact: PW-MRI with ECG and PPG had equal to or better
potential than that with dynamic CE-perfusion MRI for
regional perfusion and pulmonary functional loss assessments
in thoracic oncology patients with different underlying lung
conditions.
|
| 13:54 |
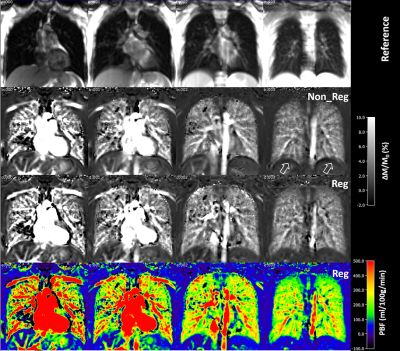 |
0910. Non-contrast
free-breathing pulmonary perfusion imaging using VSASL
K. Zhang, S. Triphan, C. Stewart, O. Sedlaczek, C. Ziener,
M. Ladd, H-P Schlemmer, H-U Kauczor, M. Wielpütz
Heidelberg University Hospital, Heidelberg, Germany
Impact: This study developed a robust VSASL sequence
with unbalanced steady-state free-precession
(ubSSFP)-readout for free-breathing perfusion measurement of
the lung parenchyma. The approach remains to be applied and
examined further in patients with lung disease.
|
| 14:06 |
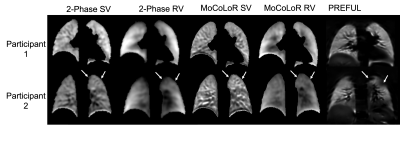 |
0911. Repeatability
of Ventilation Mapping from Free-Breathing 1H 3D UTE MRI:
Comparison with 2D PREFUL in Healthy Volunteers
A. Simmons, L. Saunders, J. Wild, N. Stewart
POLARIS, Division of Clinical Medicine, Faculty of Health, The University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom
Impact: This study reports a straightforward 2-Phase
approach for mapping ventilation using free-breathing UTE 1H-MRI,
while also providing valuable insights into the
repeatability of existing 1H-MRI-based
approaches like PREFUL and MoCoLoR.
|
| 14:18 |
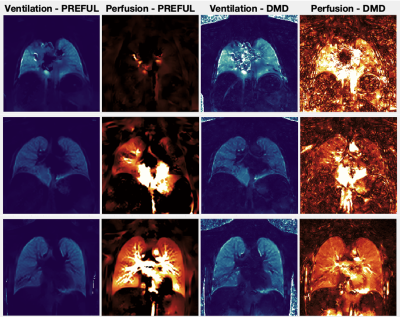 |
0912. Lung
Ventilation-Perfusion Imaging Approaches in the Single Ventricle
Heart
E. Doyle, E. Yagiz, S. Cui, J. Detterich, R. Kato, K. Nayak
Children's Hospital of Los Angeles, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, United States
Impact: These results will help to determine which
imaging approaches work best for patients with single
ventricle heart defects, which will provide functional
information for research and clinical use.
|
| 14:30 |
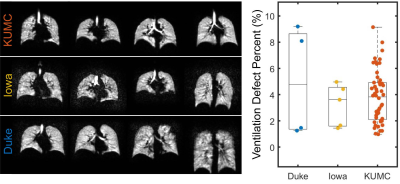 |
0913. XeLHC:
Harmonized Acquisition of Ventilation, Diffusion, and Gas
Exchange 129Xe MRI At 3 Sites in the Lung Health Cohort

I. Mali, M. Castro, D. Mummy, B. Driehuys, L. Que, S.
Fain, A. Hahn, A. Comellas, P. Niedbalski
University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, United States
Impact:
Trials using xenon MRI have been hampered by an incomplete understanding of normal variation across sites. In this preliminary analysis, we will examine the 3 major Xe-MRI contrasts (ventilation, diffusion-weighted, gas exchange) in 64 healthy volunteers imaged across three sites. |
| 14:42 |
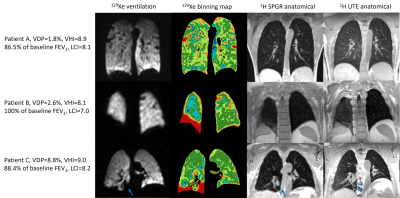 |
0914. 129Xe
ventilation and 1H anatomical MRI after lung transplant
H. Marshall, M. Driskel, A. Biancardi, L. Smith, D. Capener,
J. Bray, A. Zalewska, S. Fazal, L. Saunders, N. Stewart, A.
Swift, R. Munro, O. Rodgers, K. Santhanakrishnan, V.
Rajamiyer, J. Blaikley, J. Wild, A. Horsley
University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom
Impact: 129Xe
ventilation MRI and lung clearance index could be used for
more sensitive monitoring of lung function after lung
transplant.
|
| 14:54 |
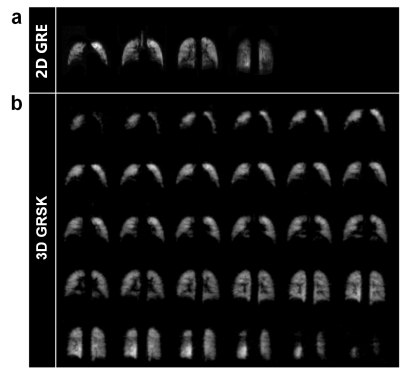 |
0915. 129Xe
multi-b Diffusion Weighted Imaging of lung with 3D Golden-Angle
Radial Sampling and Keyhole Reconstruction
L. Shen, H. Li, Y. Fang, Q. Zhou, M. Zhang, X. Zhao, L. Shi,
Y. Han, X. Zhou
State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences-Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Impact: 3D GRSK method was used to accelerate multi-b 129Xe
DWI, obtaining 4 b-values pulmonary DW images with isotropic
resolution of 5 mm within 11.4 s, and was applied in
patients with emphysema.
|
| 15:06 |
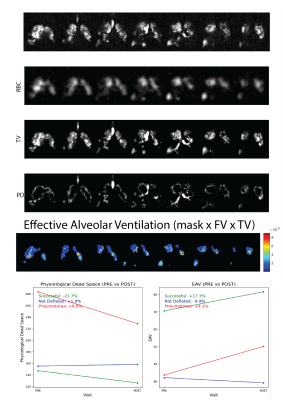 |
0916. Dynamic
Imaging of Physiological Dead Space and Alveolar Ventilation in
Patients Undergoing Endobronchial Valve Therapy with HP Xenon
MRI
H. Hamedani, L. Loza, K. Rupert, S. Kadlecek, M. Ismail, M.
Gorora, J. Chen, A. Gurevich, K. Ma, R. Rizi
University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, United States
Impact: This study offers new insights into the
physiological mechanisms underlying EBV treatment
variability, helping to tailor therapy to individual
patients and enhance long-term outcomes by integrating
advanced imaging techniques to correlate lung function with
clinical benefits.
|
| 15:18 |
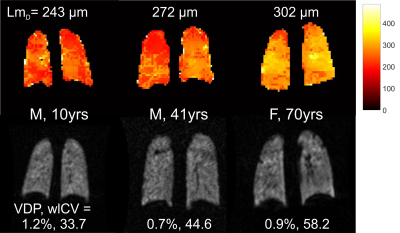 |
0917. Dependence
of diffusion and ventilation metrics on hyperpolarized 129Xe
lung MRI with demographics in healthy volunteers
G. Collier, A. Biancardi, H-F Chan, H. Marshall, L. Smith,
L. Saunders, N. Stewart, G. Norquay, P. Hughes, J. Wild
University of Sheffield, Sheffield, United Kingdom
Impact: Defining normal ranges for diffusion and
ventilation 129Xe
MRI metrics is important for clinical interpretation.
Results show a significant increase of alveolar dimensions
with age and provide an upper limit of normal for the
ventilation defect percentage metric.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.