Oral
Advanced Body Diffusion: Acquisition & Reconstruction
ISMRM & ISMRT Annual Meeting & Exhibition • 10-15 May 2025 • Honolulu, Hawai'i

| 15:45 |
Introduction
Holden Wu
|
|
| 15:57 |
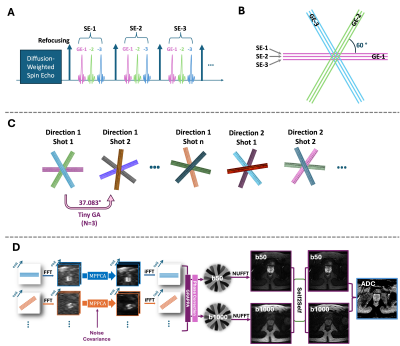 |
0664. Distortion-Free
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of the Prostate Using TGSE-Based
Golden-Angle PROPELLER Acquisition and Deep Learning Denoising

J. Chen, K. Zhou, M. Bruno, H. Chandarana, D. Sodickson,
Q. Wen, L. Feng
New York University Grossman School of Medicine, New York, United States
Impact: TGSE-PROPELLER-DWI with a novel acquisition
scheme provides distortion-free, high-resolution prostate
DWI within the same scan time as the clinical protocol, with
potential for further scan time reduction.
|
| 16:09 |
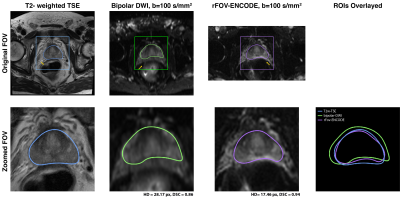 |
0665. Reducing
Geometric Distortion in Prostate Diffusion MRI using Reduced
Field-of-View ENCODE
E. Aygun, Z. Zhang, Q. Miao, E. Oh, S. S. Raman, K. Sung, H.
H. Wu
University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, United States
Impact: The rFOV-ENCODE sequence, combining rFOV
acquisition and ENCODE, can reduce geometric distortion for
prostate DWI without sacrificing scan time across different
scanner platforms. The technique can potentially improve
diagnosis of prostate cancer.
|
| 16:21 |
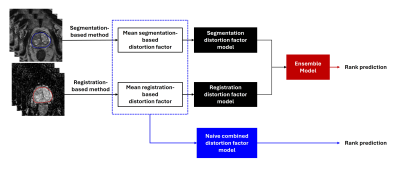 |
0666. An
Ensemble Framework for Automatic Quantification of Image
Distortion in Prostate Diffusion-Weighted Imaging
H. Sun, L. Wang, H-L Lee, V. Deshpande, F. Han, C. Gao, R.
Grimm, D. Li, Y. Xie
Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, United States
Impact:
The developed ensemble framework for automatic assessment of image distortion may assist in acquiring high-quality prostate DWI and reducing patient recalls. |
| 16:33 |
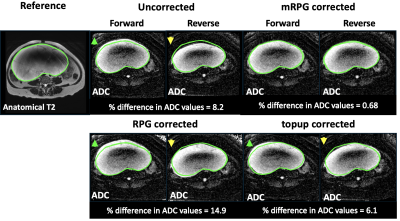 |
0667. Multi
b-value Distortion Correction for Ovarian Diffusion-Weighted MRI

S. J. Batasin, S. Loubrie, C. Conlin, H. Yu, S.
Ebrahimi, C. Moran, A. Dale, R. Rakow-Penner
UC San Diego, La Jolla, United States
Impact: mRPG improves distortion artifacts compared to
RPG and topup. It yields more accurate spatial and signal
intensity corrections which are reflected in quantitative
measures such as ADC, without significantly increasing
scanning time and with shorter computational time.
|
| 16:45 |
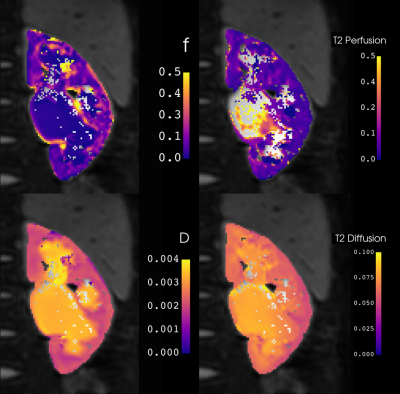 |
0668. Fast
T2-IVIM Imaging with Distortion & Motion Correction for
Quantitative Mapping in the Abdomen
L. Timms, M. Utkur, C. Ariyurek, S. Kurugol, O. Afacan
Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, United States
Impact: Using a multi-echo (ME) single-shot EPI sequence
for simultaneous IVIM and T2 fitting enables correction for
T2 biases in IVIM parameters, motion robust distortion
correction, and is suitable for general abdominal imaging
while saving scan time in clinical protocols.
|
| 16:57 |
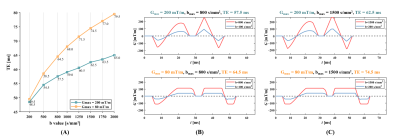 |
0669. Motion-compensated
Diffusion MRI of Liver Using High-performance Gradients
F. Liu, W. Zhong, Y. Wang, S. Li, W. Shao, W. Lyu, D. Shi,
H. Guo
Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, School of Biomedical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Impact: Our study explored the potential of
high-performance gradients in motion-compensated liver DWI.
The improved SNR in measuring Gaussian/non-Gaussian
diffusion provided more accurate evaluation of liver
microstructure.
|
| 17:09 |
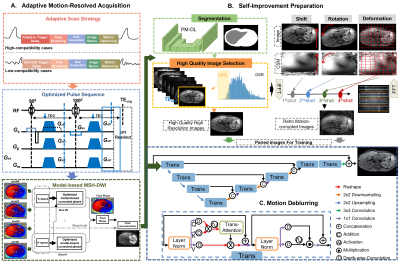 |
0670. Self-Improved
Multi-Shot Abdominal Diffusion-Weighted Imaging: A
Motion-Resolved High-Resolution Solution
H. Zhang, F. Wang, N. Shi, P. Wu, Z. Shi, Y. Wang, X. Yue,
W. Chen, R. Zheng, C. Wang, H. Wang
Institute of Science and Technology for Brain- Inspired Intelligence, Fudan University, Shanghai , China
Impact: The proposed solution enables in-vivo
high-resolution abdominal DWI in clinical practice.
|
| 17:21 |
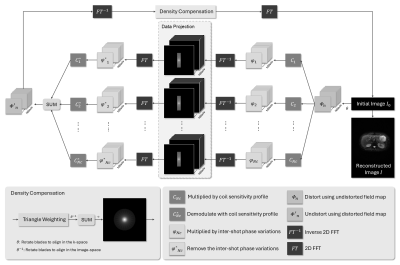 |
0671. Distortion-Free,
High-Resolution, Free-Breathing Liver DWI Using DW-PROPELLER-EPI
with Collaborative Reconstruction
H. Xiong, L. Liang, S. Chen, X. Xu, C. Yuan, Y. Li, T. Liu,
H. Chung, H-C Chang
The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Impact: DW-PROPELLER-EPI with CORPUSE may benefit
applications of liver DWI for challenging population.
|
| 17:33 |
 |
0672. Simultaneous
Multi-Slice DKI in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Correlation with
Early Recurrence
Y. Wu, Z. Ye, B. Song
West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Impact: The improved acquisition speed using SMS may
facilitate the integration of DKI into routine liver imaging
workflows. This preliminary evidence for SMS-DKI in
predicting early recurrence in HCC also encourages further
exploration of its applicability in other tumor types.
|
The International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians.